Invasive lobular carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Invasive lobular carcinoma, abbreviated ILC, is the second most common form of Invasive breast cancer.
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
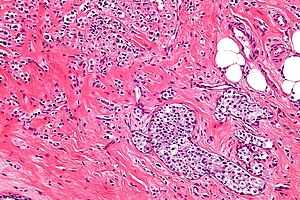 Lobular carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with lobular features, poorly differentiated carcinoma, LCIS |
| IHC | E-cadherin -ve, usu. ER and PR +ve, HER2 -ve, CK7 +ve |
| Site | breast - see invasive breast cancer |
|
| |
| Syndromes | hereditary diffuse gastric cancer |
|
| |
| Prevalence | relatively common |
| Clin. DDx | other breast tumours |
It may be referred to as lobular carcinoma; however, this may lead to confusion with lobular carcinoma in situ.
General
Microscopic
Features:
- "Single file" - cell line-up in a row.
- Cell should not be cohesive -- lymphoma should briefly come to mind.
- primary lymphoma of the breast exists... but it is extremely rare.
- Cell should not be cohesive -- lymphoma should briefly come to mind.
- NO gland formation.
- If it forms glands... it is more likely NST.
- May have signet ring morphology.
- NO desmoplastic reaction, i.e. the stroma surrounding the tumour cells should look benign and undisturbed.
Note:
- Commonly have low grade nuclear features.
DDx:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with lobular features.
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma.
- LCIS.
Images
More WC images:
Subclassification
- Classic lobular carcinoma.
- Low nuclear grade - NO significant variation of nucleus size.
- Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma.
- Significant nuclear atypia.
Note:
- Some pathologist grade lobular carcinoma like other types and avoid the term "pleomorphic lobular carcinoma."[3]
IHC
Features:
- E-cadherin -ve.
- ER and PR +ve.
- HER2 -ve.
- CK7 +ve.
Others:
- CK20 -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.asco.org/ascov2/Meetings/Abstracts?&vmview=abst_detail_view&confID=65&abstractID=33006. Accessed on: 19 April 2011.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 192090
- ↑ MUA. Jan 22, 2009.