Difference between revisions of "Eyelid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+image) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image: Closed human eye, superior view.jpg|thumb|right|A photograph showing the superior eyelid. (WC/Rapidreflex)]] | [[Image: Closed human eye, superior view.jpg|thumb|right|A photograph showing the superior eyelid. (WC/Rapidreflex)]] | ||
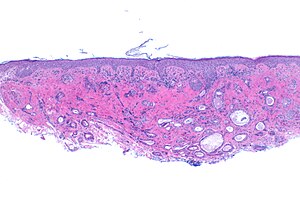
[[Image:Syringoma -- low mag.jpg|thumb|right|A [[micrograph]] showing a [[syringoma]]. These are typically lower eyelid tumours. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
The '''eyelid''' is occasionally sent to [[pathology]]. Information about the eye is found in the ''[[eye]]'' article. | The '''eyelid''' is occasionally sent to [[pathology]]. Information about the eye is found in the ''[[eye]]'' article. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:43, 1 November 2024
The eyelid is occasionally sent to pathology. Information about the eye is found in the eye article.
General
- Eyelid lesions are usually benign.
- In a series of 1,541 cases only 22 were malignant.[1]
- 21 were basal cell carcinoma
- One was squamous carcinoma.
- In a series of 1,541 cases only 22 were malignant.[1]
Common lesions
The most common lesion - as per a large series of 1,541 cases:[1]
- Squamous papilloma.
- Nevus.
- Seborrheic keratosis.
- Hydrocystomas.
- Xanthelasma.
- Epidermal cyst.
Malignant tumours of the eyelid
Malignant eyelid tumour in order of frequency:[2]
- Basal cell carcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Malignant melanoma.
- Sebaceous carcinoma.
- Lymphomas.
- Merkel cell carcinoma.
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified.
- Adnexal carcinoma not otherwise specified.
- Sweat gland carcinoma.
Specific entities
Xanthelasma
- Xanthelasma palpebrarum redirects here.
General
- ~8% of eyelid tumours in one series.[1]
- Type of xanthoma.[3]
- It is said that a xanthoma can be anywhere. If it is on the eyelid it is a xanthelasma; a xanthelasma is a xanthoma of the eyelid.[4]
- Associated with increased serum lipid levels.[5]
- Incidence of elevated cholesterol is higher in younger patients.[6]
Gross
- Exophytic lesion (on eyelid or around it) - classically yellow.
DDx:
Microscopic
Features:
- Collection of foamy histiocytes within the dermis.
DDx:
Sign out
Eyelid, Lesion Right Upper Lid, Excision: - Benign skin tag with rare foamy histiocytes in keeping with an early xanthelasma. - NEGATIVE for malignancy. Comment: Xanthelasma may be associated with metabolic abnormalities. A lipid profile is suggested if not done recently.
Chalazion
Main article: Chalazion
Syringoma
Main article: Syringoma
See also
- Eye.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gundogan, FC.; Yolcu, U.; Tas, A.; Sahin, OF.; Uzun, S.; Cermik, H.; Ozaydin, S.; Ilhan, A. et al. (2015). "Eyelid tumors: clinical data from an eye center in Ankara, Turkey.". Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16 (10): 4265-9. PMID 26028084.
- ↑ Margo CE, Mulla ZD (February 1998). "Malignant tumors of the eyelid: a population-based study of non-basal cell and non-squamous cell malignant neoplasms". Arch Ophthalmol 116 (2): 195–8. doi:10.1001/archopht.116.2.195. PMID 9488271.
- ↑ Pathania, V.; Chatterjee, M.. "Ultrapulse carbon dioxide laser ablation of xanthelasma palpebrarum: a case series.". J Cutan Aesthet Surg 8 (1): 46-9. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.155084. PMID 25949023.
- ↑ URL: https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/xanthelasma. Accessed on: May 1, 2023.
- ↑ Rubinstein, TJ.; Mehta, MP.; Schoenfield, L.; Perry, JD.. "Orbital xanthogranuloma in an adult patient with xanthelasma palpebrarum and hypercholesterolemia.". Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 30 (1): e6-8. doi:10.1097/IOP.0b013e3182873d13. PMID 23503059.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 628. ISBN 978-0443066542.