Difference between revisions of "Corneal ulcer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
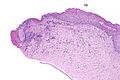
| Image = Corneal ulcer -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Corneal ulcer. [[H&E stain]]. (WC) | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = full thickness loss of epithelium | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[squamous dysplasia]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Staging = | |||
| Site = [[eye]] - cornea | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = dependent on severity | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Corneal ulcer''' is benign pathology of the [[eye]] characterized by (a focal) loss of the corneal epithelium. | '''Corneal ulcer''' is benign pathology of the [[eye]] characterized by (a focal) loss of the corneal epithelium. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 43: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Squamous dysplasia]]. | *[[Squamous dysplasia]]. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Corneal ulcer -- low mag.jpg | CU - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Corneal ulcer -- intermed mag.jpg | CU - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:31, 9 February 2016
| Corneal ulcer | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
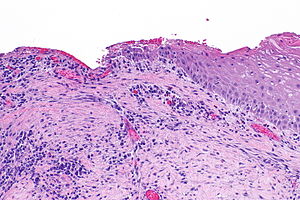 Corneal ulcer. H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
| LM | full thickness loss of epithelium |
| LM DDx | squamous dysplasia |
| Site | eye - cornea |
|
| |
| Prognosis | dependent on severity |
Corneal ulcer is benign pathology of the eye characterized by (a focal) loss of the corneal epithelium.
General
Microscopic
Feature:
- Ulceration of squamous epithelium.[citation needed]
DDx:
Images
Sign out
Corneal Button, Left Eye, Keratoplasty: - Corneal ulcer associated with neovascularization and chronic inflammation. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia.
See also
- Eye.