Difference between revisions of "Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(a few points) |
m (DLBCL vs PMBCL) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*Rare. | *Rare. | ||
*Young adults, more common in females (M:F = 1:2) | *Young adults, more common in females (M:F = 1:2) | ||
*[[Mediastinum]]. | *[[Mediastinum]] | ||
It is distinguished from DLBCL based on the patient demographics, radiological staging (showing mainly mediastinal disease) and immunoprofile (typically CD23+/CD30+). PMBCL has a better prognosis than DLBCL. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
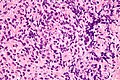
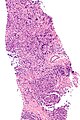
*Atypical large lymphoid cells - | *Atypical large lymphoid cells - may be morphologically indistinguishable from ''[[DLBCL]]'' | ||
*Classically associated with: | *Classically associated with: | ||
**Fibrosis | **Fibrosis | ||
Latest revision as of 21:21, 16 June 2018
Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, abbreviated PMBL, is an uncommon form of large B-cell lymphoma.
It is also known as primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.
General
- Rare.
- Young adults, more common in females (M:F = 1:2)
- Mediastinum
It is distinguished from DLBCL based on the patient demographics, radiological staging (showing mainly mediastinal disease) and immunoprofile (typically CD23+/CD30+). PMBCL has a better prognosis than DLBCL.
Microscopic
Features:
- Atypical large lymphoid cells - may be morphologically indistinguishable from DLBCL
- Classically associated with:
- Fibrosis
- Clear cells.
Note:
DDx:
- Other types of DLBCL (radiological assessment is important - PMBCL is centred in the mediastinum)
- B-cell lymphoma with features intermediate between DLBCL and classical Hodgkins lymphoma
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma.
IHC
- Pan B-cell markers
- CD10 in minority (~20%)
- CD23 and CD30 expression more common (~70% and ~85% respectively)
- EBV negative
Images
www:
Sign out
MASS, ANTERIOR MEDIASTINAL, CORE BIOPSY: - LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA IN A FIBROTIC BACKGROUND WITH NECROSIS, SEE COMMENT COMMENT: Morphology: Tumour cells: size ~2x a mature lymphocyte, a moderate quantity of grey/basophilic cytoplasm, no clear cells are identified. Cells intermixed with tumour: mature lymphocytes, rare eosinophils. Architecture: no gland formation, discohesive, no follicles apparent, extensive fibrosis. Tumour cells: POSITIVE: CD45, CD20, CD10, BCL-6, BCL-2. NEGATIVE: pankeratin, PLAP, CD3, CD30. Ki-67: 50% of large (lymphoid) cells.
See also
References
- ↑ Johnson, PW.; Davies, AJ. (2008). "Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.". Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program: 349-58. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2008.1.349. PMID 19074109.
- ↑ Coso, D.; Rey, J.; Bouabdallah, R. (Feb 2010). "[Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma]". Rev Pneumol Clin 66 (1): 32-5. doi:10.1016/j.pneumo.2009.12.007. PMID 20207294.
- ↑ van Besien, K.; Kelta, M.; Bahaguna, P. (Mar 2001). "Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma: a review of pathology and management.". J Clin Oncol 19 (6): 1855-64. PMID 11251018.