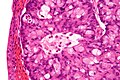
Urachal carcinoma
| Urachal carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
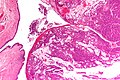
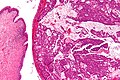
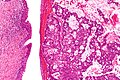
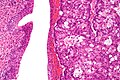
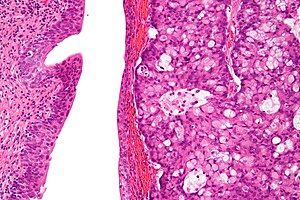 Urachal carcinoma (right of image) and benign urothelium (left of image). H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | atypical cells - usually gland forming, +/-mucinous component, +/-signet rings |
| Subtypes | enteric, mucinous, signet ring |
| LM DDx | adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder, invasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation, metastatic adenocarcinoma |
| IHC | CK20 +ve, beta-catenin +ve (non-nuclear), p63 -ve, CK34betaE12 +ve |
| Grossing notes | partial cystectomy |
| Site | urachus, urinary bladder - specifically the dome |
|
| |
| Signs | +/-hematuria |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Prognosis | usually poor |
| Clin. DDx | other bladder tumours - esp. urothelial carcinoma |
Urachal carcinoma is an uncommon malignant tumour that arises from the urachus. Most urachal carcinomas are adenocarcinomas.
General
- Very rare[1]~ 0.2% of bladder cancers.[2]
- Often younger <55 years-old.
- Poor prognosis[3] - especially for high Sheldon stage.[4]
Clinical:
- Hematuria - classic presentation.[3]
Treatment:
- Partial cystectomy +/- umbilectomy.
Gross
- Lesion must be in urachus or dome of urinary bladder.
Microscopic
Features of epithelial malignancy:
- Atypical (epithelial) cells.
- May be signet ring cells.
- Usually gland forming, i.e. adenocarcinoma.
- +/-Mucinous component.
Features making it urachal carcinoma (modified Sheldon criteria) - all required:[5]
- Located in bladder dome or anterior wall. †
- Centered on bladder wall (as opposed to the mucosa).
- No widespread cystitis cystica/glandularis outside of the bladder dome and anterior wall.
- No known urothelial carcinoma elsewhere.
Notes:
- Gopalan et al.[4] (based on Sheldon) suggests the following additional/more restrictive criteria:
- Only the dome is allowed. †
- Lesion should be sharply demarcated from the urothelium of the urinary bladder.
- Urachal remnants should be present in the tumour.
DDx:[6]
- Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder.
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation.
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma/adenocarcinoma extending from another structure, e.g. colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Villous adenoma of the urachus[7] - non-invasive.
Patterns
- Enteric - looks like colonic adenocarcinoma.
- Mucinous.
- Signet ring.
Note:
- Urachal carcinoma may be nonglandular.[5]
Images
IHC
Features:[4]
- CK20 +ve.
- CK7 +ve/-ve.
- CK34betaE12 +ve/-ve.
- Beta-catenin -- usu cytoplasmic/membranous +ve.
Others:[8]
- p63 -ve (+ve in only 3%).
UC versus CRC -- not absolute but useful:
- CK34betaE12 +ve in UC (-ve in CRC).
- Beta-catenin -ve nuclei in UC (+ve nuclei in CRC).
Sign out
- The diagnosis is a clinicopathologic diagnosis - one needs imaging to make it.[6]
- May be staged with the Sheldon system.[2]
Sheldon staging system
Staging as per Sheldon et al.:[4][9]
- pT1 - confined to urachal mucosa.
- pT2 - confined to the urachus.
- pT3a - extension into the bladder wall
- pT3b - extension into the abdominal wall.
- pT3c - structures other than the bladder.
- pT4a - metastasis to regional lymph nodes.
- pT4b - metastasis to distant sites.
See also
References
- ↑ Ashley, RA.; Inman, BA.; Sebo, TJ.; Leibovich, BC.; Blute, ML.; Kwon, ED.; Zincke, H. (Aug 2006). "Urachal carcinoma: clinicopathologic features and long-term outcomes of an aggressive malignancy.". Cancer 107 (4): 712-20. doi:10.1002/cncr.22060. PMID 16826585.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bruins, HM.; Visser, O.; Ploeg, M.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, CA.; Kiemeney, LA.; Witjes, JA. (Oct 2012). "The clinical epidemiology of urachal carcinoma: results of a large, population based study.". J Urol 188 (4): 1102-7. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.020. PMID 22901574.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Shao, GJ.; Cai, L.; Li, XS.; Song, G.; Li, XY.; He, ZS.; Zhou, LQ. (Oct 2013). "[Urachal carcinoma: experience of a clinical center within 30 years].". Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 45 (5): 774-8. PMID 24136277.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Gopalan, A.; Sharp, DS.; Fine, SW.; Tickoo, SK.; Herr, HW.; Reuter, VE.; Olgac, S. (May 2009). "Urachal carcinoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of 24 cases with outcome correlation.". Am J Surg Pathol 33 (5): 659-68. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31819aa4ae. PMID 19252435.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Paner, GP.; Barkan, GA.; Mehta, V.; Sirintrapun, SJ.; Tsuzuki, T.; Sebo, TJ.; Jimenez, RE. (Mar 2012). "Urachal carcinomas of the nonglandular type: salient features and considerations in pathologic diagnosis.". Am J Surg Pathol 36 (3): 432-42. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31823fe49c. PMID 22301493.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Amin, Mahul B. (2010). Diagnostic Pathology: Genitourinary (1st ed.). Amirsys. pp. 2-143. ISBN 978-1931884280.
- ↑ Joniau, S.; Lerut, E.; Van Poppel, H. (2009). "A Giant Mucinous Adenocarcinoma Arising within a Villous Adenoma of the Urachus: Case Report and Review of the Literature.". Case Rep Med 2009: 818646. doi:10.1155/2009/818646. PMID 20182635.
- ↑ Paner, GP.; McKenney, JK.; Barkan, GA.; Yao, JL.; Frankel, WL.; Sebo, TJ.; Shen, SS.; Jimenez, RE. (Jun 2011). "Immunohistochemical analysis in a morphologic spectrum of urachal epithelial neoplasms: diagnostic implications and pitfalls.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (6): 787-98. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182189c11. PMID 21572312.
- ↑ Sheldon, CA.; Clayman, RV.; Gonzalez, R.; Williams, RD.; Fraley, EE. (Jan 1984). "Malignant urachal lesions.". J Urol 131 (1): 1-8. PMID 6361280.