Difference between revisions of "Atypical small acinar proliferation"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Atypical small acinar proliferation''', abbreviated ''ASAP'', is a small number of [[prostate gland|prostate glands]] that are abnormal and suspicious for [[prostate carcinoma|carcinoma]]. | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
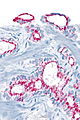
| Image = Atypical small acinar proliferation - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Atypical small acinar proliferation - top-left of image. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = suspicious for prostate carcinoma | |||
| Micro = morphology of prostate carcinoma but less than 6 glands (major criteria for prostate carcinoma: abnormal architecture (increased gland density, usu. small circular glands, "infiltrative growth" pattern), basal cells lost, cytological abnormalities (nuclear enlargement, nucleoli); minor criteria for prostate carcinoma: nuclear hyperchromasia, wispy blue mucin, pink amorphous secretions, intraluminal crystalloid, amphophilic cytoplasm, adjacent HGPIN, mitoses) | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[prostate adenocarcinoma]], benign prostate | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = AMACR +ve, [[CK34betaE12]] -ve, p63 -ve, PSA +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[prostate gland]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = ~3-5% of prostate biopsies | |||
| Bloodwork = +/-PSA elevated | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = increased risk of prostate carcinoma | |||
| Other = [[waffle diagnosis]] - used only on biopsy | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = re-biopsy, close follow-up | |||
}} | |||
'''Atypical small acinar proliferation''', abbreviated '''ASAP''', is a small number of [[prostate gland|prostate glands]] that are abnormal and suspicious for [[prostate carcinoma|carcinoma]]. | |||
It is also known as '''suspicious for carcinoma'''.<ref>THvdK. 19 June 2010.</ref> ASAP is preferred as it does not contain the word ''carcinoma'' and, thus, cannot be misread as ''carcinoma'', i.e. positive for malignancy. | It is also known as '''suspicious for carcinoma'''.<ref name=THvdK>THvdK. 19 June 2010.</ref> ASAP is preferred as it does not contain the word ''carcinoma'' and, thus, cannot be misread as ''carcinoma'', i.e. positive for malignancy. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 38: | ||
**Analogous to ''[[ASCUS]]'' on a pap test. | **Analogous to ''[[ASCUS]]'' on a pap test. | ||
*ASAP should be used sparingly. | *ASAP should be used sparingly. | ||
**One benchmark is < 3-5% of biopsies.<ref>THvdK. 19 June 2010.</ref> | **One benchmark is < 3-5% of biopsies.<ref name=THvdK>THvdK. 19 June 2010.</ref> | ||
*Never diagnosed on excision, i.e. prostatectomy specimen. | *Never diagnosed on excision, i.e. prostatectomy specimen. | ||
*Cancers diagnosed in biopsies after ASAP are not more frequently clinically significant than cancers diagnosed after a diagnosis of benign or HGPIN.<ref name=pmid28888752>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wiener | first1 = S. | last2 = Haddock | first2 = P. | last3 = Cusano | first3 = J. | last4 = Staff | first4 = I. | last5 = McLaughlin | first5 = T. | last6 = Wagner | first6 = J. | title = Incidence of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer After a Diagnosis of Atypical Small Acinar Proliferation, High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, or Benign Tissue. | journal = Urology | volume = 110 | issue = | pages = 161-165 | month = Dec | year = 2017 | doi = 10.1016/j.urology.2017.08.040 | PMID = 28888752 }}</ref> | |||
===Association with adenocarcinoma=== | ===Association with adenocarcinoma=== | ||
*On subsequent | *On a subsequent biopsy the chance of finding [[adenocarcinoma]] is approximately 40%; this is higher than if there is [[high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia]] (HGPIN).<ref name=pmid18568243>{{cite journal |author=Leite KR, Camara-Lopes LH, Cury J, Dall'oglio MF, Sañudo A, Srougi M |title=Prostate cancer detection at rebiopsy after an initial benign diagnosis: results using sextant extended prostate biopsy |journal=Clinics |volume=63 |issue=3 |pages=339–42 |year=2008 |month=June |pmid=18568243 |doi= |url=http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1807-59322008000300009&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en}}</ref> | ||
===Management=== | ===Management=== | ||
*ASAP is considered an indication for re-biopsy;<ref>{{cite journal |author=Bostwick DG, Meiers I |title=Atypical small acinar proliferation in the prostate: clinical significance in 2006 |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=130 |issue=7 |pages=952–7 |year=2006 |month=July |pmid=16831049 |doi= |url=http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=130&page=952}}</ref> in one | *ASAP is generally considered an indication for re-biopsy;<ref name=pmid16831049>{{cite journal |author=Bostwick DG, Meiers I |title=Atypical small acinar proliferation in the prostate: clinical significance in 2006 |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=130 |issue=7 |pages=952–7 |year=2006 |month=July |pmid=16831049 |doi= |url=http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=130&page=952}}</ref> in one study<ref name=pmid15223967>{{cite journal |author=Rubin MA, Bismar TA, Curtis S, Montie JE |title=Prostate needle biopsy reporting: how are the surgical members of the Society of Urologic Oncology using pathology reports to guide treatment of prostate cancer patients? |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=28 |issue=7 |pages=946–52 |year=2004 |month=July |pmid=15223967 |doi= |url=}}</ref> 41/42 (~98%) of urologists considered it a sufficient reason to re-biopsy. | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Atypical appearing acini. | *Atypical appearing acini - see criteria for ''[[prostate adenocarcinoma]]''. | ||
*Limited extent - '''key feature'''. | *Limited extent - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Less than six glands.† | **Less than six glands.† | ||
| Line 31: | Line 63: | ||
**Adenosis of the prostate. | **Adenosis of the prostate. | ||
**Sclerosing adenosis of the prostate. | **Sclerosing adenosis of the prostate. | ||
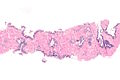
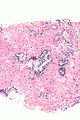
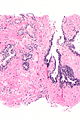
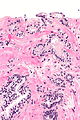
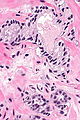
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation -- low mag.jpg | ASAP - low mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation -- intermed mag.jpg | ASAP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | ASAP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation -- high mag.jpg | ASAP - high mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation -- very high mag.jpg | ASAP - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
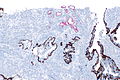
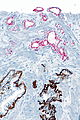
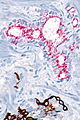
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Usually stains like cancer: | Usually stains like cancer: | ||
*AMACR +ve. | *AMACR +ve. | ||
*CK34betaE12 -ve. | *CK34betaE12 -ve. | ||
*p63 -ve. | *p63 -ve. | ||
Note: | |||
*Often ''not'' contributory. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation - AMACR-CK34betaE12 -- intermed mag.jpg | ASAP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation - AMACR-CK34betaE12 -- high mag.jpg | ASAP - high mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation - AMACR-CK34betaE12 -- very high mag.jpg | ASAP - very high mag. | |||
Image: Atypical small acinar proliferation - AMACR-CK34betaE12 - alt -- very high mag.jpg | ASAP - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
C. Prostate, Left Base: | |||
- Atypical prostatic glands, suspicious for microfocus of adenocarcinoma. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Block letters=== | |||
<pre> | |||
K. PROSTATE, LEFT LATERAL INTERIOR, BIOPSY: | |||
- ATYPICAL SMALL ACINAR PROLIFERATION. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Waffle diagnosis]]. | *[[Waffle diagnosis]]. | ||
*[[Prostate gland]]. | *[[Prostate gland]]. | ||
*[[Atypical intraductal proliferation]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 12 October 2022
| Atypical small acinar proliferation | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
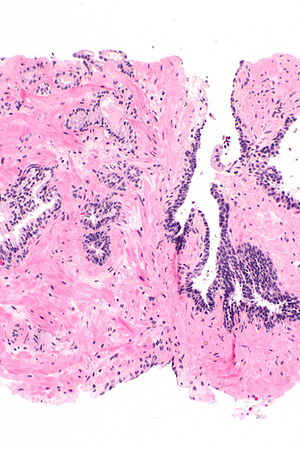 Atypical small acinar proliferation - top-left of image. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | suspicious for prostate carcinoma |
|
| |
| LM | morphology of prostate carcinoma but less than 6 glands (major criteria for prostate carcinoma: abnormal architecture (increased gland density, usu. small circular glands, "infiltrative growth" pattern), basal cells lost, cytological abnormalities (nuclear enlargement, nucleoli); minor criteria for prostate carcinoma: nuclear hyperchromasia, wispy blue mucin, pink amorphous secretions, intraluminal crystalloid, amphophilic cytoplasm, adjacent HGPIN, mitoses) |
| LM DDx | prostate adenocarcinoma, benign prostate |
| IHC | AMACR +ve, CK34betaE12 -ve, p63 -ve, PSA +ve |
| Site | prostate gland |
|
| |
| Prevalence | ~3-5% of prostate biopsies |
| Blood work | +/-PSA elevated |
| Prognosis | increased risk of prostate carcinoma |
| Other | waffle diagnosis - used only on biopsy |
| Treatment | re-biopsy, close follow-up |
Atypical small acinar proliferation, abbreviated ASAP, is a small number of prostate glands that are abnormal and suspicious for carcinoma.
It is also known as suspicious for carcinoma.[1] ASAP is preferred as it does not contain the word carcinoma and, thus, cannot be misread as carcinoma, i.e. positive for malignancy.
General
- It is a waffle diagnosis, i.e. it is not considered an entity with a distinct pathobiology.[2]
- Analogous to ASCUS on a pap test.
- ASAP should be used sparingly.
- One benchmark is < 3-5% of biopsies.[1]
- Never diagnosed on excision, i.e. prostatectomy specimen.
- Cancers diagnosed in biopsies after ASAP are not more frequently clinically significant than cancers diagnosed after a diagnosis of benign or HGPIN.[3]
Association with adenocarcinoma
- On a subsequent biopsy the chance of finding adenocarcinoma is approximately 40%; this is higher than if there is high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN).[4]
Management
- ASAP is generally considered an indication for re-biopsy;[5] in one study[6] 41/42 (~98%) of urologists considered it a sufficient reason to re-biopsy.
Microscopic
Features:
- Atypical appearing acini - see criteria for prostate adenocarcinoma.
- Limited extent - key feature.
- Less than six glands.†
Note:
- Deeper cuts didn't yield anything - important.
- † There is no agreed upon minimum number of glands; however, one paper suggests that agreement among experts is low with 5 or less glands.[7]
DDx:
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma.
- Benign prostate.
- Adenosis of the prostate.
- Sclerosing adenosis of the prostate.
Images
IHC
Usually stains like cancer:
- AMACR +ve.
- CK34betaE12 -ve.
- p63 -ve.
Note:
- Often not contributory.
Images
Sign out
C. Prostate, Left Base: - Atypical prostatic glands, suspicious for microfocus of adenocarcinoma.
Block letters
K. PROSTATE, LEFT LATERAL INTERIOR, BIOPSY: - ATYPICAL SMALL ACINAR PROLIFERATION.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 THvdK. 19 June 2010.
- ↑ Flury SC, Galgano MT, Mills SE, Smolkin ME, Theodorescu D (January 2007). "Atypical small acinar proliferation: biopsy artefact or distinct pathological entity". BJU International 99 (4): 780-5. PMID 17378841. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/118508438/abstract.
- ↑ Wiener, S.; Haddock, P.; Cusano, J.; Staff, I.; McLaughlin, T.; Wagner, J. (Dec 2017). "Incidence of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer After a Diagnosis of Atypical Small Acinar Proliferation, High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, or Benign Tissue.". Urology 110: 161-165. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2017.08.040. PMID 28888752.
- ↑ Leite KR, Camara-Lopes LH, Cury J, Dall'oglio MF, Sañudo A, Srougi M (June 2008). "Prostate cancer detection at rebiopsy after an initial benign diagnosis: results using sextant extended prostate biopsy". Clinics 63 (3): 339–42. PMID 18568243. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1807-59322008000300009&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en.
- ↑ Bostwick DG, Meiers I (July 2006). "Atypical small acinar proliferation in the prostate: clinical significance in 2006". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 130 (7): 952–7. PMID 16831049. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=130&page=952.
- ↑ Rubin MA, Bismar TA, Curtis S, Montie JE (July 2004). "Prostate needle biopsy reporting: how are the surgical members of the Society of Urologic Oncology using pathology reports to guide treatment of prostate cancer patients?". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 28 (7): 946–52. PMID 15223967.
- ↑ Van der Kwast, TH.; Evans, A.; Lockwood, G.; Tkachuk, D.; Bostwick, DG.; Epstein, JI.; Humphrey, PA.; Montironi, R. et al. (Feb 2010). "Variability in diagnostic opinion among pathologists for single small atypical foci in prostate biopsies.". Am J Surg Pathol 34 (2): 169-77. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181c7997b. PMID 20061936.