Difference between revisions of "TDP-43"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (+alzheimer) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Inclusions found== | ==Inclusions found== | ||
*[[FTLD TDP-43]] | *Frontotemporal dementias [[FTLD TDP-43]] <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Neumann | first1 = M. | title = Molecular neuropathology of TDP-43 proteinopathies. | journal = Int J Mol Sci | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | pages = 232-46 | month = Jan | year = 2009 | doi = 10.3390/ijms10010232 | PMID = 19333444 }}</ref> | ||
* Alzheimer disease.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wilson | first1 = AC. | last2 = Dugger | first2 = BN. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = DW. | last4 = Wang | first4 = DS. | title = TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 2 | pages = 147-55 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21326809 }}</ref> | * [[Alzheimer disease]].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wilson | first1 = AC. | last2 = Dugger | first2 = BN. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = DW. | last4 = Wang | first4 = DS. | title = TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 2 | pages = 147-55 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21326809 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Chronic traumatic encephalopathy]] (CTE).<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = McKee | first1 = AC. | last2 = Cairns | first2 = NJ. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = DW. | last4 = Folkerth | first4 = RD. | last5 = Keene | first5 = CD. | last6 = Litvan | first6 = I. | last7 = Perl | first7 = DP. | last8 = Stein | first8 = TD. | last9 = Vonsattel | first9 = JP. | title = The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 131 | issue = 1 | pages = 75-86 | month = Jan | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-015-1515-z | PMID = 26667418 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Lewy body disease]] (LBD).<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ling | first1 = H. | last2 = Kara | first2 = E. | last3 = Bandopadhyay | first3 = R. | last4 = Hardy | first4 = J. | last5 = Holton | first5 = J. | last6 = Xiromerisiou | first6 = G. | last7 = Lees | first7 = A. | last8 = Houlden | first8 = H. | last9 = Revesz | first9 = T. | title = TDP-43 pathology in a patient carrying G2019S LRRK2 mutation and a novel p.Q124E MAPT. | journal = Neurobiol Aging | volume = 34 | issue = 12 | pages = 2889.e5-9 | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.04.011 | PMID = 23664753 }}</ref> | |||
*In 30% of non-demented individuals 65yrs and older.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wilson | first1 = AC. | last2 = Dugger | first2 = BN. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = DW. | last4 = Wang | first4 = DS. | title = TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 2 | pages = 147-55 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21326809 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Inclusion body myositis]] (IBM).<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = D'Agostino | first1 = C. | last2 = Nogalska | first2 = A. | last3 = Engel | first3 = WK. | last4 = Askanas | first4 = V. | title = In sporadic inclusion body myositis muscle fibres TDP-43-positive inclusions are less frequent and robust than p62 inclusions, and are not associated with paired helical filaments. | journal = Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol | volume = 37 | issue = 3 | pages = 315-20 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01108.x | PMID = 20626631 }}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
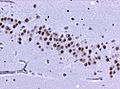
FTLD TSP43 hippocampus.jpg | Pan-TDP43 immunohistochemisty. Pathological cytoplasmic inclusions. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 5 July 2018
| TDP-43 | |
|---|---|
| Immunostain in short | |
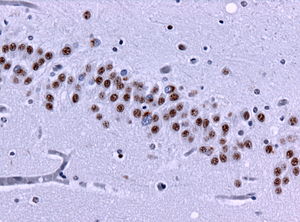 TDP-43 staining in FTLD-TDP43. (WC) | |
| Normal staining pattern | nuclear staining (physiological) |
| Positive | cytoplasmatic staining (pathological) |
TAR-DNA-binding Protein 43, abbreviated TDP-43 is a neuropathology immunostain used in neurodegenerative diseases.
- Nuclear staining.
Inclusion morphology
- fine / coarse skeins.
- dot-like.
- dense-round inclusions.
Inclusions found
- Frontotemporal dementias FTLD TDP-43 [1]
- Alzheimer disease.[2]
- Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).[3]
- Lewy body disease (LBD).[4]
- In 30% of non-demented individuals 65yrs and older.[5]
- Inclusion body myositis (IBM).[6]
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Neumann, M. (Jan 2009). "Molecular neuropathology of TDP-43 proteinopathies.". Int J Mol Sci 10 (1): 232-46. doi:10.3390/ijms10010232. PMID 19333444.
- ↑ Wilson, AC.; Dugger, BN.; Dickson, DW.; Wang, DS. (Jan 2011). "TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4 (2): 147-55. PMID 21326809.
- ↑ McKee, AC.; Cairns, NJ.; Dickson, DW.; Folkerth, RD.; Keene, CD.; Litvan, I.; Perl, DP.; Stein, TD. et al. (Jan 2016). "The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy.". Acta Neuropathol 131 (1): 75-86. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1515-z. PMID 26667418.
- ↑ Ling, H.; Kara, E.; Bandopadhyay, R.; Hardy, J.; Holton, J.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Lees, A.; Houlden, H. et al. (Dec 2013). "TDP-43 pathology in a patient carrying G2019S LRRK2 mutation and a novel p.Q124E MAPT.". Neurobiol Aging 34 (12): 2889.e5-9. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.04.011. PMID 23664753.
- ↑ Wilson, AC.; Dugger, BN.; Dickson, DW.; Wang, DS. (Jan 2011). "TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4 (2): 147-55. PMID 21326809.
- ↑ D'Agostino, C.; Nogalska, A.; Engel, WK.; Askanas, V. (Apr 2011). "In sporadic inclusion body myositis muscle fibres TDP-43-positive inclusions are less frequent and robust than p62 inclusions, and are not associated with paired helical filaments.". Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37 (3): 315-20. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01108.x. PMID 20626631.