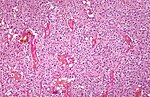
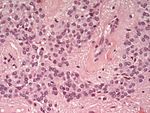
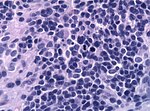
Glioma
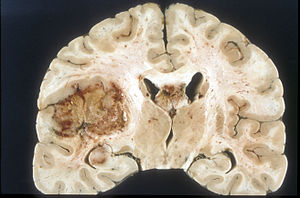
Gliomas are the most compon primary tumor in the brain and spinal cord. They originate from glial cells and their precursors.
Classification
Gliomas are classified by cell type, by WHO grade, and by location.
By type of cell
Gliomas are named according to the specific type of cell with which they share histological features, but not necessarily from which they originate. The main types of gliomas are:
- Astrocytomas—astrocytes (glioblastoma multiforme is a malignant astrocytoma and the most common primary brain tumor among adults).
- Oligodendrogliomas—oligodendrocytes
- Ependymomas—ependymal cells
- Mixed gliomas, such as oligoastrocytomas, contain cells with different morphologies
- Molecular analysis allows the tumor in most cases assigned to astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma.
Note: Some authors consider choroid plexus as a specific type of glia, but choroid plexus tumors are usually not covered under the umberella term glioma.
By WHO grade
Gliomas are further categorized according to their grade, which is determined by pathologic evaluation of the tumor.
- Low-grade gliomas [WHO grade II] are well-differentiated (not anaplastic); these tend to exhibit benign tendencies and portend a better prognosis for the patient. However, they have a uniform rate of recurrence and increase in grade over time so should be classified as malignant.
- High-grade [WHO grade III–IV] gliomas are undifferentiated or anaplastic; these are malignant and carry a worse prognosis.
Of numerous grading systems in use, the most common is the World Health Organization (WHO) grading system for astrocytoma, under which tumors are graded from I (least advanced disease—best prognosis) to IV (most advanced disease—worst prognosis).
By location
Gliomas can be classified according to whether they are above or below a membrane in the brain called the tentorium. The tentorium separates the cerebru] (above) from the cerebellum (below).
- The supratentorial is above the tentorium, in the cerebrum, and mostly found in adults (70%).
- The infratentorial is below the tentorium, in the cerebellum, and mostly found in children (70%).
- The pontine is located in the pons of the brainstem. The brainstem has three parts (pons, midbrain, and medulla); the pons controls critical functions such as breathing, making surgery on these extremely dangerous.
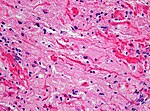
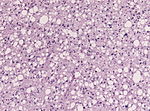
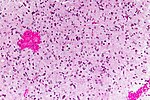
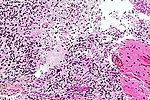
Table of common gliomas
Histomorphologic comparison of common gliomas:
| Entity | Rosenthal fibres / EGBs |
Nuclear atypia | Mitoses | Necrosis or MVP | Infiltrative | Image |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | yes | usu. no | usu. no | usu. no | no | |
| Diffuse astrocytoma | no | yes | no | no | yes | |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma | no | yes | yes | no | yes | |
| Glioblastoma | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| Oligodendroglioma | no | usu. no | yes | no | yes | |
| Ependymoma | no | usu. no | usu. no | usu. no | discrete | |
| Anaplastic ependymoma | no | yes | yes | usu. yes | discrete |
Notes:
- MVP = microvascular proliferation.
- EGBs = eosinophilic granular bodies.
Frequency
The relative frequency differs significantly between adults and children.[1]
- Adults:
- glioblastoma 55.2%
- astrocytoma grade II 9%
- anaplastic astrocytoma grade III 6.1%
- ependymoma 6.8%
- oligodendroglioma grade II 5.9%
- pilocytic astrocytoma 5.9%
- anaplastic oligodendroglioma grade III 3.3%
- not further specified 8.4%
- Children:
- pilocytic astrocytoma 33.8%
- malignant glioma, NOS 25.7%
- ependymoma 11.4%
- astroyctoma grade II 11.1%
- glioblastoma 6.3%
- oligodendroglioma 3.9%
- anaplastic astrocytoma grade III 3.6%
- not further specified 4.2%
See also
- ↑ Ostrom, QT.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Rouse, C.; Chen, Y.; Dowling, J.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C. et al. (Oct 2014). "CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007-2011.". Neuro Oncol 16 Suppl 4: iv1-63. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou223. PMID 25304271.