Difference between revisions of "Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis''' is an uncommon intestinal pathology characterized by pseudocysts filled with air. | |||
==General== | |||
*Benign, generally asymptomatic subset of [[pneumatosis intestinalis]].<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/371955-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/371955-overview]. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Small or large bowel.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Micklefield | first1 = GH. | last2 = Kuntz | first2 = HD. | last3 = May | first3 = B. | title = Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: case reports and review of the literature. | journal = Mater Med Pol | volume = 22 | issue = 2 | pages = 70-2 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 2102980 }}</ref> | |||
Possible etiologies:<ref name=pmid21864163>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wu | first1 = SS. | last2 = Yen | first2 = HH. | title = Images in clinical medicine. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 365 | issue = 8 | pages = e16 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMicm1013439 | PMID = 21864163 }}</ref> | |||
*[[IBD]]. | |||
*Infection. | |||
*Bowel necrosis. | |||
*Malignancy. | |||
*Drugs, e.g. alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. | |||
*Idiopathic. | |||
Others: | |||
*[[Necrotizing enterocolitis]]. (???) | |||
*[[Cystic fibrosis]]. (???) | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Polypoid lesions. | |||
Images: | |||
*www: | |||
**[http://biblioteca.colmed5.org.ar/consultas/pneumatosis.htm Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis - endoscopic image (colmed5.org.ar)]. | |||
**[http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/images/349/path2.jpg Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (harvard.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/349/full.html http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/349/full.html]. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
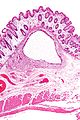
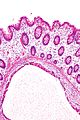
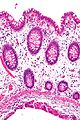
*Large submucosal pseudocysts lined by macrophages and multi-nucleated giant cells. | |||
===Images=== | |||
*www: | |||
**[http://www.wjes.org/content/6/1/15/figure/F4?highres=y Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (wjes.org)].<ref name=pmid21548980>{{Cite journal | last1 = Takami | first1 = Y. | last2 = Koh | first2 = T. | last3 = Nishio | first3 = M. | last4 = Nakagawa | first4 = N. | title = Pneumatosis intestinalis leading to perioperative hypovolemic shock: Case report. | journal = World J Emerg Surg | volume = 6 | issue = | pages = 15 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1186/1749-7922-6-15 | PMID = 21548980 |PMC = PMC3108289}}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pneumatosis_cystoides_intestinalis_-_low_mag.jpg | Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Pneumatosis_cystoides_intestinalis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Pneumatosis_cystoides_intestinalis_-_high_mag.jpg | Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:12, 21 March 2014
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis is an uncommon intestinal pathology characterized by pseudocysts filled with air.
General
- Benign, generally asymptomatic subset of pneumatosis intestinalis.[1]
- Small or large bowel.[2]
Possible etiologies:[3]
- IBD.
- Infection.
- Bowel necrosis.
- Malignancy.
- Drugs, e.g. alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
- Idiopathic.
Others:
- Necrotizing enterocolitis. (???)
- Cystic fibrosis. (???)
Gross
- Polypoid lesions.
Images:
- www:
Microscopic
Features:
- Large submucosal pseudocysts lined by macrophages and multi-nucleated giant cells.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/371955-overview. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.
- ↑ Micklefield, GH.; Kuntz, HD.; May, B.. "Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: case reports and review of the literature.". Mater Med Pol 22 (2): 70-2. PMID 2102980.
- ↑ Wu, SS.; Yen, HH. (Aug 2011). "Images in clinical medicine. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.". N Engl J Med 365 (8): e16. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1013439. PMID 21864163.
- ↑ URL: http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/349/full.html. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ Takami, Y.; Koh, T.; Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, N. (2011). "Pneumatosis intestinalis leading to perioperative hypovolemic shock: Case report.". World J Emerg Surg 6: 15. doi:10.1186/1749-7922-6-15. PMC PMC3108289. PMID 21548980. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMCPMC3108289/.