Difference between revisions of "Desmoplasia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (fix typo) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Increased stromal cellularity - '''key feature'''. | *Increased stromal cellularity - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Large (plump) spindle cells (fibroblasts) with | **Large (plump) spindle cells (fibroblasts)‡ with (large) nuclei that are pale in relation to the tumour cells. | ||
*Edema - pale spaces between the cells - may be apparent at low power.<ref>{{Ref TPoSP|15}}</ref> | *Edema - pale spaces between the cells - may be apparent at low power.<ref>{{Ref TPoSP|15}}</ref> | ||
Note: | |||
*‡ Large (plump) spindle cells: the nuclei have approximately the width of a resting lymphocyte. | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
Latest revision as of 20:08, 6 December 2018
Desmoplasia is the formation of fibrous connective tissue.[1] It is also known as the desmoplastic response, desmoplastic stroma, desmoplastic stromal response, and stromal response.
It is a stromal change that in the context of dysplasia supports the diagnosis of an invasive carcinoma.
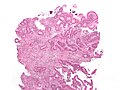
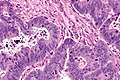
Microscopic
Features:
- Increased stromal cellularity - key feature.
- Large (plump) spindle cells (fibroblasts)‡ with (large) nuclei that are pale in relation to the tumour cells.
- Edema - pale spaces between the cells - may be apparent at low power.[2]
Note:
- ‡ Large (plump) spindle cells: the nuclei have approximately the width of a resting lymphocyte.
DDx:
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/desmoplasia. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.
- ↑ Weedman Molavi, Diana (2008). The Practice of Surgical Pathology: A Beginner's Guide to the Diagnostic Process (1st ed.). Springer. pp. 15. ISBN 978-0387744858.
- ↑ URL: http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/homepage.htm. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.