Difference between revisions of "Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(+infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
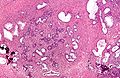
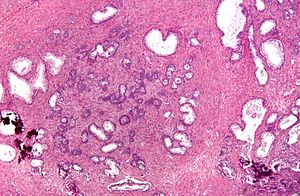
| Image = Nodular_hyperplasia_of_the_prostate.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = | |||
| Synonyms = Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = stromal and/or glandular hyperplasia | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = enlarged prostate gland, nodularity | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[prostate gland]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = very common, esp. elderly | |||
| Bloodwork = +/-elevation of PSA (mild) | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = medical, TURP | |||
}} | |||
'''Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland''', also '''benign prostatic hyperplasia''' (abbreviated '''BPH'''), is a common benign pathology of the [[prostate gland]]. | '''Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland''', also '''benign prostatic hyperplasia''' (abbreviated '''BPH'''), is a common benign pathology of the [[prostate gland]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 22 February 2014
| Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland. H&E stain. |
|
| |
| LM | stromal and/or glandular hyperplasia |
| Gross | enlarged prostate gland, nodularity |
| Site | prostate gland |
|
| |
| Prevalence | very common, esp. elderly |
| Blood work | +/-elevation of PSA (mild) |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | medical, TURP |
Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland, also benign prostatic hyperplasia (abbreviated BPH), is a common benign pathology of the prostate gland.
It is also known as prostatic nodular hyperplasia. Occasionally, it is referred to as benign prostatic hypertrophy; this is a misnomer. This pathology is not a hypertrophy.
General
- Very common.
- Incidence increases with age.
Clinical - mnemonic I WISH 2p:[1]
- Intermittency.
- Weak stream.
- Incomplete emptying.
- Straining.
- Hesitancy.
- Post-void dribbling.
- Prolonged voiding.
Treatment:
- Medications.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Gross
- Enlargement of the prostate.
- Nodularity of the prostate.
Microscopic
Features:
- Stromal and/or glandular hyperplasia.
Note:
- Should not be diagnosed on core biopsy!
DDx:
- Urothelial carcinoma - significant nuclear atypia.
Images
Sign out
Urothelium present
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION. - UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH A MILD LYMPHOCYTIC INFILTRATE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP) AND URINARY BLADDER NECK: - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION. - UROTHELIUM WITH THE CHANGES OF CYSTITIS CYSTICA ET GLANDULARIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP) AND URINARY BLADDER NECK: - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION, AND FOCAL ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION. - UROTHELIUM WITH THE CHANGES OF CYSTITIS CYSTICA ET GLANDULARIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
No urothelium present
PROSTATE GLAND, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION.
Post-TURP granuloma present
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION WITH PROMINENT BLOOD VESSELS AND SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA. - PALISADING GRANULOMA WITH NECROTIC CORE, SEE COMMENT. - UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH A MILD INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: This is morphologically consistent with a post-TURP granuloma.
See also
References
- ↑ Shiau, Carolyn; Toren, Andrew (2006). Toronto Notes 2006: Comprehensive Medical Reference (Review for MCCQE 1 and USMLE Step 2) (22nd edition (2006) ed.). Toronto Notes for Medical Students, Inc.. pp. U5. ISBN 978-0968592861.