Difference between revisions of "Peutz-Jeghers syndrome"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Clinical: +MDA) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
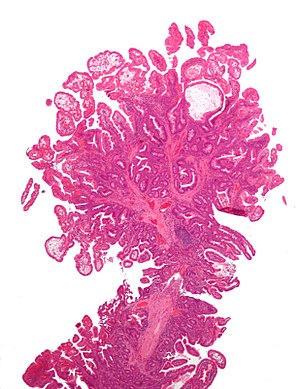
[[Image:Peutz-Jeghers_syndrome_polyp.jpg|thumb|300px | Peutz-Jeghers polyp, as may be seen in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. (WC)]] | |||
'''Peutz-Jeghers syndrome''', abbreviated '''PJS''', is a constellation of findings inherited with an autosomal dominant pattern due to a defect in the STK11 gene.<ref name=omim602216>{{OMIM|602216}}</ref> | '''Peutz-Jeghers syndrome''', abbreviated '''PJS''', is a constellation of findings inherited with an autosomal dominant pattern due to a defect in the STK11 gene.<ref name=omim602216>{{OMIM|602216}}</ref> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
Increased risk of various neoplasms - primarily: | Increased risk of various neoplasms - primarily: | ||
*Breast and gastrointestinal cancer.<ref name=pmid20581245>{{cite journal |author=Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, ''et al.'' |title=Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management |journal=Gut |volume=59 |issue=7 |pages=975–86 |year=2010 |month=July |pmid=20581245 |doi=10.1136/gut.2009.198499 |url=}}</ref> | *Breast and gastrointestinal cancer.<ref name=pmid20581245>{{cite journal |author=Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, ''et al.'' |title=Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management |journal=Gut |volume=59 |issue=7 |pages=975–86 |year=2010 |month=July |pmid=20581245 |doi=10.1136/gut.2009.198499 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* | *Other tumours:<ref>URL: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/175200 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/175200]. Accessed on: 22 December 2010.</ref> | ||
**[[Granulosa cell tumour]]. | **[[Granulosa cell tumour]]. | ||
**[[Sertoli cell tumour]] - especially with calcification. | **[[Sertoli cell tumour]] - especially with calcification. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
*# M. mucosae. | *# M. mucosae. | ||
Image | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Peutz-Jeghers_syndrome_polyp.jpg | Peutz-Jeghers syndrome polyp. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/fig_tab/3880773f3.html Peutz-Jeghers polyp (nature.com)]. | *[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/fig_tab/3880773f3.html Peutz-Jeghers polyp (nature.com)]. | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case190.html PJS - several images (upmc.edu).] | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case190.html PJS - several images (upmc.edu).] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:35, 13 March 2016
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, abbreviated PJS, is a constellation of findings inherited with an autosomal dominant pattern due to a defect in the STK11 gene.[1]
Clinical
Features:[2]
- Melanocytic macules.
- Lips, buccal mucosa, and digits.
- Multiple Peutz-Jeghers polyps.
Increased risk of various neoplasms - primarily:
- Breast and gastrointestinal cancer.[3]
- Other tumours:[4]
- Granulosa cell tumour.
- Sertoli cell tumour - especially with calcification.
- Minimal deviation adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix.[5]
Reported associations:
- Associated with (ovarian) sex cord tumour with annular tubules (SCTAT).[6]
Microscopic
- Frond-like polyp with all three components of mucosa:
- Muscosal epithelium (melanotic mucosa, goblet cells).
- Lamina propria.
- M. mucosae.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 602216
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 175200
- ↑ Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. (July 2010). "Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management". Gut 59 (7): 975–86. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.198499. PMID 20581245.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/175200. Accessed on: 22 December 2010.
- ↑ Gilks CB, Young RH, Aguirre P, DeLellis RA, Scully RE (September 1989). "Adenoma malignum (minimal deviation adenocarcinoma) of the uterine cervix. A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of 26 cases". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 13 (9): 717–29. PMID 2764221.
- ↑ Purohit RC, Alam SZ (March 1980). "Sex cord tumour of the ovary with annular tubules (SCTAT)". Histopathology 4 (2): 147–54. PMID 7358344.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 859. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Bronner, MP. (Apr 2003). "Gastrointestinal inherited polyposis syndromes.". Mod Pathol 16 (4): 359-65. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000062992.54036.E4. PMID 12692201. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880773a.html.