Difference between revisions of "SMARCB1-deficient renal medullary carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
Imaging: | |||
*Increase muscle surface area (muscle hypertrophy) - due to exercise.<ref name=pmid22686875/> | *Increase muscle surface area (muscle hypertrophy) - due to exercise.<ref name=pmid22686875/> | ||
Revision as of 01:58, 20 March 2024
| SMARCB1-deficient renal medullary carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
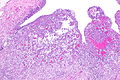
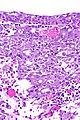
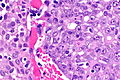
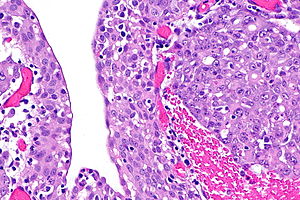 Renal medullary carcinoma (right of image), reactive urothelium and sickled red blood cells. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron) | |
| LM DDx | collecting duct carcinoma, yolk sac tumour, hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma, ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma |
| IHC | SMARCB1 (INI1) -ve, PAX8 +ve, cyclin D1 +ve, CK7 +ve, vimentin +ve, EMA +ve |
| Gross | well-circumscribed mass in renal medulla |
| Grossing notes | total nephrectomy for tumour grossing, partial nephrectomy grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney, medulla - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait |
| Clinical history | usu. young adults with sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Radiology | muscle hypertrophy (due to exercise) |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other renal tumours |
SMARCB1-deficient renal medullary carcinoma is a rare malignant kidney tumour associated with sickle cell trait and a poor prognosis.
It was previously called renal medullary carcinoma, abbreviated RMC.
General
- Rare.
- Usually young adults.
- Strong association with sickle cell trait (heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele)[1] and sickle cell disease.[2]
- A large series (217 cases) showed 88% (191/217) have sickle cell trait and 8% (16/217) have sickle cell disease.[3]
- Aggressive/poor prognosis.[4]
- Closely related to collecting duct carcinoma.[5]
- Associated with high-intensity exercise.[5]
Aside:
- Kidney disease associated with sickle cell disorders:[1]
- Papillary necrosis.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Renal infarction.
- Pyelonephritis.
Note:
- ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma is a separate entity; it was previously thought to be related to renal medullary carcinoma.[6][7]
Gross
Features:[4]
- Well circumscribed.
- Renal medulla.
Gross
Imaging:
- Increase muscle surface area (muscle hypertrophy) - due to exercise.[5]
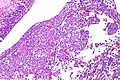
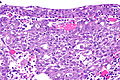
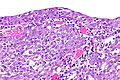
Microscopic
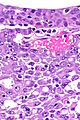
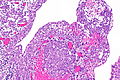
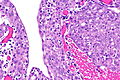
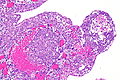
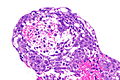
- Variable architecture:
- Reticular - classic.
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma-like appearance:
- Cystic spaces.
- Yolk sac-like.
- Tubular.
- Desmoplastic stroma - prominent.
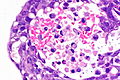
- Inflammation:
- Lymphocytes.
- Neutrophils - margination in vessels.
- +/-Drepanocytes (sickled red blood cells) - especially among extravascular red blood cells.
DDx:
- Yolk sac tumour.
- Collecting duct carcinoma.
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma.
- ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma.
Images
Case
www
- RMC (nature.com).
- RMC - low mag. (nature.com).[8]
- RMC - high mag. (nature.com).[8]
- RMC with yolk sac-like morphology (nature.com).[8]
IHC
Features:[2]
A panel:
- AE1/AE3, cyclin D1, CK7, PAX8, p63, INI-1, L-ALK, RCC, CKIT, AMACR, GATA3, CK34betaE12, CK5/6, vimentin.
Sign out
Left Kidney, Radical Nephrectomy:
- RENAL MEDULLARY CARCINOMA, see comment.
-- Margin POSITIVE for carcinoma.
-- Please see synoptic report.
- Four lymph nodes POSITIVE for carcinoma of six (4 positive/6).
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Davis CJ, Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA (January 1995). "Renal medullary carcinoma. The seventh sickle cell nephropathy". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 19 (1): 1–11. PMID 7528470.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cheng JX, Tretiakova M, Gong C, Mandal S, Krausz T, Taxy JB (June 2008). "Renal medullary carcinoma: rhabdoid features and the absence of INI1 expression as markers of aggressive behavior". Mod. Pathol. 21 (6): 647–52. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2008.44. PMID 18327209.
- ↑ Alvarez O, Rodriguez MM, Jordan L, Sarnaik S (October 2015). "Renal medullary carcinoma and sickle cell trait: A systematic review". Pediatr Blood Cancer 62 (10): 1694–9. doi:10.1002/pbc.25592. PMID 26053587.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Watanabe, IC.; Billis, A.; Guimarães, MS.; Alvarenga, M.; de Matos, AC.; Cardinalli, IA.; Filippi, RZ.; de Castro, MG. et al. (Sep 2007). "Renal medullary carcinoma: report of seven cases from Brazil.". Mod Pathol 20 (9): 914-20. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800934. PMID 17643096. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n9/full/3800934a.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Calderaro J, Moroch J, Pierron G, et al. (September 2012). "SMARCB1/INI1 inactivation in renal medullary carcinoma". Histopathology 61 (3): 428–35. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04228.x. PMID 22686875. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "pmid22686875" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Mariño-Enríquez, A.; Ou, WB.; Weldon, CB.; Fletcher, JA.; Pérez-Atayde, AR. (Mar 2011). "ALK rearrangement in sickle cell trait-associated renal medullary carcinoma.". Genes Chromosomes Cancer 50 (3): 146-53. doi:10.1002/gcc.20839. PMID 21213368.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN.; Egevad, L.; Epstein, JI.; Grignon, D.; Hes, O.; Moch, H. et al. (Oct 2013). "The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver Classification of Renal Neoplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (10): 1469-89. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1. PMID 24025519.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B. (Jun 2009). "Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 22 Suppl 2: S2-S23. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.70. PMID 19494850.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 286. ISBN 978-0781765275.