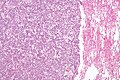
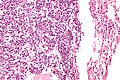
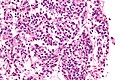
Typical carcinoid lung tumour
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Typical carcinoid lung tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
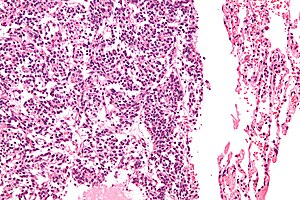 Lung carcinoid. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | lung carcinoid |
|
| |
| LM | stippled chromatin, usually nested architecture, no necrosis, low mitotic rate (see below) |
| LM DDx | atypical carcinoid lung tumour, pulmonary carcinoid tumourlet, lung adenocarcinoma |
| IHC | Ki-67 ~2% (0-7%), TTF-1 +ve/-ve, CK7 +ve/-ve, CK20 -ve |
| Gross | well-circumscribed, solid, >=5 mm (definition) |
| Site | lung - see lung tumours |
|
| |
| Syndromes | diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia |
|
| |
| Symptoms | +/-cough, +/-hemoptysis |
| Prevalence | not common |
| Radiology | usually central (85% of cases), well-circumscribed, solid |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other lung tumours, lung metastases (esp. when multiple) |
| Treatment | excision to exclude other types of lung tumours & treat symptoms |
Typical carcinoid lung tumour, also lung carcinoid and carcinoid tumour of the lung, is a benign lung tumour, that is excised to exclude malignancy.
General
- Approximately 80% of lung carcinoids.[1]
- May be multiple.[2]
- Can mimicking metastatic disease.[3]
- Often re-occur - but long term survival good.
- Can be seen in the context of diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH).[4][5]
Presentation:[6]
- Cough.
- Hemoptysis.
Treatment:
- Surgical resection.[7]
Gross
- Well-circumscribed, solid.
- Location - central airways (85%), remainder peripheral.[8]
Microscopic
Features:
- Nests of cells.
- Stippled chromatin.
- Moderate cytoplasm.
- No necrosis.
- Low mitotic rate.
- Size criterion: >= 5 mm.[9][10]
DDx:
Images
IHC
Proliferation:
- Ki-67 ~2% (range 0-7%).[12]
- Atypical carcinoid is on average 17% (range 10-26%).[12]
- Chromogranin A +ve.
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- CD56 +ve.
Others:
- TTF-1 +ve/-ve (11 +ve of 16 cases[14]).
- CK7 +ve/-ve (10 +ve of 16 cases[14]).
- CK20 -ve (0 +ve of 16 cases[14]).
Sign out
A. Lymph Node, Station 2L, Lymphadenectomy: - Lymph node, NEGATIVE for malignancy. B. Lymph Node, Station 4L, Lymphadenectomy: - Lymph node, NEGATIVE for malignancy. C. Lymph Node, Station 11L, Lymphadenectomy: - Lymph node, NEGATIVE for malignancy. D. Lung, Left Upper Lobe, Lobectomy: - Typical carcinoid tumour (12 mm maximal dimension). - Carcinoid tumourlet (2 mm maximal dimension). - Margins clear of tumour. - Please see tumour summary.
See also
References
- ↑ Naalsund, A.; Rostad, H.; Strøm, EH.; Lund, MB.; Strand, TE. (Apr 2011). "Carcinoid lung tumors--incidence, treatment and outcomes: a population-based study.". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 39 (4): 565-9. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.08.036. PMID 20888248.
- ↑ Miller, MA.; Mark, GJ.; Kanarek, D. (Aug 1978). "Multiple peripheral pulmonary carcinoids and tumorlets of carcinoid type, with restrictive and obstructive lung disease.". Am J Med 65 (2): 373-8. PMID 356600.
- ↑ Aubry, MC.; Thomas, CF.; Jett, JR.; Swensen, SJ.; Myers, JL. (Jun 2007). "Significance of multiple carcinoid tumors and tumorlets in surgical lung specimens: analysis of 28 patients.". Chest 131 (6): 1635-43. doi:10.1378/chest.06-2788. PMID 17400673.
- ↑ Wirtschafter, E.; Walts, AE.; Liu, ST.; Marchevsky, AM. (Jun 2015). "Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia of the Lung (DIPNECH): Current Best Evidence.". Lung. doi:10.1007/s00408-015-9755-1. PMID 26104490.
- ↑ Chauhan, A.; Ramirez, RA. (Jun 2015). "Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) and the Role of Somatostatin analogs: A Case Series.". Lung. doi:10.1007/s00408-015-9754-2. PMID 26112453.
- ↑ Gungor, S.; Damadoglu, E.; Aybatli, A.; Yilmaz, A.; Kir, A.; Akkaya, E. (Jul 2006). "Typical pulmonary carcinoid tumors: presentation and outcome of 24 cases.". Med Sci Monit 12 (7): CR315-8. PMID 16810137.
- ↑ Caplin, ME.; Baudin, E.; Ferolla, P.; Filosso, P.; Garcia-Yuste, M.; Lim, E.; Oberg, K.; Pelosi, G. et al. (Aug 2015). "Pulmonary neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors: European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society expert consensus and recommendations for best practice for typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoids.". Ann Oncol 26 (8): 1604-20. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv041. PMID 25646366.
- ↑ Meisinger, QC.; Klein, JS.; Butnor, KJ.; Gentchos, G.; Leavitt, BJ. (Nov 2011). "CT features of peripheral pulmonary carcinoid tumors.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 197 (5): 1073-80. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5954. PMID 22021498.
- ↑ URL: http://pathhsw5m54.ucsf.edu/case7/image75.html. Accessed on: 23 January 2012.
- ↑ He, P.; Gu, X.; Wu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Gu, Y.; He, J. (Dec 2012). "Pulmonary carcinoid tumorlet without underlying lung disease: analysis of its relationship to fibrosis.". J Thorac Dis 4 (6): 655-8. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.06.11. PMID 23205296.
- ↑ Demirci, I.; Herold, S.; Kopp, A.; Flaßhove, M.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Janßen, H. (2012). "Overdiagnosis of a typical carcinoid tumor as an adenocarcinoma of the lung: a case report and review of the literature.". World J Surg Oncol 10: 19. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-10-19. PMID 22269186.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Liu, SZ.; Staats, PN.; Goicochea, L.; Alexiev, BA.; Shah, N.; Dixon, R.; Burke, AP. (2014). "Automated quantification of Ki-67 proliferative index of excised neuroendocrine tumors of the lung.". Diagn Pathol 9: 174. doi:10.1186/s13000-014-0174-z. PMID 25318848.
- ↑ Sayeg, Y.; Sayeg, M.; Baum, RP.; Kulkarni, HR.; Presselt, N.; Mäder, I.; Kunze, A.; Sänger, J. et al. (Jul 2014). "[Pulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms].". Pneumologie 68 (7): 456-77. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1365642. PMID 25006841.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Cai, YC.; Banner, B.; Glickman, J.; Odze, RD. (Oct 2001). "Cytokeratin 7 and 20 and thyroid transcription factor 1 can help distinguish pulmonary from gastrointestinal carcinoid and pancreatic endocrine tumors.". Hum Pathol 32 (10): 1087-93. doi:10.1053/hupa.2001.28245. PMID 11679943.