Difference between revisions of "Acute myeloid leukemia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
*t(5;17). (???) | *t(5;17). (???) | ||
==Microscopic== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Comes in two flavours. | Comes in two flavours. | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
*Absence of granules on light microscopy. | *Absence of granules on light microscopy. | ||
===Images=== | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Faggot cell in AML-M3.jpg |Faggot cell in AML-M3. (WC) | Image:Faggot cell in AML-M3.jpg |Faggot cell in AML-M3. (WC) | ||
Revision as of 23:28, 27 May 2018
Acute myeloid leukemia, abbreviated AML, is a group of malignancies.
No recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities
Acute myeloid leukemia without recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities
General
- Adults.
Exclusions for this diagnosis:
- Prior MDS.
- Down syndrome.
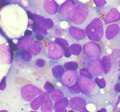
Microscopic
Features:
- Auer rods present
- Cytoplasmic granularity.
- Large cells.
Note:
- May be classified by morphology, using the (old) French-American-British (FAB) classification (M0-M7).
Image
www:
Molecular
- Must exclude all the recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities - see below.
AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities
Acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)
- t(8;21)(q22;q22).[1]
IHC:
- CD34+, CD13+, MPO+ (cytoplasm), CD33+ (weak).
- CD56+, CD117+.
- Usu. assoc. with a bad prognosis.
Flow cytometry:
- CD19+, PAX5+, CD79a +/-.
Images:
Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)
- inv(16)(p13.1q22).[2]
- Associated with myeloid sarcoma.
Microscopic:
- Blast count usu. ~20% (low).
- Eosinophilic granules.
- Used to be classified as "M4" with eosinophilia.
IHC:
- CD2+ -- common.
Acute myeloid leukemia with t(15;17)
- AKA acute promyelocytic leukemia
- Abbreviated APL.
- t(15;17)(q22;q12).
General
Clinical:
- Associated with DIC.
- Treatment: all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA).
Variants:
- t(11;17) -- ATRA doesn't work.[5]
- t(17;17) -- ATRA doesn't work.
- t(5;17). (???)
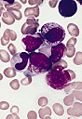
Microscopic
Comes in two flavours.
Microscopic (Hypergranular or typical APL):
- Bean-shaped nucleus or bilobed nucleus.
- Buddles of Auer rods - known as "Faggot cells".
Microscopic (Microgranular or hypogranular APL):
- Bilobed nuclei with nuclear overlap. (???)
- Absence of granules on light microscopy.
Images
www:
IHC
- CD2 +ve, CD34 +ve/-ve, CD56 +ve/-ve.
Flow cytometry
- CD34 -ve, HLA-DR -ve.
- CD33 +ve, CD13 +ve/-ve, CD117 +ve (weak), CD56 +ve/-ve.
Acute myeloid leukemia with t(9;11)
- t(9;11).
Microscopic:
- Monoblastic morphology. (???)
- Myelomonocytic morphology. (???)
Clinical:
- +/-DIC.
- Usu. children.
IHC:
- CD33+, CD65+, CD4+, HLA-DR+.
- CD34+. (???)
- CD13+. (???)
See also
References
- ↑ Berger, R. (1994). "Translocation t(8;21)(q22;q22): cytogenetics and molecular biology.". Nouv Rev Fr Hematol 36 Suppl 1: S67-9. PMID 8177719.
- ↑ Lu, CM.; Murata-Collins, JL.; Wang, E.; Siddiqi, I.; Lawrence, HJ. (Dec 2006). "Concurrent acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: molecular evidence of two separate diseases.". Am J Hematol 81 (12): 963-8. doi:10.1002/ajh.20716. PMID 16917916.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 102578
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 180240
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 623 Q2. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case457.html. Accessed on: 21 January 2012.