Difference between revisions of "Zenker's diverticulum"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum -- low mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Consistent with Zenker's diverticulum (squamous mucosa). [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = cricopharyngeal diverticulum, pharyngoesophageal diverticulum and hypopharyngeal diverticulum | |||
| Micro = squamous mucosa without [[nuclear atypia]] +/- parakeratosis | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[squamous dysplasia of the esophagus]], [[squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus]], [[squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Staging = | |||
| Site = [[esophagus]]/pharynx | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = elderly | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = dysphagia | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = excision | |||
}} | |||
'''Zenker's diverticulum''' is an outpouching of the mucosa and submucosa at the junction of the pharynx and [[esophagus]]. | '''Zenker's diverticulum''' is an outpouching of the mucosa and submucosa at the junction of the pharynx and [[esophagus]]. | ||
It is also known as '''diverticulum | It is also known as '''cricopharyngeal diverticulum''', '''pharyngoesophageal diverticulum''' and '''hypopharyngeal diverticulum'''.<ref name=pmid25759630>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nuño-Guzmán | first1 = CM. | last2 = García-Carrasco | first2 = D. | last3 = Haro | first3 = M. | last4 = Arróniz-Jáuregui | first4 = J. | last5 = Corona | first5 = JL. | last6 = Salcido | first6 = M. | title = Zenker's Diverticulum: Diagnostic Approach and Surgical Management. | journal = Case Rep Gastroenterol | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 346-52 | month = | year = | doi = 10.1159/000369130 | PMID = 25759630 }}</ref> | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*[[Clinical diagnosis]]. | *[[Clinical diagnosis]]. | ||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
**[[ | **A malignancy ([[squamous cell carcinoma]]) may arise from it;<ref name=pmid26415863>{{Cite journal | last1 = Acar | first1 = T. | last2 = Savaş | first2 = R. | last3 = Kocaçelebi | first3 = K. | last4 = Ersöz | first4 = G. | title = Squamous cell carcinoma arising from a Zenker's diverticulum: contribution of FDG-PET/CT to the diagnosis. | journal = Dis Esophagus | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Sep | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1111/dote.12406 | PMID = 26415863 }}</ref><ref name=pmid22940699>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wakita | first1 = A. | last2 = Motoyama | first2 = S. | last3 = Sato | first3 = Y. | last4 = Yoshino | first4 = K. | last5 = Sasaki | first5 = T. | last6 = Saito | first6 = H. | last7 = Minamiya | first7 = Y. | last8 = Ogawa | first8 = J. | title = Squamous cell carcinoma in an esophageal diverticulum below the aortic arch. | journal = Int J Surg Case Rep | volume = 3 | issue = 11 | pages = 574-6 | month = | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.07.010 | PMID = 22940699 }}</ref> seen in ~0.3% of cases.<ref>{{Ref GLP|7}}</ref> | ||
* | *Relatively uncommon<ref name=pmid24055983/> - but most common among esophageal diverticula.<ref>{{Ref GLP|6}}</ref> | ||
Clinical:<ref name=pmid24055983>{{Cite journal | last1 = Law | first1 = R. | last2 = Katzka | first2 = DA. | last3 = Baron | first3 = TH. | title = Zenker's Diverticulum. | journal = Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 12 | issue = 11 | pages = 1773-82; quiz e111-2 | month = Nov | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.016 | PMID = 24055983 }}</ref> | Clinical:<ref name=pmid24055983>{{Cite journal | last1 = Law | first1 = R. | last2 = Katzka | first2 = DA. | last3 = Baron | first3 = TH. | title = Zenker's Diverticulum. | journal = Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 12 | issue = 11 | pages = 1773-82; quiz e111-2 | month = Nov | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.016 | PMID = 24055983 }}</ref> | ||
*Eldery. | *Eldery. | ||
*Dysphagia. | *Dysphagia - difficultly swallowing. | ||
*May mimic a [[thyroid gland|thyroid]] nodule.<ref name=pmid20665743>{{Cite journal | last1 = Singaporewalla | first1 = RM. | last2 = Mukherjee | first2 = JJ. | last3 = Thamboo | first3 = TP. | last4 = Cheah | first4 = WK. | title = Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum resembling a thyroid nodule on ultrasound. | journal = Head Neck | volume = 33 | issue = 12 | pages = 1800-3 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/hed.21474 | PMID = 20665743 }}</ref> | |||
*+/-Aspiration of food. | *+/-Aspiration of food. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 54: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features:<ref name=pmid20665743>{{Cite journal | last1 = Singaporewalla | first1 = RM. | last2 = Mukherjee | first2 = JJ. | last3 = Thamboo | first3 = TP. | last4 = Cheah | first4 = WK. | title = Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum resembling a thyroid nodule on ultrasound. | journal = Head Neck | volume = 33 | issue = 12 | pages = 1800-3 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/hed.21474 | PMID = 20665743 }}</ref> | ||
*Squamous mucosa. | *Squamous mucosa without [[nuclear atypia]] +/- parakeratosis. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Squamous dysplasia of the esophagus]]. | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus]]. | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
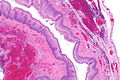
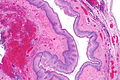
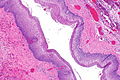
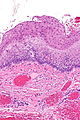
Image: Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum -- very low mag.jpg | ZD - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum - alt -- very low mag.jpg | ZD - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum -- low mag.jpg | ZD - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum -- intermed mag.jpg | ZD - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
Submitted as "Zenker's Diverticulum", Excision: | |||
- Squamous mucosa with parakeratosis, mild chronic inflammation | |||
and fibrosis; compatible with Zenker's diverticulum. | |||
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Alternate=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Submitted as "Zenker's Diverticulum", Excision: | |||
- Squamous mucosa with mild chronic inflammation and reactive | |||
changes; compatible with Zenker's diverticulum. | |||
- Benign skeletal muscle. | |||
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 21 January 2016
| Zenker's diverticulum | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Consistent with Zenker's diverticulum (squamous mucosa). H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | cricopharyngeal diverticulum, pharyngoesophageal diverticulum and hypopharyngeal diverticulum |
|
| |
| LM | squamous mucosa without nuclear atypia +/- parakeratosis |
| LM DDx | squamous dysplasia of the esophagus, squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck |
| Site | esophagus/pharynx |
|
| |
| Clinical history | elderly |
| Symptoms | dysphagia |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | excision |
Zenker's diverticulum is an outpouching of the mucosa and submucosa at the junction of the pharynx and esophagus.
It is also known as cricopharyngeal diverticulum, pharyngoesophageal diverticulum and hypopharyngeal diverticulum.[1]
General
- Clinical diagnosis.
- Benign.
- A malignancy (squamous cell carcinoma) may arise from it;[2][3] seen in ~0.3% of cases.[4]
- Relatively uncommon[5] - but most common among esophageal diverticula.[6]
Clinical:[5]
Gross
Images
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Squamous mucosa without nuclear atypia +/- parakeratosis.
DDx:
- Squamous dysplasia of the esophagus.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Images
Sign out
Submitted as "Zenker's Diverticulum", Excision: - Squamous mucosa with parakeratosis, mild chronic inflammation and fibrosis; compatible with Zenker's diverticulum. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Alternate
Submitted as "Zenker's Diverticulum", Excision: - Squamous mucosa with mild chronic inflammation and reactive changes; compatible with Zenker's diverticulum. - Benign skeletal muscle. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
See also
References
- ↑ Nuño-Guzmán, CM.; García-Carrasco, D.; Haro, M.; Arróniz-Jáuregui, J.; Corona, JL.; Salcido, M.. "Zenker's Diverticulum: Diagnostic Approach and Surgical Management.". Case Rep Gastroenterol 8 (3): 346-52. doi:10.1159/000369130. PMID 25759630.
- ↑ Acar, T.; Savaş, R.; Kocaçelebi, K.; Ersöz, G. (Sep 2015). "Squamous cell carcinoma arising from a Zenker's diverticulum: contribution of FDG-PET/CT to the diagnosis.". Dis Esophagus. doi:10.1111/dote.12406. PMID 26415863.
- ↑ Wakita, A.; Motoyama, S.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, K.; Sasaki, T.; Saito, H.; Minamiya, Y.; Ogawa, J. (2012). "Squamous cell carcinoma in an esophageal diverticulum below the aortic arch.". Int J Surg Case Rep 3 (11): 574-6. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.07.010. PMID 22940699.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 7. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Law, R.; Katzka, DA.; Baron, TH. (Nov 2014). "Zenker's Diverticulum.". Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 12 (11): 1773-82; quiz e111-2. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.016. PMID 24055983.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 6. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Singaporewalla, RM.; Mukherjee, JJ.; Thamboo, TP.; Cheah, WK. (Dec 2011). "Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum resembling a thyroid nodule on ultrasound.". Head Neck 33 (12): 1800-3. doi:10.1002/hed.21474. PMID 20665743.