Difference between revisions of "Foreign material"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Foreign material''' is something that is extrinsic to the body. | '''Foreign material''' is something that is extrinsic to the body. | ||
'''Foreign body''' redirect to this article. | '''Foreign body''' redirect to this article. | ||
Fecal material is dealt with separately in the article ''[[fecal material]]''. Sutures are dealt with separately in the article ''[[suture material]]''. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Relatively common. | *Relatively common. | ||
*Seen in a number of contexts. | *Seen in a number of contexts. | ||
**Pica - ingestion of nonfood items.<ref name=pmid12652915>{{Cite journal | last1 = Casale | first1 = LS. | last2 = Buoinincontro | first2 = S. | last3 = Capasso | first3 = L. | last4 = D'Ambrosio | first4 = R. | last5 = Borsi | first5 = E. | title = [Pica: a clinical case and therapeutic problems]. | journal = G Chir | volume = 23 | issue = 11-12 | pages = 417-9 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 12652915 }}</ref> | |||
**Trauma. | |||
**Embolization procedures. | |||
***May use gelatin sponge.<ref name=pmid25598681>{{Cite journal | last1 = Oh | first1 = JS. | last2 = Lee | first2 = HG. | last3 = Chun | first3 = HJ. | last4 = Choi | first4 = BG. | last5 = Choi | first5 = YJ. | title = Evaluation of arterial impairment after experimental gelatin sponge embolization in a rabbit renal model. | journal = Korean J Radiol | volume = 16 | issue = 1 | pages = 133-8 | month = | year = | doi = 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.133 | PMID = 25598681 }}</ref> | |||
**Previous surgery - suture material, degradable surgical sponges.<ref>URL: [http://oldfiles.bjorl.org/conteudo/acervo/print_acervo_english.asp?id=791 http://oldfiles.bjorl.org/conteudo/acervo/print_acervo_english.asp?id=791]. Accessed on: November 25, 2014.</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 23: | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Material with out nuclei. | ||
*May be honeycomb-like, cartilage-like or muscle-like. | |||
*May have a glassy appearance - see ''[[oxidized cellulose]]''. | |||
*Often homogenous or patterned. | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Fecal material]] - if in colon/rectum. | *[[Fecal material]] - if in colon/rectum. | ||
*[[Necrosis|Necrotic material]]. | *[[Necrosis|Necrotic material]]. | ||
*Tissue processing [[artifacts|artifact]]. | |||
*[[Xanthogranulomatous lymphadenitis]] - if in [[lymph node]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
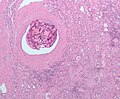
Image:Embolization_kidney.jpg | Kidney embolization. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
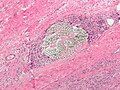
Image:Nasopharyngeal_angiofibroma_-_high_mag.jpg | Embolization of [[nasopharyngeal angiofibroma]]. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
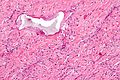
Image:Suture_micrograph.jpg | [[Suture material]]. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
<pre> | |||
A. Submitted as "Portion of IV Tubing", Removal: | |||
- Consistent with IV tubing (gross only). | |||
B. Submitted as "Fork", Removal: | |||
- Consistent with plastic fork (gross only). | |||
</pre> | |||
===History of metallic object identified by radiology=== | |||
<pre> | |||
The imaging findings are noted. No definite foreign material is seen at microscopy; however, the tissue is disrupted, as may result when a hard material is embedded in the tissue. | |||
The tissue block was examined and a fragment that had chunked-out at the time of cutting was noted. The chunked-out fragment and tissue block were x-rayed. The chunked-out fragment was highly radiodense (in keeping with a metallic fragment) and approximately 2 mm in maximal dimension. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Block letters=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
FOREIGN BODY, RIGHT LOWER LOBE, RETRIEVAL: | FOREIGN BODY, RIGHT LOWER LOBE, RETRIEVAL: | ||
| Line 35: | Line 70: | ||
WITH FOOD. | WITH FOOD. | ||
- SCANT STRIPPED BRONCHIAL LINING EPITHELIUM WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. | - SCANT STRIPPED BRONCHIAL LINING EPITHELIUM WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. | ||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
SOFT TISSUE, LEFT ARM, EXCISION: | |||
- FOREIGN BODY, APPEARANCE COMPATIBLE WITH A PIECE OF WOOD (GROSS ONLY). | |||
- FOREIGN BODY-REACTION (ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION WITH ACTIVATED FIBROBLASTS, | |||
HISTIOCYTES AND RARE GIANT CELLS). | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 83: | ||
*[[Fecal matter]]. | *[[Fecal matter]]. | ||
*[[Aspiration pneumonia]]. | *[[Aspiration pneumonia]]. | ||
*[[Artifacts]]. | |||
*[[Oxidized cellulose]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Stuff]] | [[Category:Stuff]] | ||
[[Category:Pulmonary pathology]] | [[Category:Pulmonary pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:32, 5 June 2024
Foreign material is something that is extrinsic to the body.
Foreign body redirect to this article.
Fecal material is dealt with separately in the article fecal material. Sutures are dealt with separately in the article suture material.
General
- Relatively common.
- Seen in a number of contexts.
Gross
- Looks like it doesn't belong, e.g. food.
- Obvious foreign bodies are gross only diagnoses.
- Examples:
- A dildo removed surgically from a body orifice.
- A bullet removed in surgery - should be handled with care, photographed... probably will become evidence.
- Examples:
Microscopic
Features:
- Material with out nuclei.
- May be honeycomb-like, cartilage-like or muscle-like.
- May have a glassy appearance - see oxidized cellulose.
- Often homogenous or patterned.
DDx:
- Fecal material - if in colon/rectum.
- Necrotic material.
- Tissue processing artifact.
- Xanthogranulomatous lymphadenitis - if in lymph node.
Images
Kidney embolization. H&E stain.
Embolization of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. H&E stain.
Sign out
A. Submitted as "Portion of IV Tubing", Removal: - Consistent with IV tubing (gross only). B. Submitted as "Fork", Removal: - Consistent with plastic fork (gross only).
History of metallic object identified by radiology
The imaging findings are noted. No definite foreign material is seen at microscopy; however, the tissue is disrupted, as may result when a hard material is embedded in the tissue. The tissue block was examined and a fragment that had chunked-out at the time of cutting was noted. The chunked-out fragment and tissue block were x-rayed. The chunked-out fragment was highly radiodense (in keeping with a metallic fragment) and approximately 2 mm in maximal dimension.
Block letters
FOREIGN BODY, RIGHT LOWER LOBE, RETRIEVAL: - MORPHOLOGICALLY CONSISTENT WITH A GREEN PEA (GROSS ONLY).
FOREIGN BODY, BRONCHUS INTERMEDIUS, RETRIEVAL: - MUCOUS WITH NEUTROPHILS AND MACROPHAGES. - BENIGN CALCIFICATIONS. - FOREIGN MATERIAL (HONEYCOMB-LIKE AND CARTILAGE-LIKE WITHOUT NUCLEI) -- COMPATIBLE WITH FOOD. - SCANT STRIPPED BRONCHIAL LINING EPITHELIUM WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY.
SOFT TISSUE, LEFT ARM, EXCISION: - FOREIGN BODY, APPEARANCE COMPATIBLE WITH A PIECE OF WOOD (GROSS ONLY). - FOREIGN BODY-REACTION (ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION WITH ACTIVATED FIBROBLASTS, HISTIOCYTES AND RARE GIANT CELLS). - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Casale, LS.; Buoinincontro, S.; Capasso, L.; D'Ambrosio, R.; Borsi, E.. "[Pica: a clinical case and therapeutic problems].". G Chir 23 (11-12): 417-9. PMID 12652915.
- ↑ Oh, JS.; Lee, HG.; Chun, HJ.; Choi, BG.; Choi, YJ.. "Evaluation of arterial impairment after experimental gelatin sponge embolization in a rabbit renal model.". Korean J Radiol 16 (1): 133-8. doi:10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.133. PMID 25598681.
- ↑ URL: http://oldfiles.bjorl.org/conteudo/acervo/print_acervo_english.asp?id=791. Accessed on: November 25, 2014.