Difference between revisions of "Aspergillosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
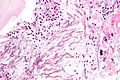
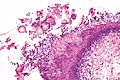
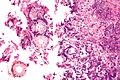
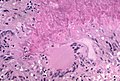
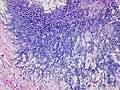
[[Image:Aspergillus_-_add_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|right|Aspergillus with classic fruiting heads. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Aspergillosis''' is a [[fungi|fungal infection]] due to ''Asperillus''. | '''Aspergillosis''' is a [[fungi|fungal infection]] due to ''Asperillus''. | ||
Revision as of 20:48, 27 May 2016

Aspergillus with classic fruiting heads. H&E stain.
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection due to Asperillus.
General
- Due to Aspergillus.
- Fungus.
- Associated with immunosuppression/immunodeficiency.
- Rarely in immune competent individuals.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Hyphae that branching with 45 degrees angle - key feature.[2]
- Uniform width - typically ~3-5 μm.
- Septated - often difficult to see.
- "Fruiting heads" when aerobic - uncommon.
- Spherical structures ~50 micrometres in diameter with radially arranged structures (like spokes of a wheel) +/- an empty centre in the plane of section.
DDx:
- Mucormycosis - irregular width.
- Scedosporium prolificans - in immunoincompetent individuals.[3]
- Candida.[4]
Images
Aspergillus - cytology. (WC)
www:
Stains
- PAS-D +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Sugimura, S.; Yoshida, K.; Oba, H.; Hashiguchi, K.; Nakajima, M.; Moriya, O.; Okimoto, N.; Niki, Y. et al. (Oct 1994). "[Two cases of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in non-immunocompromised hosts].". Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi 32 (10): 1032-7. PMID 7844909.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 682. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case290.html. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ Guarner, J.; Brandt, ME. (Apr 2011). "Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century.". Clin Microbiol Rev 24 (2): 247-80. doi:10.1128/CMR.00053-10. PMID 21482725.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ispub.com/journal/the-internet-journal-of-otorhinolaryngology/volume-6-number-1/maxillary-sinus-mycetoma-due-to-aspergillus-niger.html. Accessed on: 27 February 2012.