Difference between revisions of "Aspiration pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(→Images) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Aspiration pneumonia''' is a type of [[pneumonia]]. | |||
A special type of aspiration pneumonia is ''lipoid pneumonia''. It is dealt with in the ''[[lipoid pneumonia]]'' article. | |||
==General== | |||
*Not associated with microorganisms - though empiric antibiotics are relatively common to cover infectious pneumonias that cannot be excluded easily on clinical grounds.<ref name=pmid21263315>{{Cite journal | last1 = Raghavendran | first1 = K. | last2 = Nemzek | first2 = J. | last3 = Napolitano | first3 = LM. | last4 = Knight | first4 = PR. | title = Aspiration-induced lung injury. | journal = Crit Care Med | volume = 39 | issue = 4 | pages = 818-26 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31820a856b | PMID = 21263315 }}</ref> | |||
*Usually seen in the context of a toxin and/or pathology that affects the swallowing and cough reflexes.<ref name=pmid16082150>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ohrui | first1 = T. | title = Preventive strategies for aspiration pneumonia in elderly disabled persons. | journal = Tohoku J Exp Med | volume = 207 | issue = 1 | pages = 3-12 | month = Sep | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 16082150 }}</ref> | |||
Common associations:<ref name=pmid16082150/> | |||
*[[Stroke]]. | |||
*[[Multiple sclerosis]]. | |||
*[[Alcohol]] intoxication. | |||
Other risk factors:<ref name=pmid21263315/> | |||
*Traumatic brain injury. | |||
*Seizure disorder. | |||
*Bowel obstruction. | |||
*Drugs. | |||
*[[Obesity]]. | |||
*Labour. | |||
==Gross== | |||
*More common in the right lung. | |||
**Right main stem bronchus is more vertical. | |||
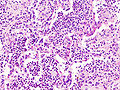
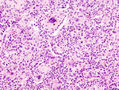
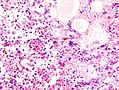
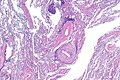
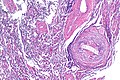
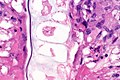
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Neutrophils. | |||
*Foreign material, e.g. plant matter. | |||
*+/-Foreign body giant cells. | |||
*+/-Microorganisms. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Acute infectious pneumonia]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Aspiration_pneumonia_%281%29.jpg | Aspiration pneumonia - 1 - (WC) | |||
Image:Aspiration_pneumonia_%282%29.jpg | Aspiration pneumonia - 2 - (WC) | |||
Image:Aspiration_pneumonia_%283%29.jpg | Aspiration pneumonia - 3 - (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Aspiration pneumonia -- very low mag.jpg | AP - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Aspiration pneumonia - alt -- low mag.jpg | AP - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Aspiration pneumonia -- intermed mag.jpg | AP - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Aspiration pneumonia - alt -- high mag.jpg | AP - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Aspiration pneumonia -- very high mag.jpg | AP - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pneumonia]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Pulmonary pathology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:37, 24 March 2019
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of pneumonia.
A special type of aspiration pneumonia is lipoid pneumonia. It is dealt with in the lipoid pneumonia article.
General
- Not associated with microorganisms - though empiric antibiotics are relatively common to cover infectious pneumonias that cannot be excluded easily on clinical grounds.[1]
- Usually seen in the context of a toxin and/or pathology that affects the swallowing and cough reflexes.[2]
Common associations:[2]
- Stroke.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Alcohol intoxication.
Other risk factors:[1]
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Seizure disorder.
- Bowel obstruction.
- Drugs.
- Obesity.
- Labour.
Gross
- More common in the right lung.
- Right main stem bronchus is more vertical.
Microscopic
Features:
- Neutrophils.
- Foreign material, e.g. plant matter.
- +/-Foreign body giant cells.
- +/-Microorganisms.
DDx:
Images
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Raghavendran, K.; Nemzek, J.; Napolitano, LM.; Knight, PR. (Apr 2011). "Aspiration-induced lung injury.". Crit Care Med 39 (4): 818-26. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31820a856b. PMID 21263315.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ohrui, T. (Sep 2005). "Preventive strategies for aspiration pneumonia in elderly disabled persons.". Tohoku J Exp Med 207 (1): 3-12. PMID 16082150.