Difference between revisions of "Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(more tumours) |
(change tumour to cyst again (KOT was renamed to odontogenic keratocyst)) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
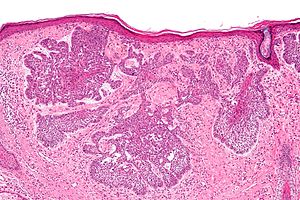
'''Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome''', also '''Gorlin syndrome''' and '''Gorlin-Goltz syndrome''', is a constellation of findings due to an autosomal dominant genetic mutation. | [[Image:Basal_cell_carcinoma_-_2_-_intermed_mag.jpg|thumb|right|Basal cell carcinoma, a component of NBCCS. [[H&E stain]].]] | ||
'''Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome''', also '''Gorlin syndrome''' and '''Gorlin-Goltz syndrome''', is a constellation of findings due to an autosomal dominant genetic mutation. The gene is ''patched'' and abbreviated ''PTCH1''.<ref name=omim601309>{{OMIM|601309}}</ref> | |||
It is abbreviated '''NBCCS'''. | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_Derm435>{{Ref Derm|435}}</ref> | Features:<ref name=Ref_Derm435>{{Ref Derm|435}}</ref> | ||
*[[Basal cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Basal cell carcinoma]] - on average have their first tumour in their 20s.<ref name=pmid9096761>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kimonis | first1 = VE. | last2 = Goldstein | first2 = AM. | last3 = Pastakia | first3 = B. | last4 = Yang | first4 = ML. | last5 = Kase | first5 = R. | last6 = DiGiovanna | first6 = JJ. | last7 = Bale | first7 = AE. | last8 = Bale | first8 = SJ. | title = Clinical manifestations in 105 persons with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. | journal = Am J Med Genet | volume = 69 | issue = 3 | pages = 299-308 | month = Mar | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9096761 }}</ref> | ||
*[[ | *[[Odontogenic keratocyst]] ~ 80% individuals with NBCCS have had one by age 20.<ref name=pmid9096761/> | ||
*Bony abnormalities: bifid ribs, scoliosis + others. | *Bony abnormalities: bifid ribs, scoliosis + others. | ||
*Falx cerebri calcification. | *Falx cerebri calcification. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 12: | ||
*[[Medulloblastoma]].<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1181>{{Ref PBoD8|1181}}</ref> | *[[Medulloblastoma]].<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1181>{{Ref PBoD8|1181}}</ref> | ||
*[[Ovarian fibroma]].<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1181>{{Ref PBoD8|1181}}</ref> | *[[Ovarian fibroma]].<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1181>{{Ref PBoD8|1181}}</ref> | ||
Images: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case109/micro.html NBCCS (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 26 May 2022

Basal cell carcinoma, a component of NBCCS. H&E stain.
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, also Gorlin syndrome and Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, is a constellation of findings due to an autosomal dominant genetic mutation. The gene is patched and abbreviated PTCH1.[1]
It is abbreviated NBCCS.
Features:[2]
- Basal cell carcinoma - on average have their first tumour in their 20s.[3]
- Odontogenic keratocyst ~ 80% individuals with NBCCS have had one by age 20.[3]
- Bony abnormalities: bifid ribs, scoliosis + others.
- Falx cerebri calcification.
- Characteristic faces.
- Medulloblastoma.[4]
- Ovarian fibroma.[4]
Images:
See also
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 601309
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 435. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kimonis, VE.; Goldstein, AM.; Pastakia, B.; Yang, ML.; Kase, R.; DiGiovanna, JJ.; Bale, AE.; Bale, SJ. (Mar 1997). "Clinical manifestations in 105 persons with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.". Am J Med Genet 69 (3): 299-308. PMID 9096761.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1181. ISBN 978-1416031215.