Difference between revisions of "Astrocytoma"
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (diffuse vs. adult category) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→Uncommon Astrocytomas: link) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
{{Main|Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant}} | {{Main|Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant}} | ||
==High-grade astrocytoma with piloid features== | |||
* Frequent in posterior fossa (75%). | |||
* 1-3% of all brain tumors. | |||
* Histology may resemble Glionblastoma or Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. | |||
* Tumor is enriched for piloid cell processes. | |||
* ATRX nuclear loss is frequent. | |||
* Usu. MAPK-pathway alterations + CDKN2A homozygous deletion. | |||
* Distinct methylation profile. | |||
{{Main|High-grade astrocytoma with piloid features}} | |||
==Gliomatosis cerebri== | ==Gliomatosis cerebri== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:48, 17 October 2022
An astrocytoma is a neoplasm thought to be derived from an astrocyte. Astrocytomas/Glioblastomas are most common type of glial tumours and grouped together with Oligodendroglioma and glioneuronal tumours in the current WHO brain tumor classficiation. Some (often circumscribed) astrocytic tumors and pediatric tumours are biologically different from adult-onset diffuse astrocytomas. An overview of other CNS tumours is found in the CNS tumours article.
Categorization
Astrocytomas can be categorized in serveral ways.
- Common vs. uncommon tumours.
- Adult vs. pediatric tumours.
- Circumscribed vs. diffusely growing astrocytomas.
Until 2016 WHO classification, roman numerals I-IV were used for grading. The current 2021 WHO classification uses arabic numbering 1-4 for CNS WHO grading instead.
Overview
These astrocytic tumors are frequently diagnosed in neuropathology practice:
| Name | Type | Age | Variants / Patterns / Other designations | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astrocytoma, IDH mutant WHO CNS grade 2 | diffuse | adults | Diffuse, protoplasmatic, fibrillar or gemistocytic astrocytoma. | |
| Astrocytoma, IDH mutant WHO CNS grade 3 | diffuse | adults | Anaplastic astrocytoma, gliomatosis cerebri | |
| Astrocytoma, IDH mutant WHO CNS grade 4 | diffuse | adults | ||
| Glioblastoma, WHO CNS grade 4 | diffuse | adults | small cell, epitheloid/rhabdoid, with PNET componet, with granular cell component, giant cell, gliosarcoma | |
| Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27M-mutant, WHO CNS grade 4 | diffuse | children | ||
| Pilocytic astrocytoma, WHO CNS grade 1 | circumscribed | children | pilomyxoid astrocytoma, anaplastic pilocytic astrocytoma | |
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, WHO CNS grade 2 (PXA) | circumscribed | young adults | ||
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, WHO CNS grade 3 (PXA) | circumscribed | young adults | Anaplastic PXA. | |
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, WHO CNS grade 1 (SEGA) | circumscribed | young adults | SEGA in tuberous sclerosis |
Adult-type astrocytomas
- Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Glioblastoma, IDH wildtype.
- High-grade astrocytoma with piloid features.
- Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma.
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
- Chordoid glioma.
Pediatric-type astrocytomas
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade glioma.
- Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma.
- Astroblastoma, MN1-altered.
Diffuse growing astrocytomas
- Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Glioblastoma, IDH wildtype.
- Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered.
- Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant.
- Diffuse astrocytoma, MYB- or MYBL-altered.
- Diffuse pediatric-type high-grade glioma, H3-wildtype and IDH-wildtype.
- Angiocentric glioma.
- Diffuse low-grade glioma, MAPK pathway-altered.
Circumscribed astrocytomas
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
- High-grade astrocytoma with piloid features.
- Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma.
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
- Chordoid glioma.
- Astroblastoma, MN1-altered.
Common Astrocytomas
Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Benign, cystic, infratentorial.
- Classic childhood tumor, surgically resectable.
- Circumscribed astrocytic glioma
- Variant: Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
Astrocytoma, IDH mutant
- Astrocytoma, IDH mutant are less common than glioblastoma.
- Grade 2-4 depends on histological and molecular criteria:
Astrocytoma, IDH mutant grade 2
- Formerly designated as Diffuse astrocytoma Grade II.
- Typically seen in adults.
- Usually shows progression to astrocytoma IDH mutant, grade 4.
Astrocytoma, IDH mutant grade 3
- Formerly designated Anaplastic astrocytoma Grade III.
- Typically seen in adults.
- Increased cellularity, cell atypia and mitotic activity.
- Lacks endothelial proliferations and necrosis of glioblastoma.
Astrocytoma, IDH mutant grade 4
- Formerly called Glioblastoma, IDH mutant.
- Endothelial proliferations and necrosis indistinguishable from glioblastoma.
- Homozygous CDKN2A deletion qualifies grade 2 and grade 3 astrocytomas as grade 4 tumor.
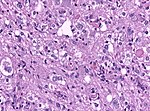
Glioblastoma
- Most common malignant brain tumor peaking around 65 years.
- Prognosis very poor.
- Variant: Giant cell glioblastoma
- Variant: Gliosarcoma
Uncommon Astrocytomas
Diffuse astrocytoma, MYB- or MYBL-altered
- Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma.
- Associated with epileptic seizures.
- Excellent prognosis.
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
- Intraventricular benign tumor of adolescents.
- Associated with Tuberous sclerosis.
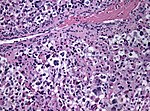
Pleomorphic xanthroastrocytoma (PXA)
- Kids & young adults usually with good prognosis.
- Large lipidized cells mimicking a malignant tumor
Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered
- High-grade astrocytic neoplasm associated with midline structures (thalamus, brain stem, spinal cord).
- Mostly in children and adolescents.
- Includes diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DPIG).
Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant
- Infiltrative hemispheric glioma of young adults.
- Glioblastoma-like appearance (CNS WHO grade 4 tumor).
- Newly defined entity in WHO 2021 classification.
- H3F3A missense mutation G34R or G34V.
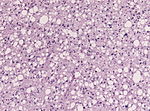
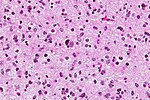
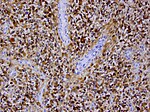
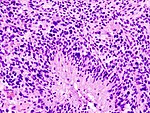
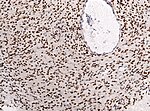
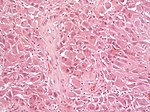
High-grade astrocytoma with piloid features
- Frequent in posterior fossa (75%).
- 1-3% of all brain tumors.
- Histology may resemble Glionblastoma or Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma.
- Tumor is enriched for piloid cell processes.
- ATRX nuclear loss is frequent.
- Usu. MAPK-pathway alterations + CDKN2A homozygous deletion.
- Distinct methylation profile.
Gliomatosis cerebri
- Depreceated entity.
- Was used for extensively diffusely growing astrocytic neoplasms.
- More than 3 lobes have to be involved, us. bilateral (radiology required).
- biologic behaviour corresponds to WHO III (ICD-O: 9381/3)
- Based on presence / absence of a solid component authors propose two types:[4]
- GC type 1: classic diffuse growth, without IDH1/2 mutation.
- GC type 2: with a solid portion, mostly IDH1 mutant.
- Genetic studies indicate strong overlap with diffuse astrocytic gliomas, oligodendrogliomas and glioblastoma.
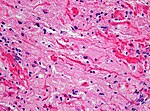
Gliosarcoma
General
- Considered to be a variant of glioblastoma by WHO.[5]
- Rare ~ 200 cases reported in the literature.[5]
- Definition: gliosarcoma = glioblastoma + sarcomatous component.[6]
- Usual location (like glioblastoma): temporal lobe.
- Prognosis is similiar to glioblastoma.[7]
- Age below 65 years is prognostic.
Microscopic
Features:
- Glioblastoma.
- Sarcomatous component (one of the following):[5][6]
- Fibroblastic.
- Cartilaginous.
- Osseous.
- Smooth muscle.
- Striated muscle.
- Adipocyte.
Images
www:
- Gliosarcoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Gliosarcoma - case 2 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Gliosarcoma - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
Gliosarcoma with smooth muscle component (gliomyosarcoma):[10]
- SMA +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
Gliofibroma
- Very rare indolent tumor in children [11]
- Usually not dura-based (DD: Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma)
- Glial tumor with non-neoplastic fibromatous component.
See also
References
- ↑ SAMUEL NEVIN - GLIOMATOSIS CEREBRI, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/brain/61.2.170 170-191 First published online: 1 June 1938
- ↑ Johnson, DR.; Guerin, JB.; Giannini, C.; Morris, JM.; Eckel, LJ.; Kaufmann, TJ.. "2016 Updates to the WHO Brain Tumor Classification System: What the Radiologist Needs to Know.". Radiographics 37 (7): 2164-2180. doi:10.1148/rg.2017170037. PMID 29028423.
- ↑ Herrlinger, U.; Jones, DT.; Glas, M.; Hattingen, E.; Gramatzki, D.; Stuplich, M.; Felsberg, J.; Bähr, O. et al. (Oct 2015). "Gliomatosis cerebri: no evidence for a separate brain tumor entity.". Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1495-z. PMID 26493382.
- ↑ Seiz, M.; Tuettenberg, J.; Meyer, J.; Essig, M.; Schmieder, K.; Mawrin, C.; von Deimling, A.; Hartmann, C. (Aug 2010). "Detection of IDH1 mutations in gliomatosis cerebri, but only in tumors with additional solid component: evidence for molecular subtypes.". Acta Neuropathol 120 (2): 261-7. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0701-2. PMID 20514489.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Han SJ, Yang I, Tihan T, Prados MD, Parsa AT (February 2010). "Primary gliosarcoma: key clinical and pathologic distinctions from glioblastoma with implications as a unique oncologic entity". J. Neurooncol. 96 (3): 313–20. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9973-6. PMC 2808523. PMID 19618114. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2808523/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ayadi L, Charfi S, Khabir A, et al. (March 2010). "[Cerebral gliosarcoma: clinico-pathologic study of 8 cases]" (in French). Tunis Med 88 (3): 142–6. PMID 20415184.
- ↑ Frandsen, J.; Orton, A.; Jensen, R.; Colman, H.; Cohen, AL.; Tward, J.; Shrieve, DC.; Suneja, G. (Jun 2017). "Patterns of care and outcomes in gliosarcoma: an analysis of the National Cancer Database.". J Neurosurg: 1-6. doi:10.3171/2016.12.JNS162291. PMID 28621623.
- ↑ Horiguchi, H.; Hirose, T.; Kannuki, S.; Nagahiro, S.; Sano, T. (Aug 1998). "Gliosarcoma: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and fluorescence in situ hybridization study.". Pathol Int 48 (8): 595-602. PMID 9736406.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case361.html. Accessed on: 15 January 2012.
- ↑ Khanna, M.; Siraj, F.; Chopra, P.; Bhalla, S.; Roy, S.. "Gliosarcoma with prominent smooth muscle component (gliomyosarcoma): a report of 10 cases.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 54 (1): 51-4. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.77324. PMID 21393877.
- ↑ Deb, P.; Sarkar, C.; Garg, A.; Singh, VP.; Kale, SS.; Sharma, MC. (Feb 2006). "Intracranial gliofibroma mimicking a meningioma: a case report and review of literature.". Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108 (2): 178-86. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2004.11.021. PMID 16412839.