Difference between revisions of "Inverted urothelial papilloma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(→Sign out: +micro) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Inverted_papilloma_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
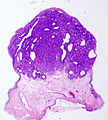
| Caption = Inverted urothelial papilloma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = like papillomas... but grow downward; '''never''' have an exophytic component; nests have peripheral palisading of nuclei - '''important''' | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]] with an inverted growth pattern | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = Ki-67 -ve, CK20 -ve, p53 -ve (rarely +ve) | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[urothelium]] - usu. [[urinary bladder]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Inverted urothelial papilloma''', also '''inverted papilloma''', is a benign [[urothelium|urothelial]] lesion that may be confused with [[urothelial carcinoma]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*May be confused with papillary urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Like papillomas... but grow downward.<ref name=Ref_WMSP310>{{Ref WMSP|310}}</ref> | |||
*According to THvdK,<ref>THvdK. 21 June 2010.</ref> ''inverted papillomas'' '''never''' have an exophytic component; if an exophytic component is present it is urothelial carcinoma. This is disputed by one paper from Mexico that examines two cases.<ref name=pmid19433293>{{cite journal |author=Albores-Saavedra J, Chable-Montero F, Hernández-Rodríguez OX, Montante-Montes de Oca D, Angeles-Angeles A |title=Inverted urothelial papilloma of the urinary bladder with focal papillary pattern: a previously undescribed feature |journal=Ann Diagn Pathol |volume=13 |issue=3 |pages=158–61 |year=2009 |month=June |pmid=19433293 |doi=10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2009.02.009 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Nests have peripheral palisading of nuclei - '''important'''. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]] with an inverted growth pattern. | |||
*[[Cystitis cystica]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
====Case 1==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
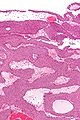
Image:Inverted_papilloma_high_mag.jpg | Inverted papilloma - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
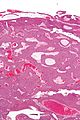
Image:Inverted_papilloma_intermed_mag.jpg | Inverted papilloma - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
====Case 2==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
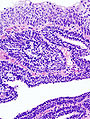
Image: Bladder inverted papilloma histopathology (1).jpg | IUP. (WC/KGH) | |||
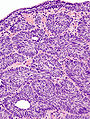
Image: Bladder inverted papilloma histopathology (2).jpg | IUP. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image: Bladder inverted papilloma histopathology (3).jpg | IUP. (WC/KGH) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
May be useful versus inverted growth pattern UCC:<ref name=pmid18043040>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jones | first1 = TD. | last2 = Zhang | first2 = S. | last3 = Lopez-Beltran | first3 = A. | last4 = Eble | first4 = JN. | last5 = Sung | first5 = MT. | last6 = MacLennan | first6 = GT. | last7 = Montironi | first7 = R. | last8 = Tan | first8 = PH. | last9 = Zheng | first9 = S. | title = Urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern can be distinguished from inverted papilloma by fluorescence in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and morphologic analysis. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 12 | pages = 1861-7 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318060cb9d | PMID = 18043040 }}</ref> | |||
*Ki-67 -ve. | |||
*CK20 -ve. | |||
*p53 -ve (rarely +ve). | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Urothelium]]. | |||
*[[Urothelial papilloma]]. | |||
*[[Cystitis cystica]]. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
Bladder Tumour, Transurthral Resection: | |||
- Inverted papilloma. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Micro=== | |||
The sections show urothelial mucosa with a densely packed urothelial nests with peripheral palisading. The cells of the urothelial nests are bland. Proliferative activity is not apparent. Definite papillae are absent. No exophytic component is apparent. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Urothelium]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:41, 7 June 2021
| Inverted urothelial papilloma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Inverted urothelial papilloma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | like papillomas... but grow downward; never have an exophytic component; nests have peripheral palisading of nuclei - important |
| LM DDx | low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern |
| IHC | Ki-67 -ve, CK20 -ve, p53 -ve (rarely +ve) |
| Site | urothelium - usu. urinary bladder |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
Inverted urothelial papilloma, also inverted papilloma, is a benign urothelial lesion that may be confused with urothelial carcinoma.
General
- May be confused with papillary urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern.
Microscopic
Features:
- Like papillomas... but grow downward.[1]
- According to THvdK,[2] inverted papillomas never have an exophytic component; if an exophytic component is present it is urothelial carcinoma. This is disputed by one paper from Mexico that examines two cases.[3]
- Nests have peripheral palisading of nuclei - important.
DDx:
- Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern.
- Cystitis cystica.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
IHC
May be useful versus inverted growth pattern UCC:[4]
- Ki-67 -ve.
- CK20 -ve.
- p53 -ve (rarely +ve).
See also
Sign out
Bladder Tumour, Transurthral Resection:
- Inverted papilloma.
Micro
The sections show urothelial mucosa with a densely packed urothelial nests with peripheral palisading. The cells of the urothelial nests are bland. Proliferative activity is not apparent. Definite papillae are absent. No exophytic component is apparent.
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 310. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ THvdK. 21 June 2010.
- ↑ Albores-Saavedra J, Chable-Montero F, Hernández-Rodríguez OX, Montante-Montes de Oca D, Angeles-Angeles A (June 2009). "Inverted urothelial papilloma of the urinary bladder with focal papillary pattern: a previously undescribed feature". Ann Diagn Pathol 13 (3): 158–61. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2009.02.009. PMID 19433293.
- ↑ Jones, TD.; Zhang, S.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Eble, JN.; Sung, MT.; MacLennan, GT.; Montironi, R.; Tan, PH. et al. (Dec 2007). "Urothelial carcinoma with an inverted growth pattern can be distinguished from inverted papilloma by fluorescence in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and morphologic analysis.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (12): 1861-7. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318060cb9d. PMID 18043040.