Glomus tumour
Glomus tumours, also known as glomangioma, are painful, perivascular tumour that are classically periungual.
| Glomus tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
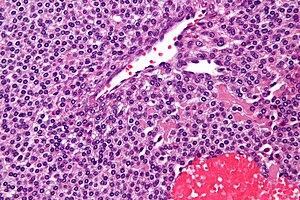 Glomus tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | sheets of equally-spaced cells ("cookie cutter appearance"), polygonal cells +/-identifiable cellular borders, thin-walled blood vessels, moderate clear cytoplasm |
| IHC | SMA +ve (100%), desmin usu. -ve, CD34 -ve, S-100 -ve |
| Site | skin/soft tissue - classically subungal (under the nail) |
|
| |
| Syndromes | +/-neurofibromatosis 1 |
|
| |
| Symptoms | painful skin lesion |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | usu. good (benign), rarely malignant |
| Treatment | excision |
It should not be confused with paraganglioma, which were once called glomus tumour.
This tumour is classified as a perivascular tumour (also pericytic tumour) which is a subset of soft tissue tumours.
General
- Tumour derived from smooth muscle cell.[1]
- Usually benign.
- Malignant variant exists (known as glomangiosarcoma) - extremely rare.[2]
- May be associated with neurofibromatosis 1.[3][4]
Clinical:
Gross
Location:
- Classically subungual (under the nail).[5]
- Reported in almost very site imaginable.
- Most common GI site: stomach.[6]
Appearance (extradigital tumours):[5]
- Purplish papule.
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Sheets of equally-spaced cells ("cookie cutter appearance") - key feature.
- Polygonal cells +/- identifiable cellular borders.
- Thin-walled blood vessels.
- May vaguely resemble antlers (staghorn vessels).
- Moderate clear cytoplasm.
Notes:
- No significant nuclear atypia.
- The regular cell spacing is called "cookie cutter appearance". It looks like the cells were created with a cookie cutter; the spacing between cell is equal and they all look very similar.
- Should be perivascular - abut endothelial cells.
- Myxoid matrix common.[8]
DDx - Why it is not a(n) ...[7]
- Spiradenoma - also vascular and 'blue' but epithelial, often on the head (or at least chest and up).
- Solid and cystic hidradenoma - epithelial and less 'blue'
- Angiosarcoma - has nuclear atypia.
- Dermatofibroma - spindle cell lesion.
- Capillary hemangioma - no epithelioid cells, more blood vessels.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[9]
- SMA +ve ~ 100%.
- Desmin usu. -ve.
- CD34 -ve.
- Rarely +ve.
Others:
- S100 -ve.
- Calponin +ve.
Sign out
LESION, RIGHT RING FINGERNAIL, EXCISION: - GLOMUS TUMOUR. COMMENT: The tumour cells are positive for SMA.
Micro
The sections show a tumour composed of polygonal cells with moderately distinct cellular borders and moderate cytoplasm. The tumour cell nuclei are round and have round nucleoli seen with the 10x objective. Thin-walled blood vessels with bland endothelial cells are found within the tumour. Tumour cells are identified immediately adjacent to the endothelial cells. No mitotic activity is apparent. Focal nuclear enlargement is present; however, no significant nuclear atypia is identified.
See also
- Painful skin lesions.
- Myopericytoma - the other perivascular (soft tissue) tumour.
References
- ↑ Gombos Z, Zhang PJ (September 2008). "Glomus tumor". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 132 (9): 1448–52. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[1448:GT]2.0.CO;2. PMID 18788860.
- ↑ "A case of malignant glomus tumor (glomangiosarcoma) of the nasal cavity". J Surg Case Rep 2022 (1): rjab641. January 2022. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjab641. PMC 8791658. PMID 35096369. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8791658/.
- ↑ Harrison B, Sammer D (September 2014). "Glomus tumors and neurofibromatosis: a newly recognized association". Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2 (9): e214. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000144. PMC 4229273. PMID 25426397. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4229273/.
- ↑ Kumar MG, Emnett RJ, Bayliss SJ, Gutmann DH (July 2014). "Glomus tumors in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1". J Am Acad Dermatol 71 (1): 44–8. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.913. PMID 24685357.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lee, DW.; Yang, JH.; Chang, S.; Won, CH.; Lee, MW.; Choi, JH.; Moon, KC. (Dec 2011). "Clinical and pathological characteristics of extradigital and digital glomus tumours: a retrospective comparative study.". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 25 (12): 1392-7. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.03979.x. PMID 21371130.
- ↑ Miettinen, M.; Paal, E.; Lasota, J.; Sobin, LH. (Mar 2002). "Gastrointestinal glomus tumors: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 32 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (3): 301-11. PMID 11859201.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/Z0B003-PQ01-M.htm. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.
- ↑ Mravic M, LaChaud G, Nguyen A, Scott MA, Dry SM, James AW (May 2015). "Clinical and histopathological diagnosis of glomus tumor: an institutional experience of 138 cases". Int J Surg Pathol 23 (3): 181–8. doi:10.1177/1066896914567330. PMC 4498398. PMID 25614464. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4498398/.
- ↑ Hatori M, Aiba S, Kato M, Kamiya N, Kokubun S (July 1997). "Expression of CD34 in glomus tumors". Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 182 (3): 241–7. PMID 9362106.