Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, abbreviated SEGA, is a low-grade astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis complex.
General
- Associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC).[1]
- WHO Grade I.
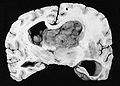
Gross/radiology
- Well-demarcated.
- Often projecting into a ventricle.
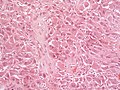
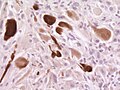
Microscopic
- Giant cells with nuclear atypia ("bizarre cells").
- Glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Abundant mast cells.[4]
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[3]
- GFAP +ve. (???)
- Vimentin +ve. (???)
- S100 +ve. (???)
See also
References
- ↑ Grajkowska, W.; Kotulska, K.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Roszkowski, M.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Matyja, E. (2011). "Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas with atypical histological features mimicking malignant gliomas.". Folia Neuropathol 49 (1): 39-46. PMID 21455842.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179.html. Accessed on: 29 July 2011.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Taraszewska, A.; Kroh, H.; Majchrowski, A. (1997). "Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: clinical, histologic and immunohistochemical characteristic of 3 cases.". Folia Neuropathol 35 (3): 181-6. PMID 9595853.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.