Difference between revisions of "Lymphangioleiomyomatosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Lymphangioleiomyomatosis''', abbreviated '''LAM''', is a rare [[medical lung disease|lung pathology]] that predominantly afflicits women of childbearing age. | |||
It is also known as '''lymphangiomyomatosis'''. | |||
==General== | |||
*Clinical: [[dyspnea]], recurrent pneumothorax. | |||
*May be an indication for lung transplantation. | |||
*Non-neoplastic muscle proliferation versus tumour that can metastasize.<ref name=pmid20235883>{{Cite journal | last1 = Taveira-DaSilva | first1 = AM. | last2 = Pacheco-Rodriguez | first2 = G. | last3 = Moss | first3 = J. | title = The natural history of lymphangioleiomyomatosis: markers of severity, rate of progression and prognosis. | journal = Lymphat Res Biol | volume = 8 | issue = 1 | pages = 9-19 | month = Mar | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1089/lrb.2009.0024 | PMID = 20235883 }}</ref> | |||
Notes: | |||
*Considered to be a [[PEComa]]. | |||
===Epidemiology=== | |||
*Associated with [[angiomyolipoma]]s.<ref name=emedicine299545>[http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-overview]</ref> | |||
*Associated with [[tuberous sclerosis]]<ref name=emedicine299545/> - abnormality in same gene (TSC2). | |||
*Usually affects women - primarily in childbearing years; case reports of LAM in men - usu. with [[TSC]].<ref name=pmid17431222>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schiavina | first1 = M. | last2 = Di Scioscio | first2 = V. | last3 = Contini | first3 = P. | last4 = Cavazza | first4 = A. | last5 = Fabiani | first5 = A. | last6 = Barberis | first6 = M. | last7 = Bini | first7 = A. | last8 = Altimari | first8 = A. | last9 = Cooke | first9 = RM. | title = Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis in a karyotypically normal man without tuberous sclerosis complex. | journal = Am J Respir Crit Care Med | volume = 176 | issue = 1 | pages = 96-8 | month = Jul | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1164/rccm.200610-1408CR | PMID = 17431222 }}</ref> | |||
*Rare. | |||
===Radiology=== | |||
*Bullae/thin walled cysts - distributed in all lung fields. | |||
*Lymphadenopathy. | |||
Radiologic DDx (of cysts): | |||
*[[Eosinophilic granuloma]] - associated with [[smoking]]. | |||
*[[Usual interstitial pneumonia]] (UIP). | |||
*[[Emphysema]]. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref>[http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-diagnosis]</ref> | |||
*Spindle cells with small nuclei + larger epithelioid cells with clear cytoplasm and round nuclei. | |||
*Cyst formation. | |||
*Thick arterial walls. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
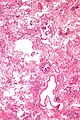
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis - very low mag.jpg| LAM - very low mag. (WC) | |||
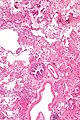
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis - low mag.jpg| LAM - low mag. (WC) | |||
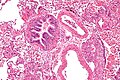
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis - intermed mag.jpg| LAM - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
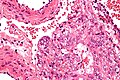
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis - very high mag.jpg| LAM - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v19/n6/fig_tab/3800610f3.html LAM (nature.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case111.html LAM - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*HMB-45 +ve. | |||
*ER +ve. | |||
*PR +ve. | |||
*SMA +ve. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Medical lung diseases]]. | |||
*[[PEComa]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Medical lung diseases]] | |||
Revision as of 05:56, 9 December 2014
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, abbreviated LAM, is a rare lung pathology that predominantly afflicits women of childbearing age.
It is also known as lymphangiomyomatosis.
General
- Clinical: dyspnea, recurrent pneumothorax.
- May be an indication for lung transplantation.
- Non-neoplastic muscle proliferation versus tumour that can metastasize.[1]
Notes:
- Considered to be a PEComa.
Epidemiology
- Associated with angiomyolipomas.[2]
- Associated with tuberous sclerosis[2] - abnormality in same gene (TSC2).
- Usually affects women - primarily in childbearing years; case reports of LAM in men - usu. with TSC.[3]
- Rare.
Radiology
- Bullae/thin walled cysts - distributed in all lung fields.
- Lymphadenopathy.
Radiologic DDx (of cysts):
- Eosinophilic granuloma - associated with smoking.
- Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP).
- Emphysema.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Spindle cells with small nuclei + larger epithelioid cells with clear cytoplasm and round nuclei.
- Cyst formation.
- Thick arterial walls.
Images
www:
IHC
- HMB-45 +ve.
- ER +ve.
- PR +ve.
- SMA +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Taveira-DaSilva, AM.; Pacheco-Rodriguez, G.; Moss, J. (Mar 2010). "The natural history of lymphangioleiomyomatosis: markers of severity, rate of progression and prognosis.". Lymphat Res Biol 8 (1): 9-19. doi:10.1089/lrb.2009.0024. PMID 20235883.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-overview
- ↑ Schiavina, M.; Di Scioscio, V.; Contini, P.; Cavazza, A.; Fabiani, A.; Barberis, M.; Bini, A.; Altimari, A. et al. (Jul 2007). "Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis in a karyotypically normal man without tuberous sclerosis complex.". Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176 (1): 96-8. doi:10.1164/rccm.200610-1408CR. PMID 17431222.
- ↑ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/299545-diagnosis