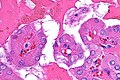
Difference between revisions of "Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity''' is a rare [[renal tumour]] and evolving entity.<ref name=pmid31135486>{{cite journal |authors=Al-Obaidy KI, Eble JN, Cheng L, Williamson SR, Sakr WA, Gupta N, Idrees MT, Grignon DJ |title=Papillary Renal Neoplasm With Reverse Polarity: A Morphologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Study |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=43 |issue=8 |pages=1099–1111 |date=August 2019 |pmid=31135486 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288 |url=}}</ref> | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
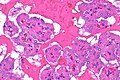
| Image = Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity - alt -- high mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = papillary structures, eosinophilic cytoplasm, reverse polarity of nuclei (nuclei at luminal aspect of cell), low nuclear grade | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = eosinophilic [[papillary renal cell carcinoma]], other [[renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = GATA3 +ve, PAX-8 +ve, CK7 +ve, CD10 +ve, CD117 -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = [[KRAS]] mutations | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = [[partial nephrectomy]], [[radical nephrectomy]] | |||
| Staging = | |||
| Site = [[kidney]] - see ''[[kidney tumours]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = rare | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = indolent - based on limited data | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other [[kidney tumours]] | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity''' is a rare [[renal tumour]] and an evolving entity.<ref name=pmid31135486>{{cite journal |authors=Al-Obaidy KI, Eble JN, Cheng L, Williamson SR, Sakr WA, Gupta N, Idrees MT, Grignon DJ |title=Papillary Renal Neoplasm With Reverse Polarity: A Morphologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Study |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=43 |issue=8 |pages=1099–1111 |date=August 2019 |pmid=31135486 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288 |url=}}</ref> It has a distinctive morphology that matches the name. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Evolving entity. | *Evolving entity. | ||
*Thought to be distinct from ''eosinophilic [[papillary renal cell carcinoma]]''.<ref name=pmid38456605>{{cite journal |authors=Castillo VF, Trpkov K, Van der Kwast T, Rotondo F, Hamdani M, Saleeb R |title=Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is biologically and clinically distinct from eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma |journal=Pathol Int |volume=74 |issue=4 |pages=222–226 |date=April 2024 |pmid=38456605 |doi=10.1111/pin.13417 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid37797754>{{cite journal |authors=Kim B, Lee S, Moon KC |title=Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a clinicopathologic study of 43 cases with a focus on the expression of KRAS signaling pathway downstream effectors |journal=Hum Pathol |volume=142 |issue= |pages=1–6 |date=December 2023 |pmid=37797754 |doi=10.1016/j.humpath.2023.09.011 |url=}}</ref> | *Thought to be distinct from ''eosinophilic [[papillary renal cell carcinoma]]''.<ref name=pmid38456605>{{cite journal |authors=Castillo VF, Trpkov K, Van der Kwast T, Rotondo F, Hamdani M, Saleeb R |title=Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is biologically and clinically distinct from eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma |journal=Pathol Int |volume=74 |issue=4 |pages=222–226 |date=April 2024 |pmid=38456605 |doi=10.1111/pin.13417 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid37797754>{{cite journal |authors=Kim B, Lee S, Moon KC |title=Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a clinicopathologic study of 43 cases with a focus on the expression of KRAS signaling pathway downstream effectors |journal=Hum Pathol |volume=142 |issue= |pages=1–6 |date=December 2023 |pmid=37797754 |doi=10.1016/j.humpath.2023.09.011 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Early data suggests an indolent behaviour.<ref name=pmid31135486>{{cite journal |authors=Al-Obaidy KI, Eble JN, Cheng L, Williamson SR, Sakr WA, Gupta N, Idrees MT, Grignon DJ |title=Papillary Renal Neoplasm With Reverse Polarity: A Morphologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Study |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=43 |issue=8 |pages=1099–1111 |date=August 2019 |pmid=31135486 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288 |url=}}</ref> | |||
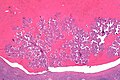
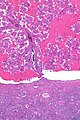
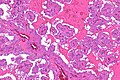
== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid31135486/> | Features:<ref name=pmid31135486/> | ||
*Branching papillae with: | *Branching papillae with: | ||
| Line 16: | Line 49: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Eosinophilic [[papillary renal cell carcinoma]] - considered distinct from this entity. | |||
*[[Renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm]]. | *[[Renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm]]. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity -- very low mag.jpg | PRNRP - very low mag. | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity -- low mag.jpg | PRNRP - low mag. | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity - alt -- low mag.jpg | PRNRP - low mag. | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity -- intermed mag.jpg | PRNRP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity -- high mag.jpg | PRNRP - high mag. | |||
Image: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity -- very high mag.jpg | PRNRP - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid31135486/> | Features:<ref name=pmid31135486/> | ||
* | *GATA3 +ve (43 of 43 cases<ref name=pmid37797754/>) - '''key stain'''. | ||
* | **Negative in other papillary RCCs.<ref name=pmid37797754/> | ||
* | *CK7 +ve (88% +ve, 37 of 42 cases<ref name=pmid37797754/>). | ||
*CD10 +ve/-ve (50% +ve, 21 of 42 cases<ref name=pmid37797754/>). | |||
*Vimentin -ve (all cases). | *Vimentin -ve (all cases). | ||
*CD117 -ve. | *CD117 -ve. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 73: | ||
*EMA +ve. | *EMA +ve. | ||
*L1CAM +ve. | *L1CAM +ve. | ||
*PAX8 +ve. | |||
*AMACR -ve (4 of 43 cases<ref name=pmid37797754/>). | |||
*RCC -ve (1 of 43 cases<ref name=pmid37797754/>). | |||
===Differentiating between papillary RCC and PRNRP=== | |||
Adapted from Kim ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid37797754/> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Diagnosis | |||
!GATA3 | |||
!AMACR | |||
!RCC | |||
!Vimentin | |||
|- | |||
|Papillary RCC | |||
| 0% +ve | |||
| 85-90% +ve | |||
| 60-75% +ve | |||
| 60-70% +ve | |||
|- | |||
|PRNRP | |||
| 100% +ve | |||
| ~10% +ve | |||
| ~2% +ve | |||
| ~2% +ve | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Molecular== | ==Molecular== | ||
*[[KRAS]] mutations.<ref name=pmid37797754/> | *[[KRAS]] mutations.<ref name=pmid37797754/> | ||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
A. Right Kidney, Tumour, Partial Nephrectomy: | |||
- Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity, clear of margin, see comment. | |||
Comment: | |||
The tumour has a papillary architecture, eosinophilic cytoplasm, low nuclear grade, and reversed nuclear polarity. | |||
It stains as follows: | |||
POSITIVE: PAX8 (moderate, diffuse), CK7 (strong, diffuse), AE1/AE3 (strong, diffuse), GATA3 (moderate, diffuse), AMACR (moderate, diffuse). | |||
NEGATIVE: vimentin (stroma), CD117, CD10. | |||
The findings are in keeping with papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity (PRNRP). PRNRP is thought to be distinct from papillary RCC.[1][2] Limited data suggests PRNRP has an indolent behaviour.[3] Follow-up is recommended. | |||
1. Pathol Int. 2024 Apr;74(4):222-226. doi: 10.1111/pin.13417. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38456605/ | |||
2. Hum Pathol. 2023 Dec:142:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2023.09.011. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37797754/ | |||
3. Am J Surg Pathol. 2019 Aug;43(8):1099-1111. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31135486/ | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 36: | Line 126: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist| | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Kidney tumours]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:09, 16 August 2024
| Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
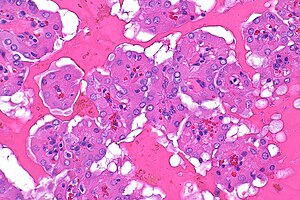 Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | papillary structures, eosinophilic cytoplasm, reverse polarity of nuclei (nuclei at luminal aspect of cell), low nuclear grade |
| LM DDx | eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma, other renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm |
| IHC | GATA3 +ve, PAX-8 +ve, CK7 +ve, CD10 +ve, CD117 -ve |
| Molecular | KRAS mutations |
| Grossing notes | partial nephrectomy, radical nephrectomy |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | indolent - based on limited data |
| Clin. DDx | other kidney tumours |
Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is a rare renal tumour and an evolving entity.[1] It has a distinctive morphology that matches the name.
General
- Evolving entity.
- Thought to be distinct from eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma.[2][3]
- Early data suggests an indolent behaviour.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Branching papillae with:
- Thin fibrovascular cores.
- Cuboidal to columnar lining cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- May have occasional cytoplasmic clearing.
- Smooth luminal borders.
- Reverse polarized nuclei (luminal nuclei; nuclei closer to lumen than basement membrane).
- Nucleoli absent or small.
DDx:
- Eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma - considered distinct from this entity.
- Renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Images
IHC
Features:[1]
- GATA3 +ve (43 of 43 cases[3]) - key stain.
- Negative in other papillary RCCs.[3]
- CK7 +ve (88% +ve, 37 of 42 cases[3]).
- CD10 +ve/-ve (50% +ve, 21 of 42 cases[3]).
- Vimentin -ve (all cases).
- CD117 -ve.
- AE1/AE3 +ve.
- EMA +ve.
- L1CAM +ve.
- PAX8 +ve.
- AMACR -ve (4 of 43 cases[3]).
- RCC -ve (1 of 43 cases[3]).
Differentiating between papillary RCC and PRNRP
Adapted from Kim et al.:[3]
| Diagnosis | GATA3 | AMACR | RCC | Vimentin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Papillary RCC | 0% +ve | 85-90% +ve | 60-75% +ve | 60-70% +ve |
| PRNRP | 100% +ve | ~10% +ve | ~2% +ve | ~2% +ve |
Molecular
Sign out
A. Right Kidney, Tumour, Partial Nephrectomy: - Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity, clear of margin, see comment. Comment: The tumour has a papillary architecture, eosinophilic cytoplasm, low nuclear grade, and reversed nuclear polarity. It stains as follows: POSITIVE: PAX8 (moderate, diffuse), CK7 (strong, diffuse), AE1/AE3 (strong, diffuse), GATA3 (moderate, diffuse), AMACR (moderate, diffuse). NEGATIVE: vimentin (stroma), CD117, CD10. The findings are in keeping with papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity (PRNRP). PRNRP is thought to be distinct from papillary RCC.[1][2] Limited data suggests PRNRP has an indolent behaviour.[3] Follow-up is recommended. 1. Pathol Int. 2024 Apr;74(4):222-226. doi: 10.1111/pin.13417. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38456605/ 2. Hum Pathol. 2023 Dec:142:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2023.09.011. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37797754/ 3. Am J Surg Pathol. 2019 Aug;43(8):1099-1111. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31135486/
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Al-Obaidy KI, Eble JN, Cheng L, Williamson SR, Sakr WA, Gupta N, Idrees MT, Grignon DJ (August 2019). "Papillary Renal Neoplasm With Reverse Polarity: A Morphologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Study". Am J Surg Pathol 43 (8): 1099–1111. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001288. PMID 31135486.
- ↑ Castillo VF, Trpkov K, Van der Kwast T, Rotondo F, Hamdani M, Saleeb R (April 2024). "Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is biologically and clinically distinct from eosinophilic papillary renal cell carcinoma". Pathol Int 74 (4): 222–226. doi:10.1111/pin.13417. PMID 38456605.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Kim B, Lee S, Moon KC (December 2023). "Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a clinicopathologic study of 43 cases with a focus on the expression of KRAS signaling pathway downstream effectors". Hum Pathol 142: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2023.09.011. PMID 37797754.