Difference between revisions of "Medulloblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→Images: images desmoplastic medulloblastoma) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (IHC + DDx) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
*Homer-Wright [[rosette]]s: | *Homer-Wright [[rosette]]s: | ||
**Rosette with a meshwork of fibers (neuropil) at the centre.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Wippold FJ, Perry A |title=Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: rosettes and pseudorosettes |journal=AJNR Am J Neuroradiol |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=488–92 |year=2006 |month=March |pmid=16551982 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | **Rosette with a meshwork of fibers (neuropil) at the centre.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Wippold FJ, Perry A |title=Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: rosettes and pseudorosettes |journal=AJNR Am J Neuroradiol |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=488–92 |year=2006 |month=March |pmid=16551982 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==IHC== | |||
* [[MAP2]] usu. +ve | |||
* Synaptophysin +ve (weak to strong) | |||
* NSE +ve/-ve | |||
* NF +ve/-ve | |||
* Chromogranin +ve/-ve | |||
* GFAP +ve/-ve (mostly along blood vessels) | |||
* Vimentin +ve | |||
* Nestin +ve | |||
* [[INI1]] retained (no loss) | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Small round cell tumours]]. | *[[Small round cell tumours]]. | ||
** [[AT/RT]] | ** [[AT/RT]] (INI1 loss) | ||
** [[PNET]] | ** CNS-[[PNET]] | ||
** ETMR (LIN28)-positive | |||
** Ewing Sarcoma family members | |||
** Small cell glioblastoma | |||
==Images== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image: Cerebellar medulloblastoma (1) in adult.JPG | Medulloblastoma. (WC/KGH) | Image: Cerebellar medulloblastoma (1) in adult.JPG | Medulloblastoma. (WC/KGH) | ||
| Line 45: | Line 59: | ||
File:Medulloblastoma nuclear moulding HE stain.jpg | Epitheloid ribboning and nuclear moulding of tumor cells. (WC/jensflorian) | File:Medulloblastoma nuclear moulding HE stain.jpg | Epitheloid ribboning and nuclear moulding of tumor cells. (WC/jensflorian) | ||
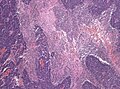
File:Medulloblastoma_geographic_necrosis.jpg | Areas of geographic necrosis. (WC/jensflorian) | File:Medulloblastoma_geographic_necrosis.jpg | Areas of geographic necrosis. (WC/jensflorian) | ||
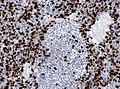
File:Medulloblastoma_MAP2_IHC.jpg | Partial MAP2 immunoreactivity. (WC/jensflorian) | File:Medulloblastoma_MAP2_IHC.jpg | Partial [[MAP2]] immunoreactivity. (WC/jensflorian) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 67: | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case685.html Medulloblastoma with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation - several images (upmc.edu)]. | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case685.html Medulloblastoma with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation - several images (upmc.edu)]. | ||
==Subtypes== | |||
*Classic medulloblastoma (~85% of all medulloblastomas). | *Classic medulloblastoma (~85% of all medulloblastomas). | ||
*Variants of medulloblastoma (~15% of all medulloblastomas together): | *Variants of medulloblastoma (~15% of all medulloblastomas together): | ||
Revision as of 09:10, 30 September 2015
Medulloblastoma is a malignant small round cell tumour that is found in the cerebellum.
Morphologically identical supratentorial tumours are called primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET).
General
- Mostly paediatric population.
- May be seen as a component of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS).
- Gene: patched (abbreviated PTCH1).[1]
- Commonly spread via cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).[2]
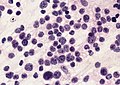
- May be detected in CSF cytopathology specimens.
Gross
- Location: cerebellum - key feature.
- Morphologically identical supratentorial tumours are called primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET).
- Supratentorial and spinal metastases from initial tumor possible.
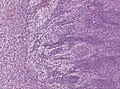
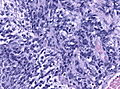
Microscopic
Features:[3]
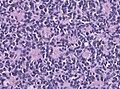
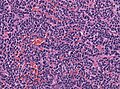
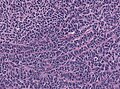
- Small round cell tumour.
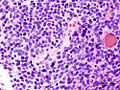
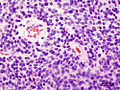
- Homer-Wright rosettes:
- Rosette with a meshwork of fibers (neuropil) at the centre.[4]
IHC
- MAP2 usu. +ve
- Synaptophysin +ve (weak to strong)
- NSE +ve/-ve
- NF +ve/-ve
- Chromogranin +ve/-ve
- GFAP +ve/-ve (mostly along blood vessels)
- Vimentin +ve
- Nestin +ve
- INI1 retained (no loss)
DDx:
Images
Case:
Partial MAP2 immunoreactivity. (WC/jensflorian)
www:
- Medulloblastoma (ouhsc.edu).
- Medulloblastoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Medulloblastoma with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation - several images (upmc.edu).
Subtypes
- Classic medulloblastoma (~85% of all medulloblastomas).
- Variants of medulloblastoma (~15% of all medulloblastomas together):
- Anaplastic variant.
- Large cell variant.
- Desmoplastic/nodular medulloblastoma (DNMB).
- Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity (MBEN).
Notes:
Anaplastic variant
Features:
- Larger cells.
- Severe anaplasia.
- Polygonal cells.
See also
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 601309
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 424 Q34. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/neurotest/Q93-Ans.htm. Accessed on: 26 October 2010.
- ↑ Wippold FJ, Perry A (March 2006). "Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: rosettes and pseudorosettes". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27 (3): 488–92. PMID 16551982.
- ↑ Gulino A, Arcella A, Giangaspero F (November 2008). "Pathological and molecular heterogeneity of medulloblastoma". Curr Opin Oncol 20 (6): 668–75. doi:10.1097/CCO.0b013e32831369f4. PMID 18841049.
- ↑ Rutkowski S, von Hoff K, Emser A, et al. (November 2010). "Survival and Prognostic Factors of Early Childhood Medulloblastoma: An International Meta-Analysis". J Clin Oncol 28 (33): 4961–4968. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.2299. PMID 20940197.