Rhinoscleroma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Rhinoscleroma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
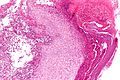
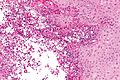
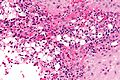
 Rhinoscleroma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | macrophages with clear-to-foamy cytoplasm, lymphocytes, plasma cells |
| LM DDx | Rosai-Dorfman disease |
| Stains | Warthin-Starry stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms) |
| IHC | CD68 +ve, S100 -ve |
| Site | head and neck - usu. nose |
|
| |
| Signs | nasal deformation (late) |
| Prevalence | rare |
Rhinoscleroma is a rare infectious condition of the head and neck.
General
- Caused by Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis.
- Nose involved +95% of the time.[1]
Gross
- Nasal mass - may be deforming.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Macrophages - clear-to-foamy cytoplasm.
- Lymphocytes.
- Plasma cells.
DDx:
- Rosai-Dorfman disease - usu. has emperipolesis.[3]
Images
www:
Stains
- Warthin-Starry stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms).
- Dieterle stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms).
IHC
- S100 -ve.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Chan, TV.; Spiegel, JH. (Oct 2007). "Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis of the membranous nasal septum.". J Laryngol Otol 121 (10): 998-1002. doi:10.1017/S0022215107006421. PMID 17359555.
- ↑ URL: http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/hn/rhinoscleroma2.html. Accessed on: 18 January 2012.
- ↑ Iyer VK, Handa KK, Sharma MC (July 2009). "Variable extent of emperipolesis in the evolution of Rosai Dorfman disease: Diagnostic and pathogenetic implications". J Cytol 26 (3): 111–6. doi:10.4103/0970-9371.59398. PMC 3168012. PMID 21938169. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3168012/.
- ↑ URL: http://www.jameswpattersonmd.com/case_studies/index.cfm?CFID=387434. Accessed on: 21 February 2012.
- ↑ Ilie M, Guevara N, Castillo L, Hofman P (March 2010). "Polypoid intranasal mass caused by Rosai-Dorfman disease: a diagnostic pitfall". J Laryngol Otol 124 (3): 345–8. doi:10.1017/S0022215109990818. PMID 19646302.