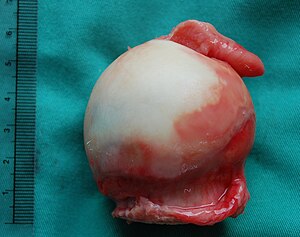
Femoral head
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The femoral head is a common ditzel in surgical pathology at centres which have orthopaedic surgeons.
Many of these can be "gross only".
Gross
Features to comment on:[1]
- Laterality (on requisition).
- Dimensions of head and neck.
- Shape of head (round? deformed?).
- Resection margin (irregular?).
- Cartilage (thinning/eburnation? separation from the cartilage).
- Bone (subchondral cysts? subchondral sclerosis?).
- Presence of soft tissue.
- Other (osteophytes? pannus?).
Notes:
- Some advocate the use of cardboard when cutting[2] -- weird.
Criteria for gross only
Main article: Gross pathology
Must be fulfilled:
- Not a fracture.
- Well developed features of osteoarthritis.
More stringent - in addition to the above:
- No history of cancer.
Diagnoses to consider
- Avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatologic disease - rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pathologic fracture.
- Infection (osteomyelitis).
Specific diagnoses
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
- AKA avascular necrosis, abbreviated AVN.
Main article: Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Osteoarthritis
- See Osteoarthritis.
Infection
- See Osteomyelitis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Main article: Rheumatoid arthritis
Fracture of bone due to metastatic carcinoma
Main article: Fracture of bone
- Pathologic fracture redirects here, as the underlying cause is usually a carcinoma.
General
- Uncommon ~ 10 of 90 suspected cases.[3]
- Usually in patients with a known malignancy and bony metastases.
- Should not be missed.
- Classically in older individuals.
Gross
Features:
- Irregular resection margin.†
- Focal, irregular, tan-white discolouration at the fracture site, i.e. margin, and in the marrow space.
Note:
- † Non-fracture resections have a flat resection margin, as they were cut by the surgeon.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
DDx:
Sign out
FEMORAL HEAD, LEFT, HIP ARTHROPLASTY: - METASTATIC SMALL CELL CARCINOMA.
Non-pathologic fracture of the femoral neck
- Hip fracture, traumatic hip fracture and traumatic fracture of the femoral neck redirect here.
General
- Common in the eldery.
- Strong association with osteoporosis.
Gross
- Irregular/jagged femoral neck margin - important.
- Hemorrhage.
Microscopic
Features:
- Non-vital bone.
- Loss of osteocytes.
DDx:
Commonly concurrent pathologies:
- Osteoporosis - thinner cortex, decreased trabecular thickness and number.[5]
- Osteoarthritis.
Sign out
FEMORAL HEAD AND SURROUNDING TISSUE, RIGHT, HIP ARTHROPLASTY: - BONE WITH CHANGES CONSISTENT WITH FRACTURE. - BENIGN FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE AND CARTILAGE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
FEMORAL HEAD AND SURROUNDING TISSUE, LEFT, HIP ARTHROPLASTY: - NON-VITAL BONE CONSISTENT WITH FRACTURE. - BENIGN FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE AND CARTILAGE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
With degenerative joint disease
FEMORAL HEAD AND SURROUNDING TISSUE, RIGHT, HIP ARTHROPLASTY: - BONE WITH CHANGES CONSISTENT WITH FRACTURE. - DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE. - BENIGN FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE AND CARTILAGE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Lester, Susan Carole (2005). Manual of Surgical Pathology (2nd ed.). Saunders. pp. 225. ISBN 978-0443066450.
- ↑ Dimenstein, IB. (Jun 2008). "Bone grossing techniques: helpful hints and procedures.". Ann Diagn Pathol 12 (3): 191-8. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2007.06.004. PMID 18486895.
- ↑ Ramisetty, NM.; Pynsent, PB.; Abudu, A. (May 2005). "Fracture of the femoral neck, the risk of serious underlying pathology.". Injury 36 (5): 622-6. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2004.08.034. PMID 15826621.
- ↑ URL: http://www.path.utah.edu/casepath/ms%20cases/ms%20case%205%20comp/case%205.htm. Accessed on: 11 October 2012.
- ↑ Blain, H.; Chavassieux, P.; Portero-Muzy, N.; Bonnel, F.; Canovas, F.; Chammas, M.; Maury, P.; Delmas, PD. (Nov 2008). "Cortical and trabecular bone distribution in the femoral neck in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.". Bone 43 (5): 862-8. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2008.07.236. PMID 18708176.