Cat scratch disease
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cat scratch disease, also cat scratch fever, is an uncommon pathology of the lymph node.
| Cat scratch disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
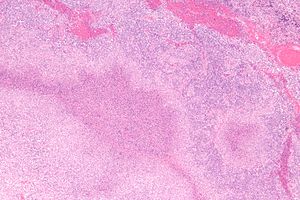 Cat scratch disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | necrotizing granulomas with neutrophils and star-shaped (stellate, +/-multinucleated giant cells, microorganisms consistent with B. henselae |
| LM DDx | sporotrichosis, lymphogranuloma venereum, tularemia |
| Stains | Warthin-Starry stain +ve |
| IHC | B. henselae +ve |
| Site | lymph node - see lymph node pathology |
|
| |
| Clinical history | contact with cats |
| Signs | fever, lymphadenopathy |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other causes of lymphadenopathy, e.g. lymphoma |
General
- Infection caused Bartonella henselae,[1] a gram-negative bacillus (0.3-1.0 x 0.6-3.0 micrometers) in chains, clumps, or singular.[2]
- Treatment: antibiotics.
Clinical
Features:[3]
- Usually unilateral.
- May be disseminated in individuals with immune dysfunction.
- Contact with cats.
Micrograph
Features:[3]
- Necrotizing granulomas with:
- Neutrophils present in microabscess (necrotic debris) - key feature.
- Microabscesses often described as "stellate" (star-shaped).
- Neutrophils present in microabscess (necrotic debris) - key feature.
- +/-Multinucleated giant cells.
- Microorganism consistent with B. henselae.
Notes:
- May involve capsule or perinodal tissue.
DDx of stellate abscess in lymph nodes - cat split:[4]
- Cat-scratch disease.
- Sporotrichosis.
- Lymphogranuloma venereum.
- Tularemia.
Images
www:
Stains
- Warthin-Starry stain +ve -- bacilli.
- Gram stain -ve.
IHC
- B. henselae IHC stain +ve -- bacilli - diagnostic.
See also
References
- ↑ Jerris, RC.; Regnery, RL. (1996). "Will the real agent of cat-scratch disease please stand up?". Annu Rev Microbiol 50: 707-25. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.707. PMID 8905096.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 110. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 113. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermpathmd.com/mnemonics/mnemonics_dermatopathology.htm. Accessed on: 23 September 2011.