Difference between revisions of "Adenocarcinoma of the lung"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out, +infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, mucinous type.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Lung adenocarcinoma, mucinous. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = nuclear atypia, eccentrically placed nuclei, usu. abundant cytoplasm (classically with mucin vacuoles), often conspicuous [[nucleoli]], +/-[[nuclear pseudoinclusions]] | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = CK7 +ve, TTF-1 +ve, CK20 -ve, p40 -ve, p63 -ve (usually) | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = +/-EGFR mutations, +/-ALK [[chromosomal translocation]] (inv(2)(p21p23) -- EML4-ALK fusion) | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[lung]] - see ''[[lung tumours]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = most common primary lung tumour | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = lung mass - typically central (close to large airways), may be multifocal | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = moderate | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other [[lung tumours]] - primary and metastatic | |||
| Tx = surgical resection if feasible | |||
}} | |||
'''Adenocarcinoma of the lung''', also '''lung adenocarcinoma''', is common malignant [[lung tumour]]. | |||
==General== | |||
Treatment: | |||
*Lung adenocarcinoma may be treated with [[EGFR inhibitors]] (e.g. gefitinib (Iressa), erlotinib (Tarceva)).<ref name=pmid20855837>{{cite journal |author=Sun Y, Ren Y, Fang Z, ''et al.'' |title=Lung adenocarcinoma from East Asian never-smokers is a disease largely defined by targetable oncogenic mutant kinases |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=28 |issue=30 |pages=4616–20 |year=2010 |month=October |pmid=20855837 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2010.29.6038 |url=}}</ref> | |||
Patients that receive EGFR inhibitors classically are:<ref name=pmid21151896>{{cite journal |author=Job B, Bernheim A, Beau-Faller M, ''et al.'' |title=Genomic Aberrations in Lung Adenocarcinoma in Never Smokers |journal=PLoS One |volume=5 |issue=12 |pages=e15145 |year=2010 |pmid=21151896 |pmc=2997777 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0015145 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Non-smokers. | |||
*Female. | |||
*Asian. | |||
**Caucasians also benefit.<ref name=pmid20973798>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rosell | first1 = R. | last2 = Moran | first2 = T. | last3 = Cardenal | first3 = F. | last4 = Porta | first4 = R. | last5 = Viteri | first5 = S. | last6 = Molina | first6 = MA. | last7 = Benlloch | first7 = S. | last8 = Taron | first8 = M. | title = Predictive biomarkers in the management of EGFR mutant lung cancer. | journal = Ann N Y Acad Sci | volume = 1210 | issue = | pages = 45-52 | month = Oct | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05775.x | PMID = 20973798 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Classically peripheral lesions. | |||
*May be multifocal. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Nuclear atypia. | |||
*Eccentrically placed nuclei. | |||
*Abundant cytoplasm - classically with mucin vacuoles. | |||
*Often conspicuous [[nucleoli]]. | |||
*+/-[[Nuclear pseudoinclusions]]. | |||
Negatives: | |||
*Lack of intercellular bridges. | |||
Patterns:<ref name=pmid21252716>{{cite journal |author=Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, ''et al.'' |title=International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma |journal=J Thorac Oncol |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=244–85 |year=2011 |month=February |pmid=21252716 |doi=10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Lepidic - tumour grows long the alveolar wall; means ''scaly covering''.<ref>URL: [http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/lepidic http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/lepidic]. Accessed on: 8 August 2013.</ref> | |||
*Acinar - berry-shaped glands. | |||
*Papillary - fibrovascular cores. | |||
*Micropapillary - nipple shaped projections without fibrovascular cores. | |||
*Solid - sheet of cells. | |||
Notes: | |||
*[[Lymphovascular invasion]] is common. | |||
*Micropapillary predominant pattern and tumours with any amount of the lepidic pattern are associated with EGFR mutations.<ref name=pmid21970488>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shim | first1 = HS. | last2 = Lee | first2 = da H. | last3 = Park | first3 = EJ. | last4 = Kim | first4 = SH. | title = Histopathologic characteristics of lung adenocarcinomas with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society lung adenocarcinoma classification. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 135 | issue = 10 | pages = 1329-34 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.5858/arpa.2010-0493-OA | PMID = 21970488 }}</ref> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Metastasis|Metastatic]] adenocarcinoma. | |||
**[[Colorectal adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
**Breast adenocarcinoma. | |||
***[[Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast]]. | |||
***[[Invasive lobular carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]]. | |||
*[[Non-small cell lung carcinoma]] - diagnosis should be avoid if possible. | |||
*[[Malignant mesothelioma]]. | |||
*[[Small cell carcinoma of the lung]]. | |||
*Adenocarcinoma in situ. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
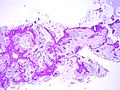
Image:Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, mucinous type 2.jpg |BAC - mucinous type - low mag. (WC/Yale Rosen) | |||
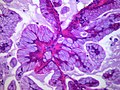
Image:Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, mucinous type.jpg | BAC - mucinous type - high mag. (WC/Yale Rosen) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.pathpedia.com/education/eatlas/histopathology/lung_and_bronchi/bronchioloalveolar_carcinoma_mucinous.aspx BAC mucinous type adjacent to benign (pathpedia.com)]. | |||
*[http://cancergrace.org/wp-content/uploads/2007/05/mucinous-vs-nonmucinous-bac-histology.jpg BAC mucinous and nonmucinous (cancergrace.org)].<ref>URL: [http://cancergrace.org/lung/2007/05/14/bac-mucinous-and-non-mucinous/ http://cancergrace.org/lung/2007/05/14/bac-mucinous-and-non-mucinous/]. Accessed on: 8 August 2013.</ref> | |||
===Classification=== | |||
Classification based on extent:<ref name=pmid21252716>{{cite journal |author=Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, ''et al.'' |title=International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma |journal=J Thorac Oncol |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=244–85 |year=2011 |month=February |pmid=21252716 |doi=10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 |url=}}</ref> | |||
#Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) - previously known as [[BAC]]. | |||
#*Subtypes: nonmucinous, mucinous, mixed mucinous/nonmucinous. | |||
#Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA). | |||
#*Lepidic growth with up to 5 mm of invasion. | |||
#*Subtypes: nonmucinous (most common), mucinous, mixed mucinous/nonmucinous. | |||
#Invasive adenocarcinoma: | |||
#*Subtypes: micropapillary, mucinous (previously ''mucinous BAC''), colloid, fetal, enteric. | |||
==IHC== | |||
Primary versus metastatic: | |||
*CK7 +ve. | |||
*TTF-1 +ve. | |||
*CK20 -ve. | |||
Adenocarcinoma versus SCC: | |||
*TTF-1 +ve. | |||
*p40 -ve.<ref name=pmid22056955>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bishop | first1 = JA. | last2 = Teruya-Feldstein | first2 = J. | last3 = Westra | first3 = WH. | last4 = Pelosi | first4 = G. | last5 = Travis | first5 = WD. | last6 = Rekhtman | first6 = N. | title = p40 (ΔNp63) is superior to p63 for the diagnosis of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 25 | issue = 3 | pages = 405-15 | month = Mar | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2011.173 | PMID = 22056955 }}</ref> | |||
*p63 -ve -- occasionally +ve. | |||
==Molecular== | |||
*EGFR mutations (typically assessed by PCR) - respond to [[TKI]]s (e.g. [[gefitinib]], [[erlotinib]]) if:<ref name=pmid19680292>{{Cite journal | last1 = John | first1 = T. | last2 = Liu | first2 = G. | last3 = Tsao | first3 = MS. | title = Overview of molecular testing in non-small-cell lung cancer: mutational analysis, gene copy number, protein expression and other biomarkers of EGFR for the prediction of response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. | journal = Oncogene | volume = 28 Suppl 1 | issue = | pages = S14-23 | month = Aug | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1038/onc.2009.197 | PMID = 19680292 }}</ref> | |||
**Exon 19 deletion. | |||
**Exon 21 L858R. | |||
***Natural history of mutation is suspected to have a better prognosis vs. wild-type.<ref>URL: [http://www.mycancergenome.org/mutation.php?dz=nsclc&gene=egfr&code=l858r http://www.mycancergenome.org/mutation.php?dz=nsclc&gene=egfr&code=l858r]. Accessed on: 27 April 2012.</ref> | |||
**KRAS mutations are absent, i.e. ''wild-type KRAS''.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pao | first1 = W. | last2 = Wang | first2 = TY. | last3 = Riely | first3 = GJ. | last4 = Miller | first4 = VA. | last5 = Pan | first5 = Q. | last6 = Ladanyi | first6 = M. | last7 = Zakowski | first7 = MF. | last8 = Heelan | first8 = RT. | last9 = Kris | first9 = MG. | title = KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. | journal = PLoS Med | volume = 2 | issue = 1 | pages = e17 | month = Jan | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020017 | PMID = 15696205 }}</ref> | |||
*ALK [[chromosomal translocation]] (inv(2)(p21p23) -- EML4-ALK fusion).<ref name=pmid21245935>{{Cite journal | last1 = Li | first1 = Y. | last2 = Ye | first2 = X. | last3 = Liu | first3 = J. | last4 = Zha | first4 = J. | last5 = Pei | first5 = L. | title = Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors. | journal = Neoplasia | volume = 13 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-11 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21245935 }}</ref> | |||
**Associated with a poor prognosis.<ref name=pmid22134072>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yang | first1 = P. | last2 = Kulig | first2 = K. | last3 = Boland | first3 = JM. | last4 = Erickson-Johnson | first4 = MR. | last5 = Oliveira | first5 = AM. | last6 = Wampfler | first6 = J. | last7 = Jatoi | first7 = A. | last8 = Deschamps | first8 = C. | last9 = Marks | first9 = R. | title = Worse disease-free survival in never-smokers with ALK+ lung adenocarcinoma. | journal = J Thorac Oncol | volume = 7 | issue = 1 | pages = 90-7 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31823c5c32 | PMID = 22134072 }}</ref> | |||
**Amenable to treatment with TKI. | |||
**See ''[[lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement]]. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
===Biopsy=== | |||
<pre> | |||
LUNG, LEFT, BIOPSY: | |||
- ADENOCARCINOMA, LEPIDIC GROWTH; INVASION CANNOT BE EXCLUDED IN THIS SMALL SPECIMEN. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Resection=== | |||
<pre> | |||
LUNG, LEFT UPPER LOBE, LOBECTOMY: | |||
- ADENOCARCINOMA WITH AN ACINAR PATTERN, SOLID PATTERN, MICROPAPILLARY PATTERN | |||
AND LEPIDIC PATTERN -- PATTERNS IN ORDER OF PREVALENCE. | |||
- MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
- THREE LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY (3 POSITIVE/4). | |||
- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
LUNG, RIGHT UPPER LOBE, LOBECTOMY: | |||
- MULTIPLE ADENOCARCINOMAS (x2) WITH AN ACINAR PATTERN, SOLID PATTERN, MICROPAPILLARY PATTERN | |||
AND LEPIDIC PATTERN -- PATTERNS IN ORDER OF PREVALENCE. | |||
- MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
- FOUR LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY (0 POSITIVE/4). | |||
- LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION PRESENT. | |||
- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY AND COMMENT. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
The histology of the two adenocarcinomas resemble one another and lymphovascular | |||
invasion is present. These findings favour that the smaller tumor is a metastasis, rather | |||
than a synchronous primary. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Micro=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Adequacy: scant tissue (<0.5 cm). | |||
Gland formation: focal, poorly formed. | |||
Cell size: large. | |||
Cytoplasm: moderate-to-abundant, grey-eosinophilic. | |||
Nucleus location: eccentric. | |||
Nuclear pleomorphism: moderate. | |||
Nuclear moulding: absent. | |||
Nucleoli: present, prominent. | |||
Nuclear pseudoinclusions: present. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
Number of cores: 3. | |||
Length of cores (total): 2.0 cm. | |||
Gland formation: present. | |||
Cell size: large. | |||
Cytoplasm: moderate, grey-eosinophilic. | |||
Necrosis: none apparent. | |||
Mucin: none. | |||
Nucleus location: eccentric. | |||
Nuclear pleomorphism: moderate. | |||
Nuclear moulding: absent. | |||
Nuclear pseudoinclusions: absent. | |||
Nuclear shape/arrangment: cigar-like/pseudostratified. | |||
Nucleoli: present. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Staging note=== | |||
*Two small tumours in one lobe is pT3. | |||
*Visceral pleural involvement upgrades small tumours. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Lung tumours]]. | |||
*[[Adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Metastasis]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 01:08, 13 January 2014
| Adenocarcinoma of the lung | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Lung adenocarcinoma, mucinous. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | nuclear atypia, eccentrically placed nuclei, usu. abundant cytoplasm (classically with mucin vacuoles), often conspicuous nucleoli, +/-nuclear pseudoinclusions |
| IHC | CK7 +ve, TTF-1 +ve, CK20 -ve, p40 -ve, p63 -ve (usually) |
| Molecular | +/-EGFR mutations, +/-ALK chromosomal translocation (inv(2)(p21p23) -- EML4-ALK fusion) |
| Site | lung - see lung tumours |
|
| |
| Prevalence | most common primary lung tumour |
| Radiology | lung mass - typically central (close to large airways), may be multifocal |
| Prognosis | moderate |
| Clin. DDx | other lung tumours - primary and metastatic |
| Treatment | surgical resection if feasible |
Adenocarcinoma of the lung, also lung adenocarcinoma, is common malignant lung tumour.
General
Treatment:
- Lung adenocarcinoma may be treated with EGFR inhibitors (e.g. gefitinib (Iressa), erlotinib (Tarceva)).[1]
Patients that receive EGFR inhibitors classically are:[2]
- Non-smokers.
- Female.
- Asian.
- Caucasians also benefit.[3]
Gross
- Classically peripheral lesions.
- May be multifocal.
Microscopic
Features:
- Nuclear atypia.
- Eccentrically placed nuclei.
- Abundant cytoplasm - classically with mucin vacuoles.
- Often conspicuous nucleoli.
- +/-Nuclear pseudoinclusions.
Negatives:
- Lack of intercellular bridges.
Patterns:[4]
- Lepidic - tumour grows long the alveolar wall; means scaly covering.[5]
- Acinar - berry-shaped glands.
- Papillary - fibrovascular cores.
- Micropapillary - nipple shaped projections without fibrovascular cores.
- Solid - sheet of cells.
Notes:
- Lymphovascular invasion is common.
- Micropapillary predominant pattern and tumours with any amount of the lepidic pattern are associated with EGFR mutations.[6]
DDx:
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma.
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Breast adenocarcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.
- Non-small cell lung carcinoma - diagnosis should be avoid if possible.
- Malignant mesothelioma.
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung.
- Adenocarcinoma in situ.
Images
www:
- BAC mucinous type adjacent to benign (pathpedia.com).
- BAC mucinous and nonmucinous (cancergrace.org).[7]
Classification
Classification based on extent:[4]
- Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) - previously known as BAC.
- Subtypes: nonmucinous, mucinous, mixed mucinous/nonmucinous.
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA).
- Lepidic growth with up to 5 mm of invasion.
- Subtypes: nonmucinous (most common), mucinous, mixed mucinous/nonmucinous.
- Invasive adenocarcinoma:
- Subtypes: micropapillary, mucinous (previously mucinous BAC), colloid, fetal, enteric.
IHC
Primary versus metastatic:
- CK7 +ve.
- TTF-1 +ve.
- CK20 -ve.
Adenocarcinoma versus SCC:
- TTF-1 +ve.
- p40 -ve.[8]
- p63 -ve -- occasionally +ve.
Molecular
- ALK chromosomal translocation (inv(2)(p21p23) -- EML4-ALK fusion).[12]
- Associated with a poor prognosis.[13]
- Amenable to treatment with TKI.
- See lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement.
Sign out
Biopsy
LUNG, LEFT, BIOPSY: - ADENOCARCINOMA, LEPIDIC GROWTH; INVASION CANNOT BE EXCLUDED IN THIS SMALL SPECIMEN.
Resection
LUNG, LEFT UPPER LOBE, LOBECTOMY: - ADENOCARCINOMA WITH AN ACINAR PATTERN, SOLID PATTERN, MICROPAPILLARY PATTERN AND LEPIDIC PATTERN -- PATTERNS IN ORDER OF PREVALENCE. - MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. - THREE LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY (3 POSITIVE/4). - PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY.
LUNG, RIGHT UPPER LOBE, LOBECTOMY: - MULTIPLE ADENOCARCINOMAS (x2) WITH AN ACINAR PATTERN, SOLID PATTERN, MICROPAPILLARY PATTERN AND LEPIDIC PATTERN -- PATTERNS IN ORDER OF PREVALENCE. - MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. - FOUR LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY (0 POSITIVE/4). - LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION PRESENT. - PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY AND COMMENT. COMMENT: The histology of the two adenocarcinomas resemble one another and lymphovascular invasion is present. These findings favour that the smaller tumor is a metastasis, rather than a synchronous primary.
Micro
Adequacy: scant tissue (<0.5 cm). Gland formation: focal, poorly formed. Cell size: large. Cytoplasm: moderate-to-abundant, grey-eosinophilic. Nucleus location: eccentric. Nuclear pleomorphism: moderate. Nuclear moulding: absent. Nucleoli: present, prominent. Nuclear pseudoinclusions: present.
Number of cores: 3. Length of cores (total): 2.0 cm. Gland formation: present. Cell size: large. Cytoplasm: moderate, grey-eosinophilic. Necrosis: none apparent. Mucin: none. Nucleus location: eccentric. Nuclear pleomorphism: moderate. Nuclear moulding: absent. Nuclear pseudoinclusions: absent. Nuclear shape/arrangment: cigar-like/pseudostratified. Nucleoli: present.
Staging note
- Two small tumours in one lobe is pT3.
- Visceral pleural involvement upgrades small tumours.
See also
References
- ↑ Sun Y, Ren Y, Fang Z, et al. (October 2010). "Lung adenocarcinoma from East Asian never-smokers is a disease largely defined by targetable oncogenic mutant kinases". J. Clin. Oncol. 28 (30): 4616–20. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.29.6038. PMID 20855837.
- ↑ Job B, Bernheim A, Beau-Faller M, et al. (2010). "Genomic Aberrations in Lung Adenocarcinoma in Never Smokers". PLoS One 5 (12): e15145. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015145. PMC 2997777. PMID 21151896. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2997777/.
- ↑ Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Cardenal, F.; Porta, R.; Viteri, S.; Molina, MA.; Benlloch, S.; Taron, M. (Oct 2010). "Predictive biomarkers in the management of EGFR mutant lung cancer.". Ann N Y Acad Sci 1210: 45-52. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05775.x. PMID 20973798.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, et al. (February 2011). "International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma". J Thorac Oncol 6 (2): 244–85. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221. PMID 21252716.
- ↑ URL: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/lepidic. Accessed on: 8 August 2013.
- ↑ Shim, HS.; Lee, da H.; Park, EJ.; Kim, SH. (Oct 2011). "Histopathologic characteristics of lung adenocarcinomas with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society lung adenocarcinoma classification.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 135 (10): 1329-34. doi:10.5858/arpa.2010-0493-OA. PMID 21970488.
- ↑ URL: http://cancergrace.org/lung/2007/05/14/bac-mucinous-and-non-mucinous/. Accessed on: 8 August 2013.
- ↑ Bishop, JA.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Westra, WH.; Pelosi, G.; Travis, WD.; Rekhtman, N. (Mar 2012). "p40 (ΔNp63) is superior to p63 for the diagnosis of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma.". Mod Pathol 25 (3): 405-15. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.173. PMID 22056955.
- ↑ John, T.; Liu, G.; Tsao, MS. (Aug 2009). "Overview of molecular testing in non-small-cell lung cancer: mutational analysis, gene copy number, protein expression and other biomarkers of EGFR for the prediction of response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.". Oncogene 28 Suppl 1: S14-23. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.197. PMID 19680292.
- ↑ URL: http://www.mycancergenome.org/mutation.php?dz=nsclc&gene=egfr&code=l858r. Accessed on: 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Pao, W.; Wang, TY.; Riely, GJ.; Miller, VA.; Pan, Q.; Ladanyi, M.; Zakowski, MF.; Heelan, RT. et al. (Jan 2005). "KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib.". PLoS Med 2 (1): e17. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020017. PMID 15696205.
- ↑ Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, J.; Zha, J.; Pei, L. (Jan 2011). "Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors.". Neoplasia 13 (1): 1-11. PMID 21245935.
- ↑ Yang, P.; Kulig, K.; Boland, JM.; Erickson-Johnson, MR.; Oliveira, AM.; Wampfler, J.; Jatoi, A.; Deschamps, C. et al. (Jan 2012). "Worse disease-free survival in never-smokers with ALK+ lung adenocarcinoma.". J Thorac Oncol 7 (1): 90-7. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31823c5c32. PMID 22134072.