Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Adenoid cystic carcinoma, abbreviated AdCC, is a malignant tumour commonly seen in the salivary gland.
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
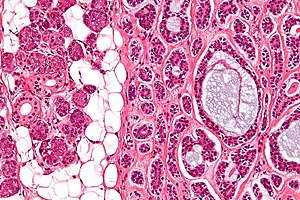 Adenoid cystic carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cribriform architecture (other patterns: solid, cords, (bilayered) tubules), cystic spaces filled with basophilic material, scant cytoplasm in most cells, nucleus - small, hyaline stroma |
| LM DDx | pleomorphic adenoma, epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma |
| Site | salivary gland, breast, lung |
|
| |
| Signs | mass |
General
- Common malignant neoplasm of salivary gland.
- AKA cylindroma.[1]
- Should not be confused with dermal cylindroma (a benign skin tumour).
- Composed of ductal cells and myoepithelial cells; myoepithelial cells > ductal cells.
Microscopic
Features:
- Cribriform architecture or pseudoglandular spaces (classic pattern) - important feature.
- Other patterns: solid, cords, (bilayered) tubules.
- Cystic spaces filled with basophilic material (that is PAS +ve) - key feature.
- Scant cytoplasm in most cells (myoepithelial cells) - clear/eosinophilic.
- Moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm in the (rare) ductal cells.
- Nucleus - small.
- May be angulated (carrot-shaped) - myoepithelial cells; round/ovoid in ductal cells.
- Hyaline stroma.
Memory device:
- AdCC - mostly DNA (scant cytoplasm), distinct nucleus (carrot-shaped).
Notes:
- Squamous differentiation is extremely rare. It presence should prompt consideration of:
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
DDx:
- Pleomorphic adenoma, esp. if encapsulated.
- Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma - esp. for AdCC tubular variant.
Images
www:
Grading
Based on solid component:
- Low grade = tubules and cribriform structures only; no solid component.
- Intermediate grade = solid component <30%.
- High grade = solid component >=30%
Stains
Special stains:
- PAS +ve material - cystic spaces.[2]
IHC
Features:[3]
- CD117 +ve.
- Cyclin D1 +ve.
- Myoepithelial markers (e.g. calponin, actin) +ve.
- Typically -ve in PLGA.
Molecular
Features:[4]
- t(6;9) MYB-NFIB.
- Seen in ~50% of cases.
- Worse prognosis if present, esp. if fusion assoc. with transcription.
See also
References
- ↑ Chest. May 1957. Vol. 31. No. 5. PP. 493-511. http://www.chestjournal.org/content/31/5/493.abstract
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970070-5. Accessed on: 12 May 2011.
- ↑ Sequeiros-Santiago, G.; García-Carracedo, D.; Fresno, MF.; Suarez, C.; Rodrigo, JP.; Gonzalez, MV. (May 2009). "Oncogene amplification pattern in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands.". Oncol Rep 21 (5): 1215-22. PMID 19360297.
- ↑ Mitani, Y.; Rao, PH.; Futreal, PA.; Roberts, D.; Stephens, P.; Zhao, YJ.; Zhang, L.; Mitani, M. et al. (Oct 2011). "Novel Chromosomal Rearrangements and breakpoints at the t(6;9) in Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: association with MYB-NFIB chimeric fusion, MYB expression, and clinical outcome.". Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1870. PMID 21976542.