Difference between revisions of "P16"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
*Breast carcinoma. | *Breast carcinoma. | ||
*[[Prostate carcinoma]]. | *[[Prostate carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Lung squamous cell carcinoma]].<ref name= | *[[Lung squamous cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid20823766>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pereira | first1 = TC. | last2 = Share | first2 = SM. | last3 = Magalhães | first3 = AV. | last4 = Silverman | first4 = JF. | title = Can we tell the site of origin of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma? An immunohistochemical tissue microarray study of 194 cases. | journal = Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 10-4 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181ecaf1c | PMID = 20823766 }}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 12 March 2015
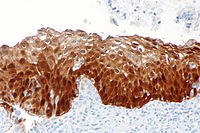
p16 is a commonly used immunostain. It can be considered a surrogate marker for HPV infection. p16, like most other "p" stains, is a nuclear stain.
Pattern
- Nuclear stain +/- cytoplasmic staining.
Use
- Squamous lesions of the uterine cervix - see HSIL.
- Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, specifically human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Tumours
Positive
- Squamous cell carcinoma - esp. cervical SCC, anal SCC, penile SCC, HPV-associated head and neck SCC.
- High grade urothelial carcinoma ~86% of cases.[1]
Negative
- Breast carcinoma.
- Prostate carcinoma.
- Lung squamous cell carcinoma.[2]
References
- ↑ Piaton, E.; Casalegno, JS.; Advenier, AS.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Mege-Lechevallier, F.; Ruffion, A.; Mekki, Y. (Oct 2014). "p16(INK4a) overexpression is not linked to oncogenic human papillomaviruses in patients with high-grade urothelial cancer cells.". Cancer Cytopathol 122 (10): 760-9. doi:10.1002/cncy.21462. PMID 25069600.
- ↑ Pereira, TC.; Share, SM.; Magalhães, AV.; Silverman, JF. (Jan 2011). "Can we tell the site of origin of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma? An immunohistochemical tissue microarray study of 194 cases.". Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 19 (1): 10-4. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181ecaf1c. PMID 20823766.