Difference between revisions of "Pancreas"
(→IPMT: update) |
m (→Pancreatic acinar metaplasia: fix typo) |
||
| (228 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
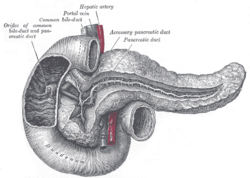
The '''pancreas''' hangs-out in the upper abdomen. It occasionally is afflicited by cancers, the most common of which is very fatal. | [[Image:Gray 1100 Pancreatic duct.png|thumb|right|250px|A drawing of the pancreas. (WC/Gray's Anatomy)]] | ||
The '''pancreas''' hangs-out in the upper abdomen. It occasionally is afflicited by cancers, the most common of which is very fatal. | |||
Pancreatic cytopathology is dealt with in the ''[[gastrointestinal cytopathology]]'' article. | |||
A general introduction to gastrointestinal pathology is in the ''[[gastrointestinal pathology]]'' article. | |||
=Introduction= | |||
==Normal anatomy== | ==Normal anatomy== | ||
Divided into three portions: head, body & tail: | Divided into three portions: head, body & tail:<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.</ref> | ||
*Head: | *Head: | ||
**Includes unicate process. | **Includes unicate process. | ||
** | **Extends to the left edge of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) - by definition. | ||
***All of the SMV is with the head. | |||
*Body: | *Body: | ||
** | **Right edge of the superior mesenteric vein to the left edge of aorta - by definition. | ||
***All of the aorta is with the body. | |||
*Tail: | *Tail: | ||
**Remainder of pancreas. | **Remainder of pancreas. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 21: | ||
==Pancreatic surgeries== | ==Pancreatic surgeries== | ||
Common pancreatic surgeries include: | Common pancreatic surgeries include: | ||
*Whipple (includes duodenum). | *Whipple procedure ([[AKA]] pancreaticoduodenal resection) - includes [[duodenum]] and usually the distal [[stomach]] (antrum). | ||
*Distal pancreatectomy. | *Distal pancreatectomy. | ||
**Removal of tail +/- body. | **Removal of tail +/- body. | ||
**Specimen usually comes with the [[spleen]]. | |||
**Typically done form [[islet cell tumour]]s. | |||
*Total pancreatectomy. | *Total pancreatectomy. | ||
** | **Specimen usually comes with the spleen. | ||
===Whipple procedure=== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''pancreaticoduodenectomy''. | |||
Indications: | |||
*Head of pancreas lesions, duodenal lesions. | |||
[[Margins]]:<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.</ref> | |||
#Proximal mucosal margin (stomach or duodenum). | |||
#Distal mucosal margin (duodenum or jejunum). | |||
#Bile duct margin. | |||
#Pancreatic retroperitoneal (uncinate process) margin. | |||
#*At SB done ''on edge'' (not ''en face''). | |||
#Pancreatic neck transection margin ([[AKA]] distal pancreatic resection margin);<ref name=pmid20485150>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jamieson | first1 = NB. | last2 = Foulis | first2 = AK. | last3 = Oien | first3 = KA. | last4 = Going | first4 = JJ. | last5 = Glen | first5 = P. | last6 = Dickson | first6 = EJ. | last7 = Imrie | first7 = CW. | last8 = McKay | first8 = CJ. | last9 = Carter | first9 = R. | title = Positive mobilization margins alone do not influence survival following pancreatico-duodenectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. | journal = Ann Surg | volume = 251 | issue = 6 | pages = 1003-10 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d77369 | PMID = 20485150 }}</ref> usu. ''en face'' and ''in toto''.<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 6 April 2012.</ref> | |||
#Sometimes superior mesenteric vein (SMV). | |||
#Rarely superior mesenteric artery (SMA) margin. | |||
[[Opening]]: | |||
#Open the proximal (stomach) and distal (small bowel) stappled margins. | |||
#Open the duodenum along it length on the anterior aspect. | |||
#Open the stomach along the greater curvature. | |||
#Join the cuts that open the stomach and duodenum. | |||
==General classification of pancreatic tumours== | ==General classification of pancreatic tumours== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 60: | ||
===Pancreas neoplasms in a table=== | ===Pancreas neoplasms in a table=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
!| Type | !| Type | ||
!| Key feature | !| Key feature | ||
| Line 42: | Line 74: | ||
| cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm | | cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm | ||
| cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | | cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | ||
| [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_serous_cystadenoma_%281%29.jpg], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_serous_cystadenoma_%282%29.jpg] | | [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_serous_cystadenoma_%281%29.jpg], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_serous_cystadenoma_%282%29.jpg (WC)], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_serous_cystadenoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg (WC)] | ||
| IHC? | | IHC? | ||
| cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm, central nucleus | | cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm, central nucleus | ||
| body or tail | | body or tail | ||
| - | | cystadenoma may be assoc. with [[von Hippel-Lindau syndrome]] | ||
| clear cell RCC, oligomucinous mucinous tumours | | [[clear cell renal cell carcinoma|clear cell RCC]], oligomucinous mucinous tumours | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Intraductal papillary | | [[Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour]] (IPMT) | ||
| mucin, no ovarian-like stroma | | mucin, no ovarian-like stroma | ||
| clear cell variant | | clear cell variant | ||
| | | [http://wjso.com/content/8/1/25/figure/F1 (wjso.com)], [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case451/images/fig01.jpg (upmc.edu)] | ||
| IHC? | | IHC? | ||
| papillae, tall columnar mucin-producing cells | | papillae, tall columnar mucin-producing cells | ||
| head | | head | ||
| - | | - | ||
| mucious neoplasms (other pancreatic, duodenal) | | mucious neoplasms (other pancreatic, duodenal), intra-ampullary papillary-tubular neoplasm (see [[ampullary carcinoma]]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Mucinous tumour | | Mucinous tumour | ||
| mucin, ovarian-like stroma | | mucin, ovarian-like stroma | ||
| cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | | cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | ||
| | | [http://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_intermed_mag.jpg (WC)], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_high_mag.jpg (WC)] | ||
| IHC? | | IHC? | ||
| tall columnar mucin-producing cells, ovarian-like stroma | | tall columnar mucin-producing cells, ovarian-like stroma | ||
| body or tail | | body or tail | ||
| - | | - | ||
| IPMT, metastatic mucinous tumours | | [[IPMT]], metastatic mucinous tumours | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Solid pseudopapillary<br>tumour | | [[Solid pseudopapillary tumour|Solid pseudopapillary<br>tumour]] | ||
| eosinophilic intracytoplasmic globules | | eosinophilic intracytoplasmic globules | ||
| clear cell variant (cytoplasm clear) | | clear cell variant (cytoplasm clear) | ||
| [http://jcp.bmj.com/content/61/11/1153/F1.large.jpg] | | [http://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Solid_pseudopapillary_tumour_-_intermed_mag.jpg (WC)], [http://jcp.bmj.com/content/61/11/1153/F1.large.jpg (bmj.com)] | ||
| | | beta-catenin +ve, E-cadherin +ve, <br>synaptophysin +ve, chromogranin -ve | ||
| sheets of cells, focally loosely cohesive, eosinophilic cytoplasm, uniform nuclei with grooves | | sheets of cells, focally loosely cohesive, eosinophilic cytoplasm, uniform nuclei with grooves | ||
| none | | none (head, body or tail) | ||
| | | usu. younger women | ||
| ductal adenocarcinoma | | [[pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma|ductal adenocarcinoma]], [[neuroendocrine tumour]]s | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Ductal adenocarcinoma | | [[Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas|Ductal adenocarcinoma]] | ||
| irregular shaped glands, cytologic atypia | | irregular shaped glands, cytologic atypia | ||
| mucinous, spindle cell, mixed ductal-endocrine | | mucinous, spindle cell, mixed ductal-endocrine | ||
| [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_%284%29_Case_01.jpg], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_%282%29_Case_01.jpg] | | [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_%284%29_Case_01.jpg (WC)], [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_%282%29_Case_01.jpg (WC)] | ||
| IHC? | | IHC? | ||
| glands, sheets, single cells, nuc. atypia, +/-mitoses, +/-necrosis | | glands, sheets, single cells, nuc. atypia, +/-mitoses, +/-[[necrosis]] | ||
| head | | head | ||
| | | arises from the precursor ''PanIN'' | ||
| | | ampullary carcinoma, [[chronic pancreatitis]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Pancreatoblastoma | | [[Pancreatoblastoma]] | ||
| squamoid nests, whorling | | squamoid nests, whorling | ||
| - | | - | ||
| | | [http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n1s/fig_tab/3800686f16.html#figure-title (nature.com)] | ||
| | | [[CK7]] (acinar comp.), CK8, CK18, [[CK19]] | ||
| squamoid nests of cells, whorling, nested growth, +/-keratinization | | squamoid nests of cells, whorling, nested growth, +/-keratinization | ||
| none | | none | ||
| | | usu. paediatric population | ||
| acinar cell carcinoma | | [[acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas|acinar cell carcinoma]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Acinar cell carcinoma | | [[Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas|Acinar cell carcinoma]] | ||
| acinar arch. | | acinar arch. | ||
| - | | - | ||
| [http://www.histopathology-india.net/acinar%20cell%20ca.JPG] | | [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acinar_cell_carcinoma_of_the_pancreas_-_very_high_mag.jpg (WC)], [http://www.histopathology-india.net/acinar%20cell%20ca.JPG (histopathology-india.net)] | ||
| | | trypsin, lipase | ||
| nests or trabeculae, nucleolus, mod. basophilic granular cytoplasm | | nests or [[trabeculae]], nucleolus, mod. basophilic granular cytoplasm | ||
| head (slight predilection) | | head (slight predilection) | ||
| - | | - | ||
| pancreatoblastoma | | pancreatoblastoma | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant | | Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like [[giant cell]]s | ||
| giant cells | | giant cells | ||
| - | | - | ||
| Line 119: | Line 151: | ||
| anaplastic carcinoma | | anaplastic carcinoma | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Chronic pancreatitis | | [[Chronic pancreatitis]] | ||
| fibrosis, loss of acinar tissue | | fibrosis, loss of acinar tissue, preservation of lobular arch. | ||
| - | | - | ||
| [http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/education/gi/lab1.b.html] | | [http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/education/gi/lab1.b.html] | ||
| Line 126: | Line 158: | ||
| loss of acinar tissue with preservation of islets, fibrosis | | loss of acinar tissue with preservation of islets, fibrosis | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| | | not a neoplasm, included here as it is in the (clinical) DDx | ||
| ductal adenocarcinoma | | [[pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma|ductal adenocarcinoma]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Most important cystic lesions== | ===WHO classification=== | ||
Benign epithelial: | |||
*[[Pancreatic serous cystadenoma|Serous cystadenoma]]. | |||
*[[Pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma|Mucinous cystadenoma]]. | |||
*[[Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm|Intraductal papillary mucinous adenoma]]. | |||
*[[Mature teratoma]]. | |||
Borderline epithelial: | |||
*Mucinous cystic neoplasm with moderate dysplasia. | |||
*[[Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm|Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with moderate dysplasia]]. | |||
*[[Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm]] | |||
Malignant epithelial: | |||
*[[Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma|Ductal adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
**Mucinous noncystic carcinoma. | |||
**[[Signet ring cell carcinoma]]. | |||
**[[Adenosquamous carcinoma]]. | |||
**Undifferentiated carcinoma. | |||
**Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells. | |||
**Mixed ductal-endocrine carcinoma. | |||
*[[Pancreatic serous cystadenocarcinoma|Serous cystadenocarcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Pancreatic mucinous cystadenocarcinoma|Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma]]. | |||
**Invasive. | |||
**Noninvasive. | |||
*[[Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm|Intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma]]. | |||
**Invasive. | |||
**Noninvasive. | |||
*[[Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas|Acinar cell carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Pancreatoblastoma]]. | |||
*[[Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm|Solid pseudopapillary carcinoma]]. | |||
Soft tissue tumours: | |||
*See ''[[soft tissue lesions]]''. | |||
=Ectopic pancreatic tissue= | |||
It comes in two flavours:<ref>URL: [http://test.pathologyportal.org/newindex.htm?92nd/specgasth2.htm http://test.pathologyportal.org/newindex.htm?92nd/specgasth2.htm]. Accessed on: 14 March 2011.</ref> | |||
*Pancreatic ectopia. | |||
*Pancreatic (acinar) metaplasia. | |||
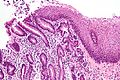
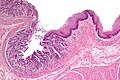
==Pancreatic acinar metaplasia== | |||
*Abbreviated ''PAM''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''pancreatic metaplasia''.<ref name=pmid8724024>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stachura | first1 = J. | last2 = Konturek | first2 = JW. | last3 = Urbanczyk | first3 = K. | last4 = Bogdal | first4 = J. | last5 = Mach | first5 = T. | last6 = Domschke | first6 = W. | title = Endoscopic and histological appearance of pancreatic metaplasia in the human gastric mucosa: a preliminary report on a recently recognized new type of gastric mucosal metaplasia. | journal = Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 239-43 | month = Mar | year = 1996 | doi = | PMID = 8724024 }}</ref> | |||
===General=== | |||
*Common in the GI tract. | |||
*Found in ~ 17-19% of [[stomach|gastro]][[esophagus|esophageal]] junction biopsies.<ref name=pmid23989798/><ref name=pmid20012917>{{cite journal |author=Johansson J, Håkansson HO, Mellblom L, ''et al.'' |title=Pancreatic acinar metaplasia in the distal oesophagus and the gastric cardia: prevalence, predictors and relation to GORD |journal=J. Gastroenterol. |volume=45 |issue=3 |pages=291–9 |year=2010 |month=March |pmid=20012917 |doi=10.1007/s00535-009-0161-4 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Associated with intestinal metaplasia.<ref name=pmid23989798>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schneider | first1 = NI. | last2 = Plieschnegger | first2 = W. | last3 = Geppert | first3 = M. | last4 = Wigginghaus | first4 = B. | last5 = Höss | first5 = GM. | last6 = Eherer | first6 = A. | last7 = Wolf | first7 = EM. | last8 = Rehak | first8 = P. | last9 = Vieth | first9 = M. | title = Pancreatic acinar cells-a normal finding at the gastroesophageal junction? Data from a prospective Central European multicenter study. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Aug | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-013-1471-8 | PMID = 23989798 }}</ref> | |||
**Not associated with changes of [[GERD]], or [[Helicobacter gastritis]].<ref name=pmid23989798/> | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*May be a single lesion or a cluster of lesions.<ref name=pmid8724024/> | |||
Note: | |||
*''Not'' associated with the endoscopic diagnosis of esophagitis or [[Barrett's esophagus]].<ref name=pmid23989798/> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Pancreatic acini - only. | |||
**Intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
Negatives: | |||
*No pancreatic ducts. | |||
*No islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets). | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pancreatic_acinar_metaplasia_-_high_mag.jpg | PAM - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Pancreatic_acinar_metaplasia_-_low_mag.jpg | PAM - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===IHC=== | |||
Features:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Doglioni | first1 = C. | last2 = Laurino | first2 = L. | last3 = Dei Tos | first3 = AP. | last4 = De Boni | first4 = M. | last5 = Franzin | first5 = G. | last6 = Braidotti | first6 = P. | last7 = Viale | first7 = G. | title = Pancreatic (acinar) metaplasia of the gastric mucosa. Histology, ultrastructure, immunocytochemistry, and clinicopathologic correlations of 101 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 17 | issue = 11 | pages = 1134-43 | month = Nov | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8214258 }}</ref> | |||
*Trypase +ve. | |||
*Lipase +ve. | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
It can be debated whether it is worth reporting. | |||
<pre> | |||
ESOPHAGUS (DISTAL), BIOPSY: | |||
- COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH MODERATE CHRONIC, FOCALLY ACTIVE, INFLAMMATION, AND | |||
PANCREATIC ACINAR METAPLASIA. | |||
- REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
==Pancreatic ectopia== | |||
===General=== | |||
*May be confused with something pathologic. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Consists of pancreatic acini ''and'' pancreatic ducts. | |||
*+/-Islets of Langerhans. | |||
=Inflammatory= | |||
==Pancreatitis== | |||
===Classification=== | |||
*[[Acute pancreatitis]]. | |||
*[[Chronic pancreatitis]]. | |||
===Etiology=== | |||
Mnemonic ''I GET SMASHED'': | |||
*Idiopathic. | |||
*[[Gallstones]] ~45%. | |||
*Ethanol ~35%. | |||
*Tumours (pancreas, ampulla). | |||
*Scorpion bites, snake bites. | |||
*Microbial - mumps (paramyxovirus), [[Epstein-Barr virus]] (EBV), [[cytomegalovirus]] (CMV), mycoplasma. | |||
*Autoimmune - [[Crohn's disease]], [[polyarteritis nodosa]] (PAN), [[systemic lupus erythematosus]] (SLE). | |||
*Surgery/trauma, e.g. ERCP, motor vehicle collision. | |||
*Hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia/hypertriglyceridemia, [[hypothermia]]. | |||
*Emboli, e.g. post-[[CABG]]. | |||
*Drugs - ''SAND'' = steroids & sulfonamides, azathioprine, [[NSAID]]s, diuretics, such as furosemide. | |||
==Acute pancreatitis== | |||
{{Main|Acute pancreatitis}} | |||
==Chronic pancreatitis== | |||
{{Main|Chronic pancreatitis}} | |||
=Cystic lesions - overview= | |||
===General=== | |||
*True cystic lesions are uncommon. | |||
**A true cystic lesion: ''must'' have an epithelial lining. | |||
***Only 10% of cystic lesions are true cystic lesions, i.e. 90% of cystic lesions are really [[Pancreatic pseudocyst|pseudocysts]]. | |||
*It is hard to differentiate pseudocysts & cysts. | |||
===Cystic tumours - clinical=== | |||
General: | |||
*Usually diagnosed by imaging (CT/MRI, ERCP, Endoscopic ultrasound). | |||
**50% incidental finding. | |||
*Vague symptoms | |||
*Abdominal mass. | |||
*Weight loss. | |||
*Jaundice. | |||
*Usually favourable prognosis - mostly benign. | |||
===Most important cystic lesions=== | |||
*Serous. | *Serous. | ||
*Mucinous. | *Mucinous. | ||
| Line 140: | Line 309: | ||
Mnemonic ''SIMS'': Serous, IPMT, Mucinous, Solid pseudopapillary tumour. | Mnemonic ''SIMS'': Serous, IPMT, Mucinous, Solid pseudopapillary tumour. | ||
===Mucinous vs. IMPT=== | ====Useful stains==== | ||
*PAS-D. | |||
====Mucinous vs. IMPT==== | |||
IMPT: | IMPT: | ||
*No ovarian-like stroma. | *No ovarian-like stroma. | ||
*Usually has total pancreatectomy. | *Usually has total pancreatectomy. | ||
==Cystic | ===Cystic tumours of the pancreas=== | ||
Khalifa's table of cystic tumours: | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Tumour | |||
!Usual sex | |||
!Age (years) | |||
!Usual site | |||
!Typical <br>size (cm) | |||
![[Gross pathology]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[serous microcystic adenoma|Serous microcystic<br> adenoma]] | |||
|female | |||
|66 | |||
|body & tail | |||
|11 | |||
|[http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/25_fig06.jpg (joplink.net]<ref>URL: [http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/25.html http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/25.html]. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.</ref>, [http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/images/cpc5/33.jpg (jhmi.edu)]<ref name=jhmi>URL: [http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/cases/cpc5/cpc5_answer.html http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/cases/cpc5/cpc5_answer.html]. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.</ref> | |||
|- | |||
|[[IPMN|Intraductal papillary<br>mucinous tumour (IPMT)]] | |||
|male | |||
|62 | |||
|head | |||
|4 | |||
|[http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/images/cpc5/28.jpg (jhmi.edu)]<ref name=jhmi>URL: [http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/cases/cpc5/cpc5_answer.html http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/cases/cpc5/cpc5_answer.html]. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.</ref> | |||
|- | |||
|Mucinous tumour | |||
|female | |||
|49 | |||
|body & tail | |||
|10 | |||
|[http://radiology.rsna.org/content/251/1/77/F8.expansion.html (rsna.org)] | |||
|- | |||
|[[solid pseudopapillary tumour|Solid pseudopapillary<br> tumour]] | |||
|female | |||
|35 | |||
|any | |||
|7.5 | |||
|[http://www.ajronline.org/content/195/4/947/F4.expansion.html (ajronline.org)], [http://www.flickr.com/photos/35441329@N05/5249538296/ (flickr.com/humpath)] | |||
|} | |||
=Cystic lesions= | |||
==Serous tumours - overview== | |||
==Serous | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Cell of origin: intralobular duct cells (ductular cells). | *Cell of origin: intralobular duct cells (ductular cells). | ||
*Glycogen rich - but do not produce mucin. | *Glycogen rich - but do not produce mucin. | ||
===Subclassication=== | ====Subclassication==== | ||
*Serous microcystic adenoma. | *[[Serous microcystic adenoma]] ([[AKA]] serous cystadenoma<ref name=Ref_Sternberg4_1630>{{Ref Sternberg4|1630}}</ref>). | ||
** Many small cysts. | ** Many small cysts. | ||
*Serous oligocystic adenoma. | *Serous oligocystic adenoma. | ||
** Large cysts. | ** Large cysts. | ||
*Serous | *Serous cystadenocarcinoma - very rare.<ref name=pmid22009426>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bano | first1 = S. | last2 = Upreti | first2 = L. | last3 = Puri | first3 = SK. | last4 = Chaudhary | first4 = V. | last5 = Sakuja | first5 = P. | title = Imaging of pancreatic serous cystadenocarcinoma. | journal = Jpn J Radiol | volume = 29 | issue = 10 | pages = 730-4 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/s11604-011-0617-3 | PMID = 22009426 }}</ref> | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*If one mucin +ve cell, tumour = a mucinous tumour. | *If one mucin +ve cell, tumour = a mucinous tumour. | ||
=== | ==Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''serous microcystic adenoma'',<ref name=Ref_Sternberg4_1630>{{Ref Sternberg4|1630}}</ref> [[AKA]] ''pancreatic serous cystadenoma''. | |||
{{Main|Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas}} | |||
==Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas== | |||
==Mucinous cystic | |||
*Gastro-entero-pancreatic cell differentiation with hypercellular ovarian-type stroma. | *Gastro-entero-pancreatic cell differentiation with hypercellular ovarian-type stroma. | ||
**Stroma --> cellular. | **Stroma --> cellular. | ||
| Line 227: | Line 389: | ||
===Subclassification=== | ===Subclassification=== | ||
* | *Mucinous cystadenoma. | ||
*Borderline mucinous cystic tumour. | *Borderline mucinous cystic tumour. | ||
*Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. | *Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. | ||
| Line 244: | Line 406: | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
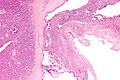
====Mucinous cystadenoma==== | ====Mucinous cystadenoma==== | ||
Features:<ref>GLP | Features:<ref name=Ref_GLP489>{{Ref GLP|489}}</ref> | ||
*Simple tall columnar epithelium with large mucin vacuole on apical aspect. | *Simple tall columnar epithelium with large mucin vacuole on apical aspect. | ||
*"Ovarian-type stroma" under epithelium. | *"Ovarian-type stroma" under epithelium. | ||
**Ovarin-type stroma: high density of small (non-wavy) spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. | **Ovarin-type stroma: high density of small (non-wavy) spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Appearance similar to ''mucinous cystadenoma'' in the [[ovarian tumours|ovary]]. | *Appearance similar to ''mucinous cystadenoma'' in the [[ovarian tumours|ovary]]. | ||
*Mucin stains +ve (intracytoplasmic). | *Mucin stains +ve (intracytoplasmic). | ||
=====Images===== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_very_low_mag.jpg | Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_low_mag.jpg | Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm - low mag.(WC) | |||
Image:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Benign_pancreatic_mucinous_cystic_neoplasm_-_high_mag.jpg | Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm - showing stroma - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/Images/GYN/5705b.gif Mucinous cystadenoma - ovary (uchc.edu)]. | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 1.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 2.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 3.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 4.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 5.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 6.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]] | |||
[[File:4 477025809 sl 7.png|Mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas]]<br> | |||
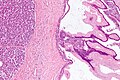
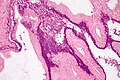
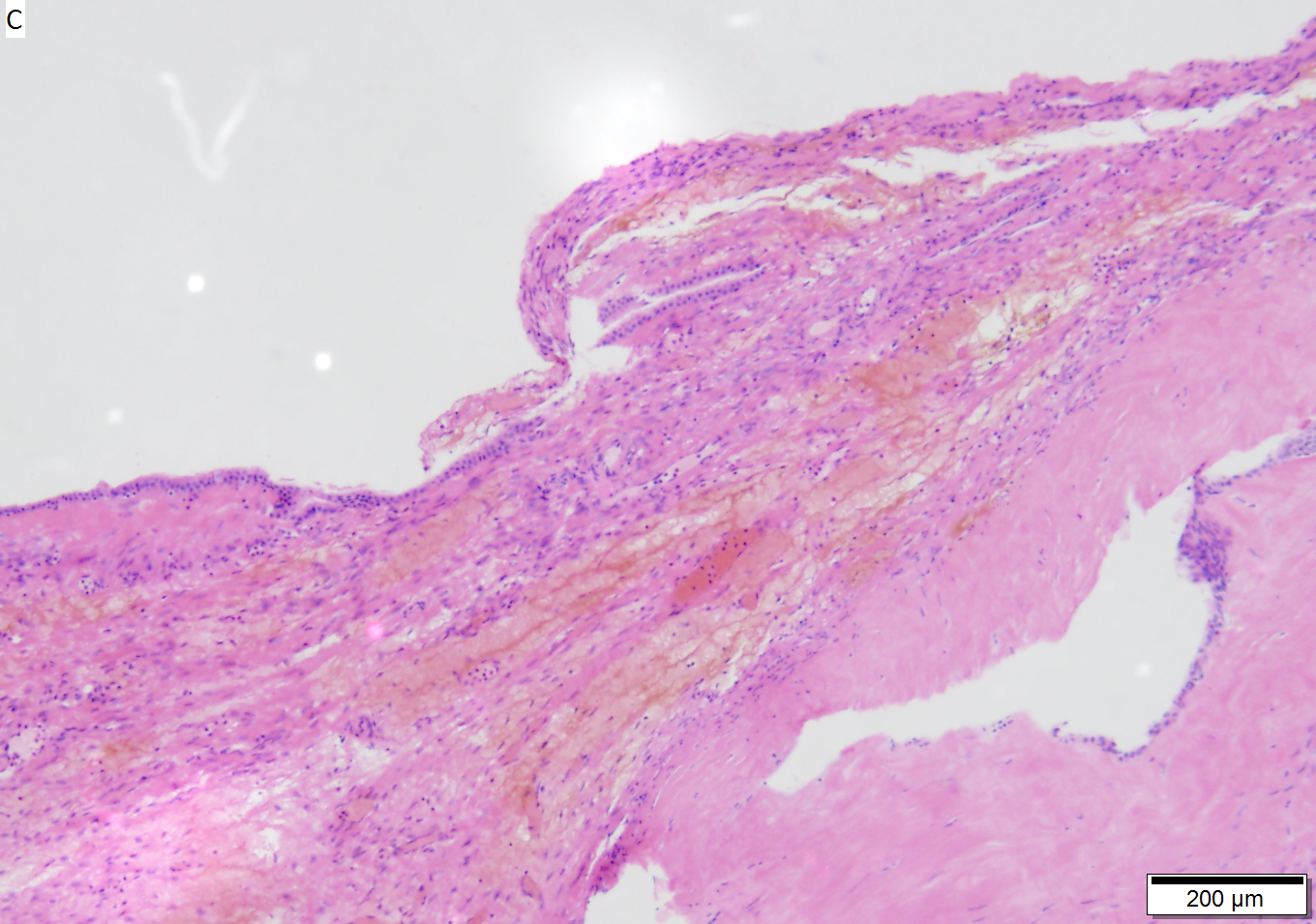
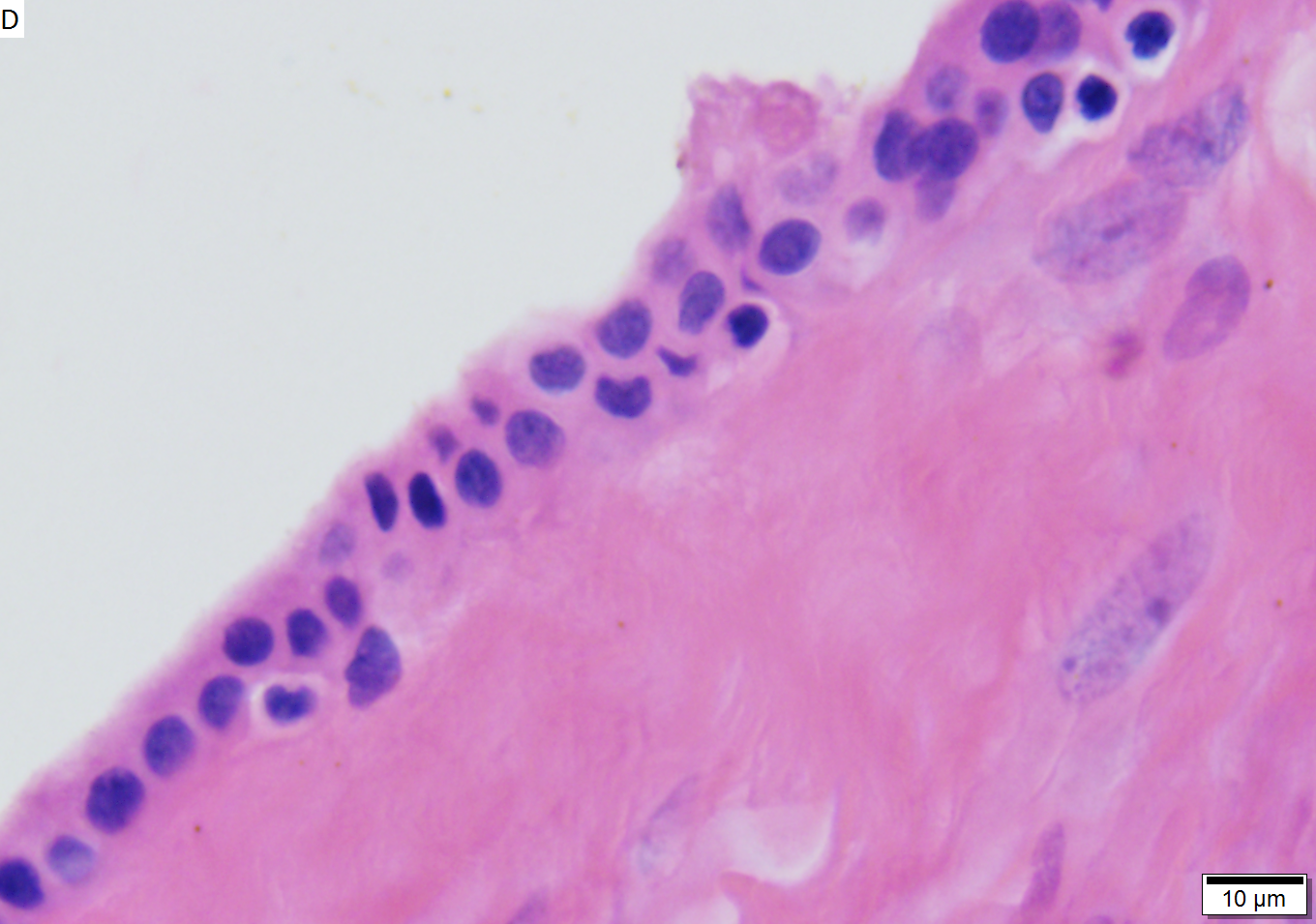
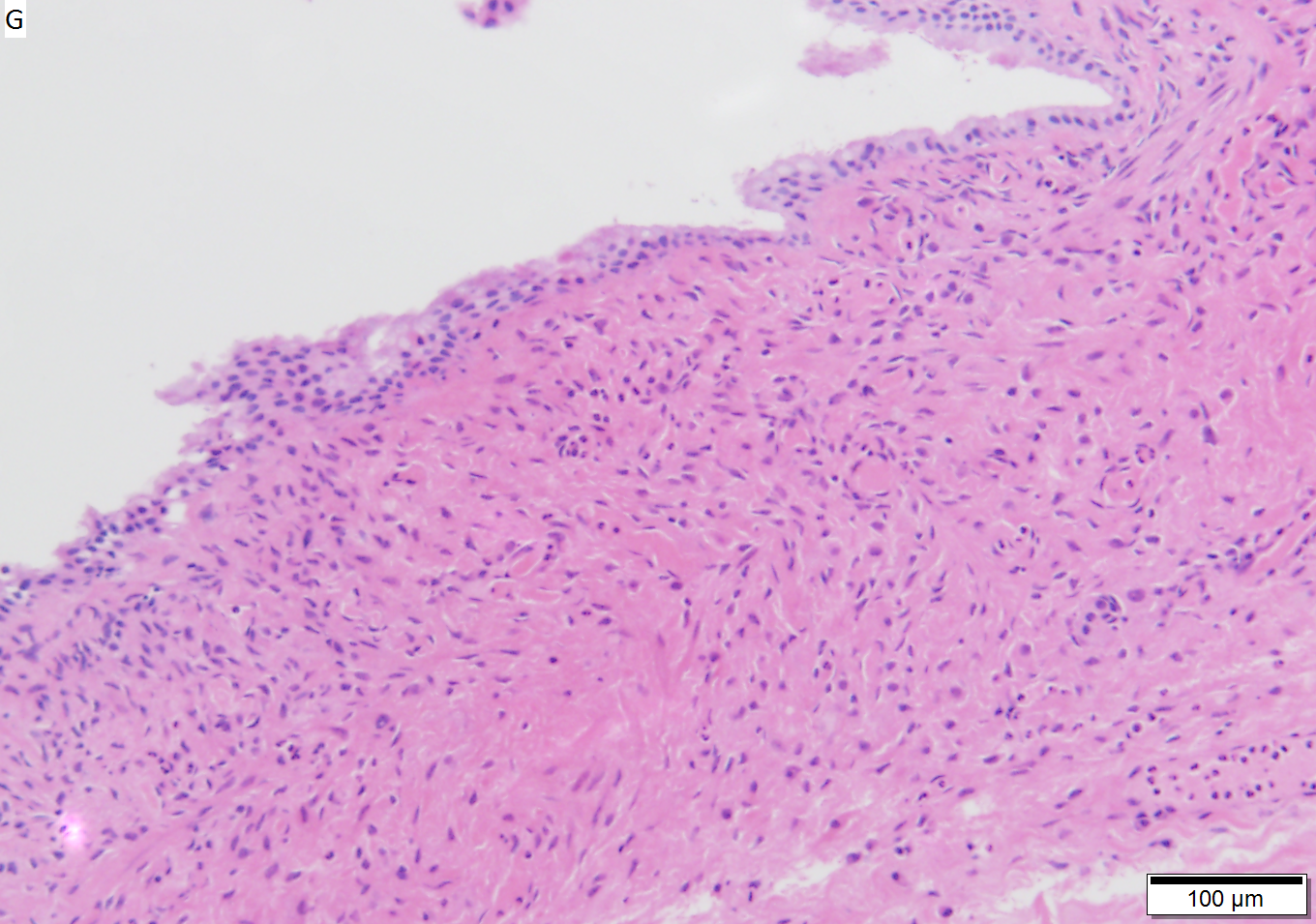
Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas in a 62 year old woman. A. CT scan showed a peripherally calcified spheroidal mass at the tail of the pancreas. Cytology only showed debris and inflammatory cells, but CEA of the fluid was 2875.2 ng/mL. B. Almost all sections of the cyst showed acellular debris topping a fibrous, often calcified wall, consistent with a pseudocyst. C. Extensive sampling, undertaken because of the high CEA, revealed rare sections with a lining. D. Lining nuclei are bland, with even chromatin. Shape and size variation, as well as darkening when shrunken, are all explicable by degeneration. E. Within distal pancreas, a focus of changes of chronic pancreatitis is seen upper left, while a pancreatic duct in lower right shows an intraductal proliferation. F. Tumor cells show mucinous vacuoles, with better preserved nuclei. Nuclear appearances remain bland. G. Cellular ovarian stroma appeared beneath epithelium of a separate focus of the cystic neoplasm. | |||
====Borderline mucinous cystic tumour==== | ====Borderline mucinous cystic tumour==== | ||
| Line 268: | Line 446: | ||
*Cells floating in mucin. | *Cells floating in mucin. | ||
====Mucinous tumour | ====Mucinous tumour versus pseudocyst==== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Finding | |||
! Mucinous tumour | |||
CEA, | ! Pseudocyst | ||
|- | |||
|Amylase & lipase || low || high | |||
|- | |||
|Viscosity || high || low | |||
|- | |||
|[[CEA]], CA125 || high || low | |||
|} | |||
Prognosis: | Prognosis: | ||
| Line 281: | Line 466: | ||
==Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour== | ==Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour== | ||
*Abbreviated ''IPMT''. | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm'', abbreviated ''IPMN''. | ||
* | {{Main|Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour}} | ||
==Solid pseudopapillary tumour== | ==Solid pseudopapillary tumour== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''solid pseudopapillary neoplasm'', abbreviation ''SPN''. | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm'', abbreviated ''SPEN''.<ref>URL: [http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/360/full.html http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/360/full.html]. Accessed on: 31 October 2011.</ref> | ||
* | {{Main|Solid pseudopapillary tumour}} | ||
=== | =Pre-malignant lesions= | ||
==Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia== | |||
* | *Abbreviated ''PanIN''. | ||
{{Main|Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia}} | |||
=== | =Solid tumours= | ||
==Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''ductal adenocarcinoma''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''pancreatic adenocarcinoma''. | |||
{{Main|Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas}} | |||
== | ==Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour== | ||
*Abbreviated ''PanNET''.<ref name=pmid22198808/> | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''pancreatic islet cell tumour''<ref name=pmid22198808>{{Cite journal | last1 = Burns | first1 = WR. | last2 = Edil | first2 = BH. | title = Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Tumors: Guidelines for Management and Update. | journal = Curr Treat Options Oncol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/s11864-011-0172-2 | PMID = 22198808 }}</ref> - considered to be an outdated term. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''islet cell tumour'' - considered to be an outdated term. | |||
{{Main|Neuroendocrine tumour of the pancreas}} | |||
* | |||
==Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas== | |||
:'''Not''' to be confused with ''[[acinic cell carcinoma]]''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''acinar cell carcinoma''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma''.<ref name=pmid>{{Cite journal | last1 = Thomas | first1 = PC. | last2 = Nash | first2 = GF. | last3 = Aldridge | first3 = MC. | title = Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma presenting as acute pancreatitis. | journal = HPB (Oxford) | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 111-3 | month = | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1080/13651820310001153 | PMID = 18332967 }}</ref> | |||
{{Main|Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas}} | |||
=== | ==Pancreatoblastoma== | ||
{{Main|Pancreatoblastoma}} | |||
== | =See also= | ||
* | *[[Duodenum]]. | ||
*[[Gallbladder]]. | |||
*[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | |||
*[[Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome]]. | |||
*[[IgG4-related systemic disease]]. | |||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
== | |||
== | ==Further reading== | ||
{{Cite journal | last1 = Klimstra | first1 = DS. | last2 = Pitman | first2 = MB. | last3 = Hruban | first3 = RH. | title = An algorithmic approach to the diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 133 | issue = 3 | pages = 454-64 | month = Mar | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1043/1543-2165-133.3.454 | PMID = 19260750 }} | |||
=== | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|10 | |||
| | |||
=External links= | |||
*[http://pancreaticcancer2000.com/page1.htm Pancreatic cancer - PanINs - pancreaticcancer2000.com]. | *[http://pancreaticcancer2000.com/page1.htm Pancreatic cancer - PanINs - pancreaticcancer2000.com]. | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:19, 7 December 2020
The pancreas hangs-out in the upper abdomen. It occasionally is afflicited by cancers, the most common of which is very fatal.
Pancreatic cytopathology is dealt with in the gastrointestinal cytopathology article.
A general introduction to gastrointestinal pathology is in the gastrointestinal pathology article.
Introduction
Normal anatomy
Divided into three portions: head, body & tail:[1]
- Head:
- Includes unicate process.
- Extends to the left edge of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) - by definition.
- All of the SMV is with the head.
- Body:
- Right edge of the superior mesenteric vein to the left edge of aorta - by definition.
- All of the aorta is with the body.
- Right edge of the superior mesenteric vein to the left edge of aorta - by definition.
- Tail:
- Remainder of pancreas.
Pancreatic surgeries
Common pancreatic surgeries include:
- Whipple procedure (AKA pancreaticoduodenal resection) - includes duodenum and usually the distal stomach (antrum).
- Distal pancreatectomy.
- Removal of tail +/- body.
- Specimen usually comes with the spleen.
- Typically done form islet cell tumours.
- Total pancreatectomy.
- Specimen usually comes with the spleen.
Whipple procedure
- AKA pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Indications:
- Head of pancreas lesions, duodenal lesions.
- Proximal mucosal margin (stomach or duodenum).
- Distal mucosal margin (duodenum or jejunum).
- Bile duct margin.
- Pancreatic retroperitoneal (uncinate process) margin.
- At SB done on edge (not en face).
- Pancreatic neck transection margin (AKA distal pancreatic resection margin);[3] usu. en face and in toto.[4]
- Sometimes superior mesenteric vein (SMV).
- Rarely superior mesenteric artery (SMA) margin.
- Open the proximal (stomach) and distal (small bowel) stappled margins.
- Open the duodenum along it length on the anterior aspect.
- Open the stomach along the greater curvature.
- Join the cuts that open the stomach and duodenum.
General classification of pancreatic tumours
- Metstatses.
- Most common = renal cell carcinoma.
- Primary.
- Endocrine.
- Usually small as hormonally active.
- Exocrine.
- Endocrine.
Pancreas neoplasms in a table
| Type | Key feature | Subtypes | Image | IHC | Detailed microscopic | Usual location | Other | DDx |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serous tumours | cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm | cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | [1], (WC), (WC) | IHC? | cuboidal cells, clear cytoplasm, central nucleus | body or tail | cystadenoma may be assoc. with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome | clear cell RCC, oligomucinous mucinous tumours |
| Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour (IPMT) | mucin, no ovarian-like stroma | clear cell variant | (wjso.com), (upmc.edu) | IHC? | papillae, tall columnar mucin-producing cells | head | - | mucious neoplasms (other pancreatic, duodenal), intra-ampullary papillary-tubular neoplasm (see ampullary carcinoma) |
| Mucinous tumour | mucin, ovarian-like stroma | cystadenoma, borderline t., cystadenocarcinoma | (WC), (WC) | IHC? | tall columnar mucin-producing cells, ovarian-like stroma | body or tail | - | IPMT, metastatic mucinous tumours |
| Solid pseudopapillary tumour |
eosinophilic intracytoplasmic globules | clear cell variant (cytoplasm clear) | (WC), (bmj.com) | beta-catenin +ve, E-cadherin +ve, synaptophysin +ve, chromogranin -ve |
sheets of cells, focally loosely cohesive, eosinophilic cytoplasm, uniform nuclei with grooves | none (head, body or tail) | usu. younger women | ductal adenocarcinoma, neuroendocrine tumours |
| Ductal adenocarcinoma | irregular shaped glands, cytologic atypia | mucinous, spindle cell, mixed ductal-endocrine | (WC), (WC) | IHC? | glands, sheets, single cells, nuc. atypia, +/-mitoses, +/-necrosis | head | arises from the precursor PanIN | ampullary carcinoma, chronic pancreatitis |
| Pancreatoblastoma | squamoid nests, whorling | - | (nature.com) | CK7 (acinar comp.), CK8, CK18, CK19 | squamoid nests of cells, whorling, nested growth, +/-keratinization | none | usu. paediatric population | acinar cell carcinoma |
| Acinar cell carcinoma | acinar arch. | - | (WC), (histopathology-india.net) | trypsin, lipase | nests or trabeculae, nucleolus, mod. basophilic granular cytoplasm | head (slight predilection) | - | pancreatoblastoma |
| Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells | giant cells | - | Image? | IHC? | giant cells, usu. with AIS or inv. ductal adenocarcinoma | head | - | anaplastic carcinoma |
| Chronic pancreatitis | fibrosis, loss of acinar tissue, preservation of lobular arch. | - | [2] | IHC? | loss of acinar tissue with preservation of islets, fibrosis | ? | not a neoplasm, included here as it is in the (clinical) DDx | ductal adenocarcinoma |
WHO classification
Benign epithelial:
Borderline epithelial:
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm with moderate dysplasia.
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with moderate dysplasia.
- Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm
Malignant epithelial:
- Ductal adenocarcinoma.
- Mucinous noncystic carcinoma.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma.
- Adenosquamous carcinoma.
- Undifferentiated carcinoma.
- Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells.
- Mixed ductal-endocrine carcinoma.
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma.
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
- Invasive.
- Noninvasive.
- Intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma.
- Invasive.
- Noninvasive.
- Acinar cell carcinoma.
- Pancreatoblastoma.
- Solid pseudopapillary carcinoma.
Soft tissue tumours:
- See soft tissue lesions.
Ectopic pancreatic tissue
It comes in two flavours:[5]
- Pancreatic ectopia.
- Pancreatic (acinar) metaplasia.
Pancreatic acinar metaplasia
General
- Common in the GI tract.
- Found in ~ 17-19% of gastroesophageal junction biopsies.[7][8]
- Associated with intestinal metaplasia.[7]
- Not associated with changes of GERD, or Helicobacter gastritis.[7]
Gross
- May be a single lesion or a cluster of lesions.[6]
Note:
- Not associated with the endoscopic diagnosis of esophagitis or Barrett's esophagus.[7]
Microscopic
Features:
- Pancreatic acini - only.
- Intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Negatives:
- No pancreatic ducts.
- No islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets).
Images
IHC
Features:[9]
- Trypase +ve.
- Lipase +ve.
Sign out
It can be debated whether it is worth reporting.
ESOPHAGUS (DISTAL), BIOPSY: - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH MODERATE CHRONIC, FOCALLY ACTIVE, INFLAMMATION, AND PANCREATIC ACINAR METAPLASIA. - REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. - NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Pancreatic ectopia
General
- May be confused with something pathologic.
Microscopic
Features:
- Consists of pancreatic acini and pancreatic ducts.
- +/-Islets of Langerhans.
Inflammatory
Pancreatitis
Classification
Etiology
Mnemonic I GET SMASHED:
- Idiopathic.
- Gallstones ~45%.
- Ethanol ~35%.
- Tumours (pancreas, ampulla).
- Scorpion bites, snake bites.
- Microbial - mumps (paramyxovirus), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), mycoplasma.
- Autoimmune - Crohn's disease, polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- Surgery/trauma, e.g. ERCP, motor vehicle collision.
- Hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia/hypertriglyceridemia, hypothermia.
- Emboli, e.g. post-CABG.
- Drugs - SAND = steroids & sulfonamides, azathioprine, NSAIDs, diuretics, such as furosemide.
Acute pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
Cystic lesions - overview
General
- True cystic lesions are uncommon.
- A true cystic lesion: must have an epithelial lining.
- Only 10% of cystic lesions are true cystic lesions, i.e. 90% of cystic lesions are really pseudocysts.
- A true cystic lesion: must have an epithelial lining.
- It is hard to differentiate pseudocysts & cysts.
Cystic tumours - clinical
General:
- Usually diagnosed by imaging (CT/MRI, ERCP, Endoscopic ultrasound).
- 50% incidental finding.
- Vague symptoms
- Abdominal mass.
- Weight loss.
- Jaundice.
- Usually favourable prognosis - mostly benign.
Most important cystic lesions
- Serous.
- Mucinous.
- Ovarian-like stroma.
- Solid pseudopapillay tumours.
- Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour (IPMT).
- No ovarian-like stroma.
Mnemonic SIMS: Serous, IPMT, Mucinous, Solid pseudopapillary tumour.
Useful stains
- PAS-D.
Mucinous vs. IMPT
IMPT:
- No ovarian-like stroma.
- Usually has total pancreatectomy.
Cystic tumours of the pancreas
Khalifa's table of cystic tumours:
| Tumour | Usual sex | Age (years) | Usual site | Typical size (cm) |
Gross pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serous microcystic adenoma |
female | 66 | body & tail | 11 | (joplink.net[10], (jhmi.edu)[11] |
| Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour (IPMT) |
male | 62 | head | 4 | (jhmi.edu)[11] |
| Mucinous tumour | female | 49 | body & tail | 10 | (rsna.org) |
| Solid pseudopapillary tumour |
female | 35 | any | 7.5 | (ajronline.org), (flickr.com/humpath) |
Cystic lesions
Serous tumours - overview
General
- Cell of origin: intralobular duct cells (ductular cells).
- Glycogen rich - but do not produce mucin.
Subclassication
- Serous microcystic adenoma (AKA serous cystadenoma[12]).
- Many small cysts.
- Serous oligocystic adenoma.
- Large cysts.
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma - very rare.[13]
Note:
- If one mucin +ve cell, tumour = a mucinous tumour.
Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas
Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas
- Gastro-entero-pancreatic cell differentiation with hypercellular ovarian-type stroma.
- Stroma --> cellular.
- 2-2.5% of all exocrine pancreatic tumours.
- Almost exclusively in women.
- Mean age - 49 years.
- >80% in body and tail.
- Average size ~10 cm.
Note:
- Looks different than serous tumour.
Subclassification
- Mucinous cystadenoma.
- Borderline mucinous cystic tumour.
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
Borderline vs. Carcinoma
- Few mitoses in borderline.
Radiology
- Mucinous tumours: multilocular.
- Generally larger than serous.
- Often partially solid and cystic.
- Often calcified.
- Calcification rare in serous.
- Usually tail & body.
Microscopic
Mucinous cystadenoma
Features:[14]
- Simple tall columnar epithelium with large mucin vacuole on apical aspect.
- "Ovarian-type stroma" under epithelium.
- Ovarin-type stroma: high density of small (non-wavy) spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Notes:
- Appearance similar to mucinous cystadenoma in the ovary.
- Mucin stains +ve (intracytoplasmic).
Images
www:
Benign mucinous cystic neoplasm of pancreas in a 62 year old woman. A. CT scan showed a peripherally calcified spheroidal mass at the tail of the pancreas. Cytology only showed debris and inflammatory cells, but CEA of the fluid was 2875.2 ng/mL. B. Almost all sections of the cyst showed acellular debris topping a fibrous, often calcified wall, consistent with a pseudocyst. C. Extensive sampling, undertaken because of the high CEA, revealed rare sections with a lining. D. Lining nuclei are bland, with even chromatin. Shape and size variation, as well as darkening when shrunken, are all explicable by degeneration. E. Within distal pancreas, a focus of changes of chronic pancreatitis is seen upper left, while a pancreatic duct in lower right shows an intraductal proliferation. F. Tumor cells show mucinous vacuoles, with better preserved nuclei. Nuclear appearances remain bland. G. Cellular ovarian stroma appeared beneath epithelium of a separate focus of the cystic neoplasm.
Borderline mucinous cystic tumour
Features:
- May have finger like projections.
- Pseudostratification of epithelium.
Notes:
- Surgery does not change based on diagnosis on frozen section.
- Only question is "Is the margin clear?".
- Borderline tumours are rare.
Carcinoma
- Cells floating in mucin.
Mucinous tumour versus pseudocyst
| Finding | Mucinous tumour | Pseudocyst |
|---|---|---|
| Amylase & lipase | low | high |
| Viscosity | high | low |
| CEA, CA125 | high | low |
Prognosis:
- Benign looking tumours have the potential to transform into carcinoma.
- No report of assoc. pseudomyxoma peritonei.
- US boards question -- it is an exception ... others one cause it.
- Prognosis of m. cystadenocarcinoma is slightly better than that of ductal adenocarcinoma.
Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour
- Abbreviated IPMT.
- AKA intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, abbreviated IPMN.
Solid pseudopapillary tumour
- AKA solid pseudopapillary neoplasm, abbreviation SPN.
- AKA solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm, abbreviated SPEN.[15]
Pre-malignant lesions
Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- Abbreviated PanIN.
Solid tumours
Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour
- Abbreviated PanNET.[16]
- AKA pancreatic islet cell tumour[16] - considered to be an outdated term.
- AKA islet cell tumour - considered to be an outdated term.
Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas
- Not to be confused with acinic cell carcinoma.
Pancreatoblastoma
See also
- Duodenum.
- Gallbladder.
- Gastrointestinal pathology.
- Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
- IgG4-related systemic disease.
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.
- ↑ Jamieson, NB.; Foulis, AK.; Oien, KA.; Going, JJ.; Glen, P.; Dickson, EJ.; Imrie, CW.; McKay, CJ. et al. (Jun 2010). "Positive mobilization margins alone do not influence survival following pancreatico-duodenectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.". Ann Surg 251 (6): 1003-10. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d77369. PMID 20485150.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/PancreasEndo_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 6 April 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://test.pathologyportal.org/newindex.htm?92nd/specgasth2.htm. Accessed on: 14 March 2011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Stachura, J.; Konturek, JW.; Urbanczyk, K.; Bogdal, J.; Mach, T.; Domschke, W. (Mar 1996). "Endoscopic and histological appearance of pancreatic metaplasia in the human gastric mucosa: a preliminary report on a recently recognized new type of gastric mucosal metaplasia.". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 8 (3): 239-43. PMID 8724024.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Schneider, NI.; Plieschnegger, W.; Geppert, M.; Wigginghaus, B.; Höss, GM.; Eherer, A.; Wolf, EM.; Rehak, P. et al. (Aug 2013). "Pancreatic acinar cells-a normal finding at the gastroesophageal junction? Data from a prospective Central European multicenter study.". Virchows Arch. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1471-8. PMID 23989798.
- ↑ Johansson J, Håkansson HO, Mellblom L, et al. (March 2010). "Pancreatic acinar metaplasia in the distal oesophagus and the gastric cardia: prevalence, predictors and relation to GORD". J. Gastroenterol. 45 (3): 291–9. doi:10.1007/s00535-009-0161-4. PMID 20012917.
- ↑ Doglioni, C.; Laurino, L.; Dei Tos, AP.; De Boni, M.; Franzin, G.; Braidotti, P.; Viale, G. (Nov 1993). "Pancreatic (acinar) metaplasia of the gastric mucosa. Histology, ultrastructure, immunocytochemistry, and clinicopathologic correlations of 101 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 17 (11): 1134-43. PMID 8214258.
- ↑ URL: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/25.html. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 URL: http://oac.med.jhmi.edu/cpc/cases/cpc5/cpc5_answer.html. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1630. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ Bano, S.; Upreti, L.; Puri, SK.; Chaudhary, V.; Sakuja, P. (Dec 2011). "Imaging of pancreatic serous cystadenocarcinoma.". Jpn J Radiol 29 (10): 730-4. doi:10.1007/s11604-011-0617-3. PMID 22009426.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 489. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ URL: http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/360/full.html. Accessed on: 31 October 2011.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Burns, WR.; Edil, BH. (Dec 2011). "Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Tumors: Guidelines for Management and Update.". Curr Treat Options Oncol. doi:10.1007/s11864-011-0172-2. PMID 22198808.
- ↑ Thomas, PC.; Nash, GF.; Aldridge, MC. (2003). "Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma presenting as acute pancreatitis.". HPB (Oxford) 5 (2): 111-3. doi:10.1080/13651820310001153. PMID 18332967.
Further reading
Klimstra, DS.; Pitman, MB.; Hruban, RH. (Mar 2009). "An algorithmic approach to the diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 133 (3): 454-64. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-133.3.454. PMID 19260750.