Difference between revisions of "Suture material"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Alessandro (talk | contribs) m (→Microscopic) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Suture are often used to orient a specimen and/or mark the true [[surgical margin]]. | *Suture are often used to orient a specimen<ref name=pmid23287819>{{Cite journal | last1 = Volleamere | first1 = AJ. | last2 = Kirwan | first2 = CC. | title = National survey of breast cancer specimen orientation marking systems. | journal = Eur J Surg Oncol | volume = 39 | issue = 3 | pages = 255-9 | month = Mar | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejso.2012.12.008 | PMID = 23287819 }}</ref> and/or mark the true [[surgical margin]].<ref name=pmid7544556>{{Cite journal | last1 = Seitz | first1 = SE. | last2 = Foley | first2 = GL. | last3 = Marretta | first3 = SM. | title = Evaluation of marking materials for cutaneous surgical margins. | journal = Am J Vet Res | volume = 56 | issue = 6 | pages = 826-33 | month = Jun | year = 1995 | doi = | PMID = 7544556 }}</ref> | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*Glassy appearance - sharply circumscribed. | *Glassy appearance - sharply circumscribed. | ||
*+/-Tearing surrounding tissue. | *+/-Tearing surrounding tissue. | ||
*Foreign body-type [[granuloma]]s with multinucleated giant cells. | *+/-Foreign body-type [[granuloma]]s with multinucleated giant cells. | ||
**Seen only if the suture has been in place for at least several days. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Histology artifacts]]. | *[[Histology artifacts]]. | ||
*[[Foreign material]]. | |||
*[[Granuloma]]. | *[[Granuloma]]. | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Basics]] | [[Category:Basics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:17, 11 February 2019
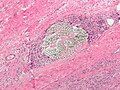
Suture material is occasionally seen under the microscope. It is usually easy to identified and typically polarizes.
General
- Suture are often used to orient a specimen[1] and/or mark the true surgical margin.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Glassy appearance - sharply circumscribed.
- +/-Tearing surrounding tissue.
- +/-Foreign body-type granulomas with multinucleated giant cells.
- Seen only if the suture has been in place for at least several days.
Images
Suture material adjacent to a SFT.
See also
References
- ↑ Volleamere, AJ.; Kirwan, CC. (Mar 2013). "National survey of breast cancer specimen orientation marking systems.". Eur J Surg Oncol 39 (3): 255-9. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2012.12.008. PMID 23287819.
- ↑ Seitz, SE.; Foley, GL.; Marretta, SM. (Jun 1995). "Evaluation of marking materials for cutaneous surgical margins.". Am J Vet Res 56 (6): 826-33. PMID 7544556.