Difference between revisions of "Viruses and cancer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
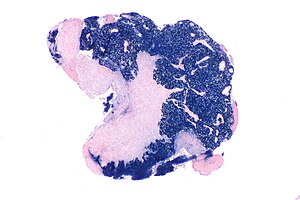
This article deals with '''[[ | [[Image:Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - EBER -- very low mag.jpg |thumb|right|Micrograph showing an EBER ('''E'''pstein-'''B'''arr virus (EBV)-'''e'''ncoded small '''R'''NAs) positive [[nasopharyngeal carcinoma]]. ''[[Epstein-Barr virus]]'' is a virus that causes cancer. (WC)]] | ||
This article deals with '''[[viruses]] and [[cancer]].''' | |||
'''Cancer viruses''' and '''cancer and viruses''' redirect here. | |||
*[[Human lymphotropic virus type | Several virus are known to cause cancer.<ref name=pmid31236460>{{cite journal |authors=Holm A, Schindele A, Allard A, Eriksson I, Sandström K, Laurell G, Nylander K, Olofsson K |title=Mapping of human papilloma virus, p16, and epstein-barr virus in non-malignant tonsillar disease |journal=Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=285–291 |date=June 2019 |pmid=31236460 |pmc=6580074 |doi=10.1002/lio2.260 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Human | |||
*[[Merkel cell | ==Cancer causing viruses== | ||
*[[Epstein-Barr virus]] (EBV).<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
*[[Hepatitis B virus]].<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
*[[Hepatitis C virus]].<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
*[[Human herpesvirus-8]].<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
*Human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I).<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Manns A, Hisada M, La Grenade L |title=Human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection |journal=Lancet |volume=353 |issue=9168 |pages=1951–8 |date=June 1999 |pmid=10371587 |doi=10.1016/s0140-6736(98)09460-4 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Human papillomavirus]] (HPV).<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
*[[Merkel cell polyomavirus]].<ref name=pmid31236460/> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:41, 12 December 2021

Micrograph showing an EBER (Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded small RNAs) positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Epstein-Barr virus is a virus that causes cancer. (WC)
This article deals with viruses and cancer.
Cancer viruses and cancer and viruses redirect here.
Several virus are known to cause cancer.[1]
Cancer causing viruses
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).[1]
- Hepatitis B virus.[1]
- Hepatitis C virus.[1]
- Human herpesvirus-8.[1]
- Human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I).[2]
- Human papillomavirus (HPV).[1]
- Merkel cell polyomavirus.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Holm A, Schindele A, Allard A, Eriksson I, Sandström K, Laurell G, Nylander K, Olofsson K (June 2019). "Mapping of human papilloma virus, p16, and epstein-barr virus in non-malignant tonsillar disease". Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 4 (3): 285–291. doi:10.1002/lio2.260. PMC 6580074. PMID 31236460. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6580074/.
- ↑ Manns A, Hisada M, La Grenade L (June 1999). "Human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection". Lancet 353 (9168): 1951–8. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(98)09460-4. PMID 10371587.