Warthin tumour
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Warthin tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
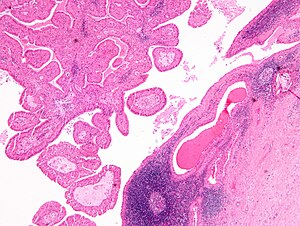 Warthin tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
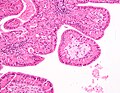
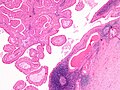
| LM | papillae with a two rows of pink (eosinophilic) epithelial cells (with cuboidal basal cells and columnar luminal cells), fibrous capsule, cystic space filled with debris, lymphoid stroma |
| LM DDx | lymphoepithelial cyst. |
| Site | salivary gland - parotid gland only |
|
| |
| Clinical history | strong association of smoking |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good, benign |
| Clin. DDx | other salivary gland tumours |
Warthin tumour is a relative common benign tumour of the parotid gland. It is also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum.
General
- Benign.
Epidemiology:
- May be multicentric ~ 15% of the time.
- May be bilateral ~10% of the time.
- Classically: male > female -- changing with more women smokers.
- Smokers.
- Old - usually 60s, very rarely < 40 years old.
Notes:
- No malignant transformation.
- Not in submandibular gland.
- Not in sublingual gland.
- Not in children.
Gross
- Motor-oil like fluid.
- Cystic component larger in larger lesions.
- Small lesions may be solid.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Papillae (nipple-shaped structures) with a two rows of pink (eosinophilic) epithelial cells (with cuboidal basal cells and columnar luminal cells) -- key feature.
- Fibrous capsule - pink & homogenous on H&E stain.
- Cystic space filled with debris in situ (not necrosis).
- Lymphoid stroma.
Notes:
- +/-Squamous differentiation.
- +/-Goblet cell differentiation.
DDx:
- Lymphoepithelial cyst.
- Cyst within a lymph node.