Difference between revisions of "Astrocytoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (Table with overview) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (cleanup) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
=Common= | =Common= | ||
==Pilocytic astrocytoma== | ==Pilocytic astrocytoma== | ||
* Benign, cystic, infratentorial. | |||
* Classic childhood tumor, surgically resectable. | |||
* Variant: [[Pilomyxoid astrocytoma]] | |||
{{Main|Pilocytic astrocytoma}} | {{Main|Pilocytic astrocytoma}} | ||
==Diffuse astrocytoma== | ==Diffuse astrocytoma== | ||
* Grade II | * Grade II astrocytic tumors typically seen in adults. | ||
* | * Usually show progression to glioblastoma. | ||
{{Main|Diffuse astrocytoma}} | |||
==Anaplastic astrocytoma== | |||
* Grade III astrocytic tumors typically seen in adults. | |||
* Lacks endothelial proliferations and necrosis of glioblastoma. | |||
{{Main|Anaplastic astrocytoma}} | |||
==Glioblastoma== | ==Glioblastoma== | ||
* Most common malignant brain tumor peaking around 65 years. | |||
* Prognosis very poor. | |||
* Variant: [[Giant cell glioblastoma]] | |||
* Variant: [[Gliosarcoma]] | |||
{{Main|Glioblastoma}} | {{Main|Glioblastoma}} | ||
=Uncommon= | =Uncommon= | ||
==Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma== | ==Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma== | ||
* Intraventricular benign tumor of adolescents. | |||
* Assoicated with [[Tuberous sclerosis]]. | |||
{{Main|Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma}} | {{Main|Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma}} | ||
==Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma | ==Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma (PXA)== | ||
* Kids & young adults usually with good prognosis. | |||
* Large lipidized cells mimicking a malignant tumor | |||
*Kids & young adults | {{Main|Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma}} | ||
*Large cells | |||
==Gliomatosis cerebri== | ==Gliomatosis cerebri== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 78: | ||
* More than 3 lobes have to be involved, us. bilateral (radiology). | * More than 3 lobes have to be involved, us. bilateral (radiology). | ||
* biologic behaviour corresponds to WHO III (ICD-O: 9381/3) | * biologic behaviour corresponds to WHO III (ICD-O: 9381/3) | ||
==H3.3 K27M mutated glioma of the midline== | ==H3.3 K27M mutated glioma of the midline== | ||
| Line 109: | Line 106: | ||
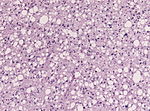
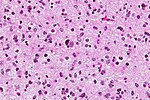
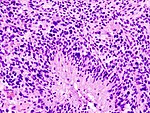
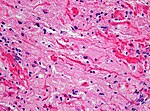
====Images==== | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
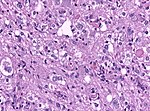
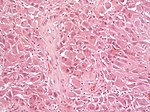
Image:Gliosarcoma_Histopathology_200x_EVG.jpg | Gliosarcoma - | Image:Gliosarcoma_Histopathology_200x_EVG.jpg | Gliosarcoma - elastica van Giesson. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 123: | Line 120: | ||
*SMA +ve. | *SMA +ve. | ||
*Factor VIII +ve. | *Factor VIII +ve. | ||
==Gliofibroma== | |||
* Very rare indolent tumor in children <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Deb | first1 = P. | last2 = Sarkar | first2 = C. | last3 = Garg | first3 = A. | last4 = Singh | first4 = VP. | last5 = Kale | first5 = SS. | last6 = Sharma | first6 = MC. | title = Intracranial gliofibroma mimicking a meningioma: a case report and review of literature. | journal = Clin Neurol Neurosurg | volume = 108 | issue = 2 | pages = 178-86 | month = Feb | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1016/j.clineuro.2004.11.021 | PMID = 16412839 }}</ref> | |||
* Usually not dura-based (DD: Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma) | |||
* Glial tumor with non-neoplastic fibromatous component. | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 20 July 2015
An astrocytoma is a neoplasm derived from an astrocyte. Astrocytomas are common. This article is a brief introduction them. An overview of CNS tumours is found in the CNS tumours article.
Overview
| Name | Type | Variants / Patterns | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse Astrocytoma, WHO II | diffuse | protoplasmatic, fibrillar, gemistocytic | |
| Anaplastic Astrocytoma, WHO III | diffuse | gliomatosis cerebri | |
| Glioblastoma, WHO IV | diffuse | small cell, epitheloid/rhabdoid, with PNET componet, with granular cell component, giant cell, gliosarcoma | |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma, WHO I | circumscribed | pilomyxoid astrocytoma, anaplastic pilocytic astrocytoma | |
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, WHO II (PXA) | circumscribed | anaplastic PXA | |
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, WHO I (SEGA) | circumscribed | SEGA in tuberous sclerosis |
Common
Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Benign, cystic, infratentorial.
- Classic childhood tumor, surgically resectable.
- Variant: Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
Main article: Pilocytic astrocytoma
Diffuse astrocytoma
- Grade II astrocytic tumors typically seen in adults.
- Usually show progression to glioblastoma.
Main article: Diffuse astrocytoma
Anaplastic astrocytoma
- Grade III astrocytic tumors typically seen in adults.
- Lacks endothelial proliferations and necrosis of glioblastoma.
Main article: Anaplastic astrocytoma
Glioblastoma
- Most common malignant brain tumor peaking around 65 years.
- Prognosis very poor.
- Variant: Giant cell glioblastoma
- Variant: Gliosarcoma
Main article: Glioblastoma
Uncommon
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
- Intraventricular benign tumor of adolescents.
- Assoicated with Tuberous sclerosis.
Main article: Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma (PXA)
- Kids & young adults usually with good prognosis.
- Large lipidized cells mimicking a malignant tumor
Main article: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Gliomatosis cerebri
- Extensively diffusely growing astrocytic neoplasm.
- Currently considered a pattern of diffuse glioma infiltration.
- More than 3 lobes have to be involved, us. bilateral (radiology).
- biologic behaviour corresponds to WHO III (ICD-O: 9381/3)
H3.3 K27M mutated glioma of the midline
- High-grade astrocytic neoplasm associated with midline structures
- Mostly in children and adolescents
- Includes diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DPIG)
- Will become provisonal variant in upcoming WHO 2016 classification
- Distinct biological and clinical group with poor prognosis [1]
Gliosarcoma
General
- Considered to be a variant of glioblastoma by WHO.[2]
- Rare ~ 200 cases reported in the literature.[2]
- Definition: gliosarcoma = glioblastoma + sarcomatous component.[3]
- Usual location (like glioblastoma): temporal lobe.
Microscopic
Features:
- Glioblastoma.
- Sarcomatous component (one of the following):[2][3]
- Fibroblastic.
- Cartilaginous.
- Osseous.
- Smooth muscle.
- Striated muscle.
- Adipocyte.
Images
www:
- Gliosarcoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Gliosarcoma - case 2 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Gliosarcoma - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
Gliosarcoma with smooth muscle component (gliomyosarcoma):[6]
- SMA +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
Gliofibroma
- Very rare indolent tumor in children [7]
- Usually not dura-based (DD: Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma)
- Glial tumor with non-neoplastic fibromatous component.
See also
References
- ↑ Khuong-Quang, DA.; Buczkowicz, P.; Rakopoulos, P.; Liu, XY.; Fontebasso, AM.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; Albrecht, S. et al. (Sep 2012). "K27M mutation in histone H3.3 defines clinically and biologically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas.". Acta Neuropathol 124 (3): 439-47. doi:10.1007/s00401-012-0998-0. PMID 22661320.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Han SJ, Yang I, Tihan T, Prados MD, Parsa AT (February 2010). "Primary gliosarcoma: key clinical and pathologic distinctions from glioblastoma with implications as a unique oncologic entity". J. Neurooncol. 96 (3): 313–20. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9973-6. PMC 2808523. PMID 19618114. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2808523/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ayadi L, Charfi S, Khabir A, et al. (March 2010). "[Cerebral gliosarcoma: clinico-pathologic study of 8 cases]" (in French). Tunis Med 88 (3): 142–6. PMID 20415184.
- ↑ Horiguchi, H.; Hirose, T.; Kannuki, S.; Nagahiro, S.; Sano, T. (Aug 1998). "Gliosarcoma: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and fluorescence in situ hybridization study.". Pathol Int 48 (8): 595-602. PMID 9736406.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case361.html. Accessed on: 15 January 2012.
- ↑ Khanna, M.; Siraj, F.; Chopra, P.; Bhalla, S.; Roy, S.. "Gliosarcoma with prominent smooth muscle component (gliomyosarcoma): a report of 10 cases.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 54 (1): 51-4. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.77324. PMID 21393877.
- ↑ Deb, P.; Sarkar, C.; Garg, A.; Singh, VP.; Kale, SS.; Sharma, MC. (Feb 2006). "Intracranial gliofibroma mimicking a meningioma: a case report and review of literature.". Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108 (2): 178-86. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2004.11.021. PMID 16412839.