Difference between revisions of "Metaphyseal fibrous defect"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→External links: fix) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| EHVSC_mult = | | EHVSC_mult = | ||
| pathprotocols = | | pathprotocols = | ||
| wikipedia = | | wikipedia = Nonossifying fibroma | ||
| pathoutlines = {{Pathologyoutlines|topic/bonemetaphysealfibrousdefect}} | | pathoutlines = {{Pathologyoutlines|topic/bonemetaphysealfibrousdefect}} | ||
| rosaicollection = | | rosaicollection = | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
*Often small lesions discovered as an radiographic incidentaloma. | *Often small lesions discovered as an radiographic incidentaloma. | ||
*Rarely seen as a pathologic specimen (should not be biopsied). | *Rarely seen as a pathologic specimen (should not be biopsied). | ||
*May be seen in the context of ''Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome''.<ref>URL: [http://www.bonetumor.org/plasma-cell-tumors/jaffe-campanacci-syndrome http://www.bonetumor.org/plasma-cell-tumors/jaffe-campanacci-syndrome]. Accessed on: October 14, 2014.</ref> | *May be seen in the context of ''Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome'' which may be a presentation of Neurofibromatosis Type 1.<ref>URL: [http://www.bonetumor.org/plasma-cell-tumors/jaffe-campanacci-syndrome http://www.bonetumor.org/plasma-cell-tumors/jaffe-campanacci-syndrome]. Accessed on: October 14, 2014.</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stewart | first1 = DR. | last2 = Brems | first2 = H. | last3 = Gomes | first3 = AG. | last4 = Ruppert | first4 = SL. | last5 = Callens | first5 = T. | last6 = Williams | first6 = J. | last7 = Claes | first7 = K. | last8 = Bober | first8 = MB. | last9 = Hachen | first9 = R. | title = Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome, revisited: detailed clinical and molecular analyses determine whether patients have neurofibromatosis type 1, coincidental manifestations, or a distinct disorder. | journal = Genet Med | volume = 16 | issue = 6 | pages = 448-59 | month = Jun | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1038/gim.2013.163 | PMID = 24232412 }} | ||
</ref> | |||
*Radiographic diagnosis. | *Radiographic diagnosis. | ||
| Line 77: | Line 78: | ||
*Eccentric location. | *Eccentric location. | ||
===Radiology=== | |||
*Sharply demarcated, lucent, loculated, meta-diaphyseal lesion. | *Sharply demarcated, lucent, loculated, meta-diaphyseal lesion. | ||
*Surrounded by a rim of sclerotic bone. | *Surrounded by a rim of sclerotic bone. | ||
<gallery> | |||
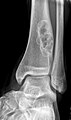
Image:NOF 1.jpg|Nonossifying fibroma. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:43, 18 October 2014
| Metaphyseal fibrous defect | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | nonossifying fibroma, fibrous cortical defect, fibrous metaphyseal defect, fibroxanthoma of bone |
| LM DDx | giant cell tumour of bone, others |
| Site | metaphysis of bone - usu. lower extremity |
|
| |
| Clinical history | incidental radiograhic finding |
| Prevalence | common |
| Radiology | lucent defect |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | none |
| Metaphyseal fibrous defect | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| Wikipedia | Nonossifying fibroma |
| Pathology Outlines | topic/bonemetaphysealfibrousdefect |
Metaphyseal fibrous defect, abbreviated MFD, is a common benign abnormality of the metaphysis, classically seen in children and young adults.
They are also known as fibrous cortical defect, fibrous metaphyseal defect, and fibroxanthoma of bone. Nonossifying fibroma is a larger lesion but otherwise identical.
General
- Common.
- Non-neoplastic.
- Self-limited.
- Skeletally immature individuals, children and adolescents.
- Often small lesions discovered as an radiographic incidentaloma.
- Rarely seen as a pathologic specimen (should not be biopsied).
- May be seen in the context of Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome which may be a presentation of Neurofibromatosis Type 1.[1][2]
- Radiographic diagnosis.
Clinical history:
- Incidental radiographic finding.
- Pathologic fracture.
Treatment:
- None (spontaneously resolve by ossification).
- Diagnosis is part of the skeletal do not touch list.[3]
Notes:
- May resolve into a bone island.
Clinical DDx:
- FOG MACHINES acronym for radiographically lytic bone lesions.[4]
Gross
- Firm, granular, brown to yellow to red.
Site:
- Metaphysis of distal femur or proximal tibia (80%).
- Cortical.
- Metaphysis.
- Long bones.
- Eccentric location.
Radiology
- Sharply demarcated, lucent, loculated, meta-diaphyseal lesion.
- Surrounded by a rim of sclerotic bone.
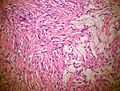
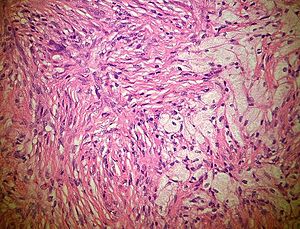
Microscopic
Features:
- Spindle cells without cytologic atypia are arranged in a storiform pattern.
- Scattered chronic inflammatory cells and benign giant cells.
- Foam cells and hemosiderin deposition are present.
- Mitoses are seen but cytologic atypia is absent.
DDx (microscopic):
- Giant cell tumour of bone - epiphyseal location, occurs in adults.
- Other giant cell lesions of bone.
- Spindle cell lesions of bone.
Images
www:
Stains
- Not relevant.
IHC
- Not relevant.
Molecular
- Not relevant.
Sign out
BONE, CURETTAGE: - METAPHYSEAL FIBROUS DEFECT / NONOSSIFYING FIBROMA.
See also
- Bone.
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.bonetumor.org/plasma-cell-tumors/jaffe-campanacci-syndrome. Accessed on: October 14, 2014.
- ↑ Stewart, DR.; Brems, H.; Gomes, AG.; Ruppert, SL.; Callens, T.; Williams, J.; Claes, K.; Bober, MB. et al. (Jun 2014). "Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome, revisited: detailed clinical and molecular analyses determine whether patients have neurofibromatosis type 1, coincidental manifestations, or a distinct disorder.". Genet Med 16 (6): 448-59. doi:10.1038/gim.2013.163. PMID 24232412.
- ↑ URL: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/skeletal-do-not-touch-lesions-1. Accessed on: October 14, 2014.
- ↑ URL: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lytic-bone-lesion-mnemonic. Accessed on: October 14, 2014.