Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. | |
|
| |
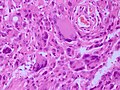
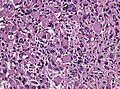
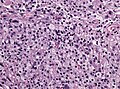
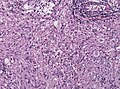
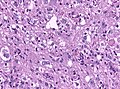
| LM | marked nuclear atypia, eosinophilic granular bodies - very common, inflammation (chronic), no necrosis |
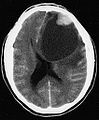
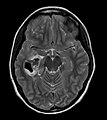
| Site | brain - typical temporal lobe |
|
| |
| Clinical history | seizure, children & young adults |
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, abbreviated PXA, is neuropathology tumour classically associated with seizures in children.
General
Features:
- Rare (less than 1% of all astrocytic tumors).
- Classically in the temporal lobe in children and young adults.
- Associated with seizures.
- Moderately aggressive (WHO Grade II).[1]
- ICD-O: 9424/3.
Gross
- Temporal lobe - classic.
- Usually assoc. with the leptomeninges,[1] i.e. superficial (in up 96%).
Microscopic
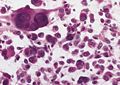
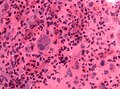
Features:[2]
- Fibrillary background.
- Large cells with marked nuclear atypia.
- Multinuclear cells possible.
- Reticulin meshwork.
- Lipidized cells.
- Eosinophilic granular bodies - very common.[1]
- Inflammatory cells (lymophocytic perivascular cuffs).
- Mitotic activity is low (except in anaplastic PXA, more than 5/10 HPF).
- Usually no necrosis (except in anaplastic PXA).
Notes:
- No mitoses.
- No necrosis.
DDx:
Images
www:
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - another case - several images (upmc.edu).
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Cerebellar pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - case 4 - several image (upmc.edu).
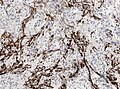
Stains
- Reticulin stain - intercellular, prominent.[3]
Image:
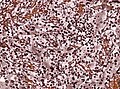
IHC
- GFAP +ve.
- S-100 +ve.
- CD68 +ve.
- CD34 frequently.
- MAP2+ve and Synapto+ve pleomorphic cells
- MIB-1 usually low.
Molecular
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Fouladi, M.; Jenkins, J.; Burger, P.; Langston, J.; Merchant, T.; Heideman, R.; Thompson, S.; Sanford, A. et al. (Jul 2001). "Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: favorable outcome after complete surgical resection.". Neuro Oncol 3 (3): 184-92. PMID 11465399.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1333. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dias-Santagata, D.; Lam, Q.; Vernovsky, K.; Vena, N.; Lennerz, JK.; Borger, DR.; Batchelor, TT.; Ligon, KL. et al. (2011). "BRAF V600E mutations are common in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: diagnostic and therapeutic implications.". PLoS One 6 (3): e17948. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017948. PMID 21479234.
- ↑ Schindler, G.; Capper, D.; Meyer, J.; Janzarik, W.; Omran, H.; Herold-Mende, C.; Schmieder, K.; Wesseling, P. et al. (Mar 2011). "Analysis of BRAF V600E mutation in 1,320 nervous system tumors reveals high mutation frequencies in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, ganglioglioma and extra-cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma.". Acta Neuropathol 121 (3): 397-405. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0802-6. PMID 21274720.
- ↑ Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Wöhrer, A.; Jeibmann, A.; Schittenhelm, J.; Kohlhof, P.; Preusser, M.; Romeike, B. et al. (Apr 2014). "BRAF-mutated pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma is associated with temporal location, reticulin fiber deposition and CD34 expression.". Brain Pathol 24 (3): 221-9. doi:10.1111/bpa.12111. PMID 24345274.