Difference between revisions of "Hepatic adenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(hepatic adenoma) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Hepatic_adenoma_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Hepatic adenoma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = hepatocellular adenoma | |||
| Micro = sheets or cords of cells with mild variation of cell and nuclear size; cords of cells up to 3 cells thick, vascular (large arteries, dilated thin-walled veins), +/-cytoplasmic clearing/pale (due to glycogen); negatives: no bile ducts, no portal tracts, no [[cirrhosis]] | |||
| Subtypes = inflammatory hepatic adenoma ([[AKA]] ''telangiectatic adenoma''), hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-mutated hepatic adenoma, beta-catenin-mutated hepatic adenoma, unclassified hepatic adenoma | |||
| LMDDx = [[hepatocellular carcinoma]] (well-differentiated), [[focal nodular hyperplasia]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = well-circumscribed, typically subcapsular | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[liver]] - see ''[[liver neoplasms]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = women +/-[[OCP]] use | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = subcapsular, well-circumscribed | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Hepatic adenoma''', also known as '''hepatocellular adenoma''' (abbreviated '''HCA'''), is a benign [[liver neoplasms|neoplasm of the liver]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Grow under the influence of sex hormones. | |||
**Associated with ''[[oral contraceptive pill]]'' (OCP) use<ref name=Ref_WMSP221>{{Ref WMSP|221}}</ref><ref name=pmid221698>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rooks | first1 = JB. | last2 = Ory | first2 = HW. | last3 = Ishak | first3 = KG. | last4 = Strauss | first4 = LT. | last5 = Greenspan | first5 = JR. | last6 = Hill | first6 = AP. | last7 = Tyler | first7 = CW. | title = Epidemiology of hepatocellular adenoma. The role of oral contraceptive use. | journal = JAMA | volume = 242 | issue = 7 | pages = 644-8 | month = Aug | year = 1979 | doi = | PMID = 221698 }}</ref> - may regress with discontinuation. | |||
**May rupture in [[pregnancy]]. | |||
*Usually diagnosed by radiology. | |||
==Gross== | |||
Features:<ref>STC S.20, 19 Jan 2009.</ref> | |||
*Often subcapsular location. | |||
*Well-circumscribed, but not encapsulated. | |||
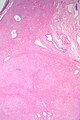
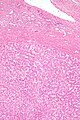
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Sheets or cords of cells with mild variation of cell and nuclear size.<ref name=Ref_PBoD923>{{Ref PBoD|923}}</ref> | |||
*Cords of cells up to 3 cells thick.<ref>STC S.19, 19 Jan 2009.</ref> | |||
*Cells may have cytoplasmic clearing due to glycogen or be pale - '''obvious if seen'''. | |||
*Vascular - large arteries, dilated thin-walled veins. | |||
Negatives: | |||
*No bile ducts. | |||
*No portal tracts. | |||
*No [[cirrhosis]]! If cirrhosis is present it isn't a hepatic adenoma - '''important'''. | |||
DDx: | |||
*Well-differentiated [[hepatocellular carcinoma]].<ref>SN. 29 May 2009.</ref> | |||
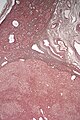
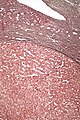
**Hepatic adenoma is differentiated from ''well-differentiated HCC'' by its architecture; adenomas have cords of cells upto 3 cells thick & have preserved reticulin architecture. | |||
*[[Focal nodular hyperplasia]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Hepatic adenoma low mag.jpg | Low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hepatic_adenoma_high_mag.jpg | High mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hepatic_adenoma_low_mag_reticulin.jpg | Low mag. - reticulin (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hepatic_adenoma_high_mag_reticulin.jpg | High mag. - reticulin (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content-nw/full/182/6/1520/FIG3 Hepatic adenoma (ajronline.org)]. | |||
*[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/22/5/1023.figures-only Series of liver micrographs including hepatic adenoma (radiographics.rsna.org)]. | |||
===Subclassification=== | |||
Based on molecular changes:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Katabathina | first1 = VS. | last2 = Menias | first2 = CO. | last3 = Shanbhogue | first3 = AK. | last4 = Jagirdar | first4 = J. | last5 = Paspulati | first5 = RM. | last6 = Prasad | first6 = SR. | title = Genetics and imaging of hepatocellular adenomas: 2011 update. | journal = Radiographics | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 1529-43 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1148/rg.316115527 | PMID = 21997980 }}</ref><ref name=pmid21883740>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sasaki | first1 = M. | last2 = Yoneda | first2 = N. | last3 = Kitamura | first3 = S. | last4 = Sato | first4 = Y. | last5 = Nakanuma | first5 = Y. | title = Characterization of hepatocellular adenoma based on the phenotypic classification: The Kanazawa experience. | journal = Hepatol Res | volume = 41 | issue = 10 | pages = 982-8 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00851.x | PMID = 21883740 }}</ref> | |||
#Inflammatory hepatic adenoma. | |||
#*[[AKA]] ''telangiectatic adenoma''.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Maylee | first1 = H. | last2 = Harada | first2 = K. | last3 = Igarashi | first3 = S. | last4 = Tohda | first4 = G. | last5 = Yamamoto | first5 = M. | last6 = Ren | first6 = XS. | last7 = Osawa | first7 = T. | last8 = Hasegawa | first8 = Y. | last9 = Takahashi | first9 = N. | title = Case of telangiectatic/inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma arising in a patient with primary sclerosing cholangitis. | journal = Hepatol Res | volume = 42 | issue = 6 | pages = 611-8 | month = Jun | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00962.x | PMID = 22568458 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
#*Associated with obesity.{{fact}} | |||
#Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-mutated hepatic adenoma. | |||
#*Inactivating mutation. | |||
#Beta-catenin-mutated hepatic adenoma | |||
#*Activating mutation. | |||
#Unclassified hepatic adenoma. | |||
Note: | |||
*Beta-catenin is considered an [[oncogene]]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*[[AFP]] -ve. (???) | |||
*HNF1alpha +ve/-ve. | |||
*Beta-catenin +ve/-ve. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Liver neoplasms]]. | |||
*[[Hepatocellular carcinoma]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | |||
[[Category:Liver neoplasms]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:54, 29 September 2015
| Hepatic adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
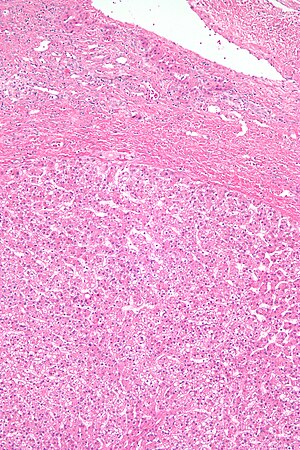 Hepatic adenoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | hepatocellular adenoma |
|
| |
| LM | sheets or cords of cells with mild variation of cell and nuclear size; cords of cells up to 3 cells thick, vascular (large arteries, dilated thin-walled veins), +/-cytoplasmic clearing/pale (due to glycogen); negatives: no bile ducts, no portal tracts, no cirrhosis |
| Subtypes | inflammatory hepatic adenoma (AKA telangiectatic adenoma), hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-mutated hepatic adenoma, beta-catenin-mutated hepatic adenoma, unclassified hepatic adenoma |
| LM DDx | hepatocellular carcinoma (well-differentiated), focal nodular hyperplasia |
| Gross | well-circumscribed, typically subcapsular |
| Site | liver - see liver neoplasms |
|
| |
| Clinical history | women +/-OCP use |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | subcapsular, well-circumscribed |
| Prognosis | benign |
Hepatic adenoma, also known as hepatocellular adenoma (abbreviated HCA), is a benign neoplasm of the liver.
General
- Grow under the influence of sex hormones.
- Associated with oral contraceptive pill (OCP) use[1][2] - may regress with discontinuation.
- May rupture in pregnancy.
- Usually diagnosed by radiology.
Gross
Features:[3]
- Often subcapsular location.
- Well-circumscribed, but not encapsulated.
Microscopic
Features:
- Sheets or cords of cells with mild variation of cell and nuclear size.[4]
- Cords of cells up to 3 cells thick.[5]
- Cells may have cytoplasmic clearing due to glycogen or be pale - obvious if seen.
- Vascular - large arteries, dilated thin-walled veins.
Negatives:
- No bile ducts.
- No portal tracts.
- No cirrhosis! If cirrhosis is present it isn't a hepatic adenoma - important.
DDx:
- Well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma.[6]
- Hepatic adenoma is differentiated from well-differentiated HCC by its architecture; adenomas have cords of cells upto 3 cells thick & have preserved reticulin architecture.
- Focal nodular hyperplasia.
Images
www:
- Hepatic adenoma (ajronline.org).
- Series of liver micrographs including hepatic adenoma (radiographics.rsna.org).
Subclassification
Based on molecular changes:[7][8]
- Inflammatory hepatic adenoma.
- AKA telangiectatic adenoma.[9]
- Associated with obesity.[citation needed]
- Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-mutated hepatic adenoma.
- Inactivating mutation.
- Beta-catenin-mutated hepatic adenoma
- Activating mutation.
- Unclassified hepatic adenoma.
Note:
- Beta-catenin is considered an oncogene.
IHC
- AFP -ve. (???)
- HNF1alpha +ve/-ve.
- Beta-catenin +ve/-ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 221. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Rooks, JB.; Ory, HW.; Ishak, KG.; Strauss, LT.; Greenspan, JR.; Hill, AP.; Tyler, CW. (Aug 1979). "Epidemiology of hepatocellular adenoma. The role of oral contraceptive use.". JAMA 242 (7): 644-8. PMID 221698.
- ↑ STC S.20, 19 Jan 2009.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 923. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ STC S.19, 19 Jan 2009.
- ↑ SN. 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Katabathina, VS.; Menias, CO.; Shanbhogue, AK.; Jagirdar, J.; Paspulati, RM.; Prasad, SR. (Oct 2011). "Genetics and imaging of hepatocellular adenomas: 2011 update.". Radiographics 31 (6): 1529-43. doi:10.1148/rg.316115527. PMID 21997980.
- ↑ Sasaki, M.; Yoneda, N.; Kitamura, S.; Sato, Y.; Nakanuma, Y. (Oct 2011). "Characterization of hepatocellular adenoma based on the phenotypic classification: The Kanazawa experience.". Hepatol Res 41 (10): 982-8. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00851.x. PMID 21883740.
- ↑ Maylee, H.; Harada, K.; Igarashi, S.; Tohda, G.; Yamamoto, M.; Ren, XS.; Osawa, T.; Hasegawa, Y. et al. (Jun 2012). "Case of telangiectatic/inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma arising in a patient with primary sclerosing cholangitis.". Hepatol Res 42 (6): 611-8. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00962.x. PMID 22568458.