Difference between revisions of "Seminal vesicles"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''seminal vesicles''' are a pair of organs closely associated with the [[prostate gland]] that fluid to the ejaculate. They are seen attached to prostatectomy specimens. | The '''seminal vesicles''', abbreviated '''SV''', are a pair of organs closely associated with the [[prostate gland]] that add fluid to the ejaculate. They are seen attached to [[radical prostatectomy]] specimens. | ||
=Normal seminal vesicles= | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Seen in radical prostatectomies and occasionally in core biopsies. | *Seen in radical prostatectomies and occasionally in core biopsies. | ||
*Very rarely a site of a [[primary seminal vesicle carcinoma|primary cancer]]. | *Very rarely a site of a [[primary seminal vesicle carcinoma|primary cancer]]. | ||
==Gross== | |||
*Worm-like paired organs. | |||
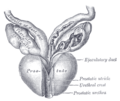
*Empty into the ejaculatory ducts (as does the [[vas deferens]]). | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Gray1153.png | Relationship between the SVs, ejaculatory ducts and [[vas deferens]]. | |||
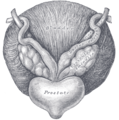
Image:Gray1152.png | Relationship between the SVs, prostate and bladder. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 35: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*PSA -ve.<ref name=pmid22895132>{{Cite journal | last1 = Itami | first1 = Y. | last2 = Nagai | first2 = Y. | last3 = Kobayashi | first3 = Y. | last4 = Shimizu | first4 = N. | last5 = Yamamoto | first5 = Y. | last6 = Minami | first6 = T. | last7 = Hayashi | first7 = T. | last8 = Nozawa | first8 = M. | last9 = Yoshimura | first9 = K. | title = [A case of prostatic cancer with a low PSA level accompanied with cystic formation requiring differentiation from adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle]. | journal = Hinyokika Kiyo | volume = 58 | issue = 7 | pages = 349-53 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22895132 }}</ref> | *[[PSA]] -ve.<ref name=pmid22895132>{{Cite journal | last1 = Itami | first1 = Y. | last2 = Nagai | first2 = Y. | last3 = Kobayashi | first3 = Y. | last4 = Shimizu | first4 = N. | last5 = Yamamoto | first5 = Y. | last6 = Minami | first6 = T. | last7 = Hayashi | first7 = T. | last8 = Nozawa | first8 = M. | last9 = Yoshimura | first9 = K. | title = [A case of prostatic cancer with a low PSA level accompanied with cystic formation requiring differentiation from adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle]. | journal = Hinyokika Kiyo | volume = 58 | issue = 7 | pages = 349-53 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22895132 }}</ref> | ||
*CK7 +ve.<ref name=pmid19468449>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tarján | first1 = M. | last2 = Ottlecz | first2 = I. | last3 = Tot | first3 = T. | title = Primary adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle. | journal = Indian J Urol | volume = 25 | issue = 1 | pages = 143-5 | month = Jan | year = 2009 | doi = 10.4103/0970-1591.45557 | PMID = 19468449 }}</ref><ref name=pmid22076175>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = Monstrous epithelial cell clusters in the seminal vesicle. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 7 | pages = 727-30 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 22076175 }}</ref> | *[[CK7]] +ve.<ref name=pmid19468449>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tarján | first1 = M. | last2 = Ottlecz | first2 = I. | last3 = Tot | first3 = T. | title = Primary adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle. | journal = Indian J Urol | volume = 25 | issue = 1 | pages = 143-5 | month = Jan | year = 2009 | doi = 10.4103/0970-1591.45557 | PMID = 19468449 }}</ref><ref name=pmid22076175>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = Monstrous epithelial cell clusters in the seminal vesicle. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 7 | pages = 727-30 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 22076175 }}</ref> | ||
*[[CK20]] -ve.<ref name=pmid19468449/> | *[[CK20]] -ve.<ref name=pmid19468449/> | ||
*p63 +ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | *[[p63]] +ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | ||
*CK34betaE12 -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | *[[CK34betaE12]] -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | ||
*AMACR -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | *[[AMACR]] -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 49: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==See also | =Pathology= | ||
==Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma== | |||
{{Main|Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma}} | |||
==Amyloid in the seminal vesicles== | |||
{{Main|Amyloid in the seminal vesicles}} | |||
=Benign= | |||
==Stromal lipofuscinosis of the seminal vesicle== | |||
{{Main|Stromal lipofuscinosis of the seminal vesicle}} | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[Prostate gland]]. | *[[Prostate gland]]. | ||
*[[Prostate cancer staging]]. | |||
*[[Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma]]. | *[[Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma]]. | ||
=References= | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Genitourinary pathology]] | [[Category:Genitourinary pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 4 August 2022
The seminal vesicles, abbreviated SV, are a pair of organs closely associated with the prostate gland that add fluid to the ejaculate. They are seen attached to radical prostatectomy specimens.
Normal seminal vesicles
General
- Seen in radical prostatectomies and occasionally in core biopsies.
- Very rarely a site of a primary cancer.
Gross
- Worm-like paired organs.
- Empty into the ejaculatory ducts (as does the vas deferens).
Relationship between the SVs, ejaculatory ducts and vas deferens.
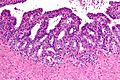
Microscopic
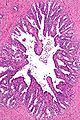
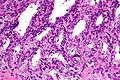
- Fern-like architecture - epithelial component clustered closely, looks like it connects.
- Epithelium surrounded by a thick layer of muscle (>10 cells across ~80 microns).
- Lipofuscin (coarse cytoplasmic yellow granules approximately 1-2 micrometers) - key feature.
- Nucleoli - common.
- Nuclear inclusions - common.[1]
Notes:
- The ejaculatory ducts have the same epithelium as the seminal vesicles.[2]
Images
www:
IHC
Sign out
B. PROSTATE, RIGHT MEDIAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE. - BENIGN SEMINAL VESICLE/EJACULATORY DUCT.
Pathology
Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma
Main article: Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma
Amyloid in the seminal vesicles
Main article: Amyloid in the seminal vesicles
Benign
Stromal lipofuscinosis of the seminal vesicle
Main article: Stromal lipofuscinosis of the seminal vesicle
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/prostate/adenocarcinoma/benign-vs-carcinoma.html. Accessed on: 10 January 2013.
- ↑ Leroy X, Ballereau C, Villers A, et al. (April 2003). "MUC6 is a marker of seminal vesicle-ejaculatory duct epithelium and is useful for the differential diagnosis with prostate adenocarcinoma". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 27 (4): 519–21. PMID 12657938.
- ↑ Itami, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Minami, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nozawa, M. et al. (Jul 2012). "[A case of prostatic cancer with a low PSA level accompanied with cystic formation requiring differentiation from adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle].". Hinyokika Kiyo 58 (7): 349-53. PMID 22895132.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Tarján, M.; Ottlecz, I.; Tot, T. (Jan 2009). "Primary adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle.". Indian J Urol 25 (1): 143-5. doi:10.4103/0970-1591.45557. PMID 19468449.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Terada, T. (2011). "Monstrous epithelial cell clusters in the seminal vesicle.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4 (7): 727-30. PMID 22076175.