Difference between revisions of "Primary sclerosing cholangitis"
(→Images) |
(→Images: Added a case) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
*[http://www.onmedica.com/getresource.aspx?resourceid=e398a3f2-e030-40e6-823b-2e8e2cbbe4bb PSC (onmedica.com)].<ref>URL: [http://www.onmedica.com/NewsArticle.aspx?id=d7f992b5-6dee-46c6-8383-bbdfb4528ccc http://www.onmedica.com/NewsArticle.aspx?id=d7f992b5-6dee-46c6-8383-bbdfb4528ccc]. Accessed on: 1 January 2011.</ref> | *[http://www.onmedica.com/getresource.aspx?resourceid=e398a3f2-e030-40e6-823b-2e8e2cbbe4bb PSC (onmedica.com)].<ref>URL: [http://www.onmedica.com/NewsArticle.aspx?id=d7f992b5-6dee-46c6-8383-bbdfb4528ccc http://www.onmedica.com/NewsArticle.aspx?id=d7f992b5-6dee-46c6-8383-bbdfb4528ccc]. Accessed on: 1 January 2011.</ref> | ||
*[http://www.nature.com/nrgastro/journal/v7/n11/fig_tab/nrgastro.2010.155_F2.html PSC (nature.com)].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mendes | first1 = F. | last2 = Lindor | first2 = KD. | title = Primary sclerosing cholangitis: overview and update. | journal = Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 7 | issue = 11 | pages = 611-9 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.155 | PMID = 20938459 }}</ref> | *[http://www.nature.com/nrgastro/journal/v7/n11/fig_tab/nrgastro.2010.155_F2.html PSC (nature.com)].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mendes | first1 = F. | last2 = Lindor | first2 = KD. | title = Primary sclerosing cholangitis: overview and update. | journal = Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 7 | issue = 11 | pages = 611-9 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.155 | PMID = 20938459 }}</ref> | ||
{| | |||
[[File:1 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
[[File:2 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:3 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
[[File:4 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:5 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
[[File:6 PSC 1 680x512px.tif| Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.]] | |||
|} | |||
<br>Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis. <br>Low power shows inflamed bands [green arrows] and a rare scar at the edge of a triad [black arrow] (Row 1 Left 40X). A triad with a characteristic periductal fibrosis [black arrows] is seen (Row 1 Right 200X). Reticulin shows the space about the duct [green arrows], as well as some foci of piecemeal necrosis [blue arrows] (Row 2 Left 200X). Trichrome shows fibrous bridges [black arrows] (Row 2 Right 200X). Damage to bile ducts is seen by peripheral proliferated bile ductules [green arrows] with neutrophils [blue arrows] (Row 3 Left 400X). Also seen is a small periportal bile infarct with necrotic hepatocyte nuclei [black arrows] (Row 3 Right 400X). | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:21, 11 September 2016
Primary sclerosing cholangitis, abbreviated PSC, is an uncommon medical liver disease that can afflicts the young and old, and is often associated with ulcerative colitis.
Pericholangitis is considered a synonym for small duct PSC.[1]
General
- Strongly associated with ulcerative colitis; 75-90% of PSC patients have inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).[2]
- Risk for cholangiocarcinoma.[3]
Serology:
- p-ANCA (MPO-ANCA) +ve in ~ 90% of cases.[4]
Diagnosis
- Diagnosed radiologically.
- Classically described as a chain of lakes.
- Liver biopsy is rarely useful diagnostically[5] - as the disease may be patchy.
- The utility of the biopsy is staging.
Treatment
- None very good.
- May be indication for transplant.
Microscopic
Features:
- Classic: "onion-skinning" - cells layer around the bile ducts; "onion skin" present in approx. 40% of cases.[6]
- Not pathognomonic for PSC[6] - but not too much else looks like this on microscopy (ergo good fellowship exam question).
- +/-Ductopenia.
- +/-Ductal proliferation.
Notes:
- PSC often has minimal inflammation.[7]
DDx:
- IgG4-associated cholangitis - see IgG4-related disease.[8]
- Others.
Staging
Features:[9]
- Stage I - focal portal inflammation, +/- duct abnormalities, no fibrosis.
- Stage II - portal enlargement (fibrosis), +/- inflammation.
- Stage III - bridging fibrosis + necrosis.
- Stage IV - cirrhosis.
Notes:
- Similar to PBC staging.
Images
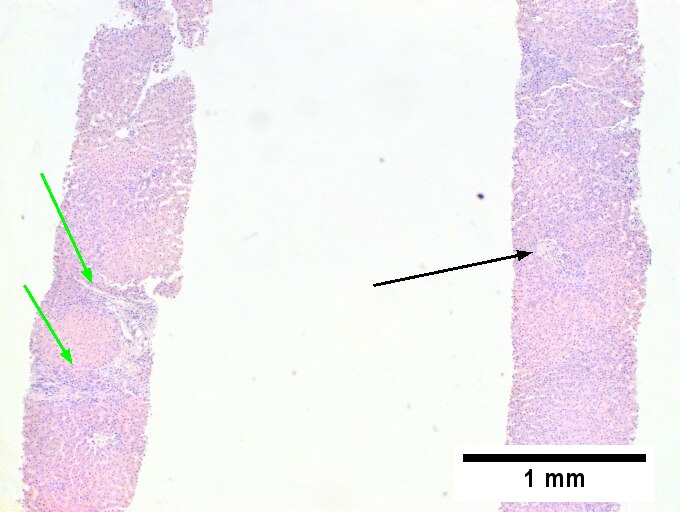
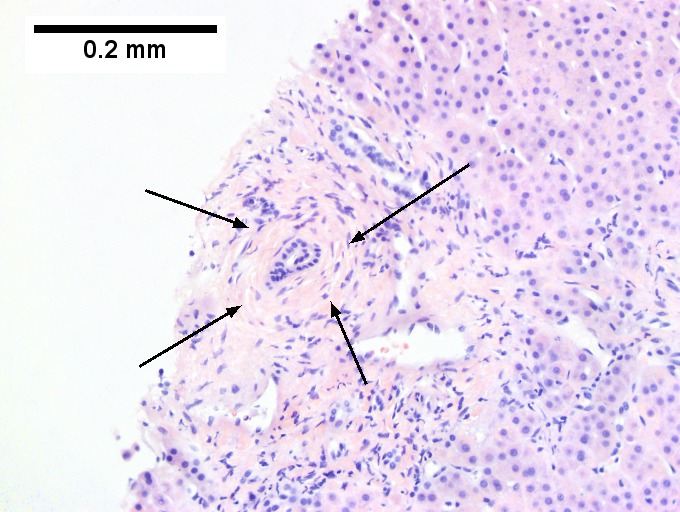
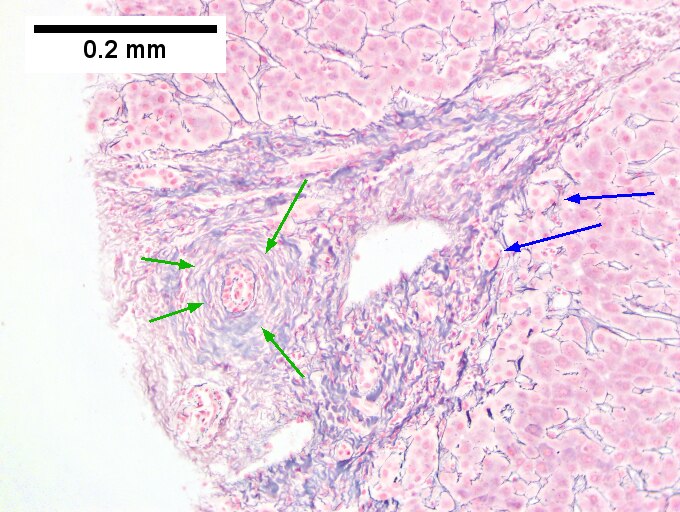
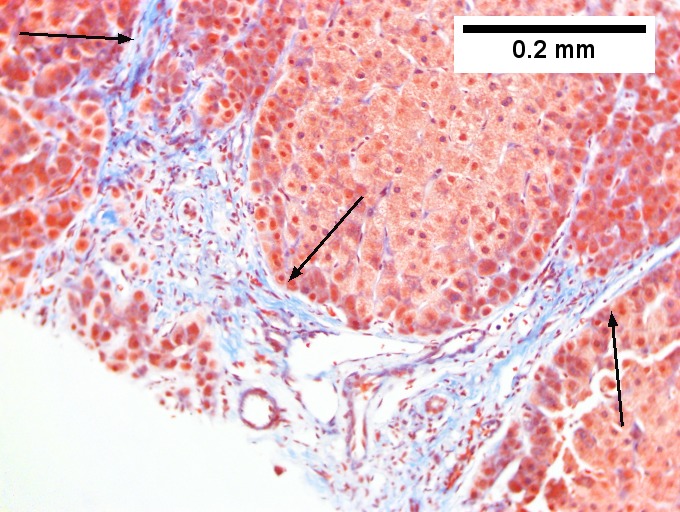
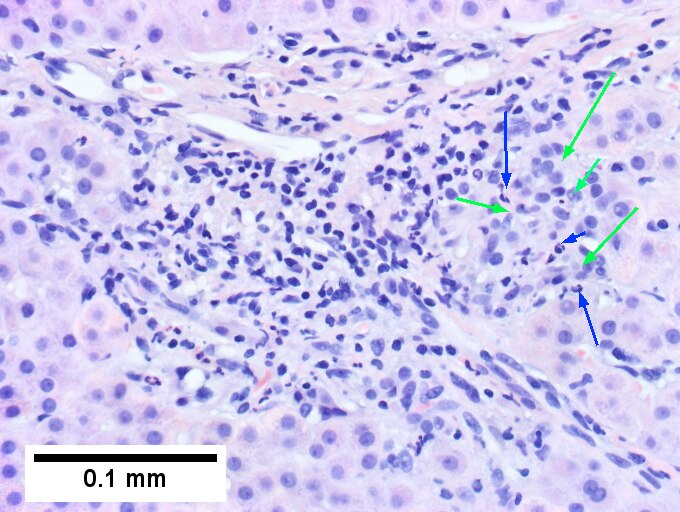
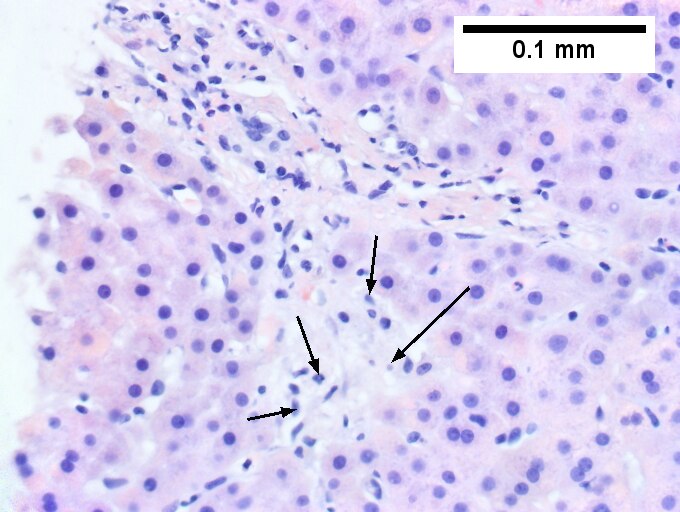
Primary sclerosing cholangitis in patient with history of ulcerative colitis.
Low power shows inflamed bands [green arrows] and a rare scar at the edge of a triad [black arrow] (Row 1 Left 40X). A triad with a characteristic periductal fibrosis [black arrows] is seen (Row 1 Right 200X). Reticulin shows the space about the duct [green arrows], as well as some foci of piecemeal necrosis [blue arrows] (Row 2 Left 200X). Trichrome shows fibrous bridges [black arrows] (Row 2 Right 200X). Damage to bile ducts is seen by peripheral proliferated bile ductules [green arrows] with neutrophils [blue arrows] (Row 3 Left 400X). Also seen is a small periportal bile infarct with necrotic hepatocyte nuclei [black arrows] (Row 3 Right 400X).
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/181889-overview. Accessed on: 25 January 2012.
- ↑ Khurana V, Singh T. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. eMedicine.com. URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/187724-overview. Accessed on: 29 November 2009.
- ↑ Jesudian, AB.; Jacobson, IM. (2009). "Screening and diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis.". Rev Gastroenterol Disord 9 (2): E41-7. PMID 19668124.
- ↑ Terjung, B.; Worman, HJ. (Aug 2001). "Anti-neutrophil antibodies in primary sclerosing cholangitis.". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 15 (4): 629-42. doi:10.1053/bega.2001.0209. PMID 11492972.
- ↑ Khurana V, Singh T. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. eMedicine.com. URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/187724-diagnosis. Accessed on: 29 November 2009.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Steele et al. URL: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/552500_6. Accessed on: 29 November 2009.
- ↑ STC. 9 December 2010.
- ↑ Deshpande, V.; Sainani, NI.; Chung, RT.; Pratt, DS.; Mentha, G.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Lauwers, GY. (Oct 2009). "IgG4-associated cholangitis: a comparative histological and immunophenotypic study with primary sclerosing cholangitis on liver biopsy material.". Mod Pathol 22 (10): 1287-95. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.94. PMID 19633647.
- ↑ Steele et al. URL: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/552500_6. Accessed on: 29 November 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://trialx.com/curebyte/2011/07/08/clinical-trials-and-images-of-primary-sclerosing-cholangitis/. Accessed on: 1 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.onmedica.com/NewsArticle.aspx?id=d7f992b5-6dee-46c6-8383-bbdfb4528ccc. Accessed on: 1 January 2011.
- ↑ Mendes, F.; Lindor, KD. (Nov 2010). "Primary sclerosing cholangitis: overview and update.". Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7 (11): 611-9. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.155. PMID 20938459.