Difference between revisions of "High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma"
(+infobox) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = | | Image = High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma -- intermed mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = papillae with "architectural complexity" (fused papillae, branching of papillae), +/-nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear enlargement - often 4-5x the size of stromal lymphocytes, mitoses (common), +/-invasion into the lamina propria (common) | | Micro = papillae with "architectural complexity" (fused papillae, branching of papillae), +/-nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear enlargement - often 4-5x the size of stromal lymphocytes, mitoses (common), +/-invasion into the lamina propria (common) | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = subtype of [[urothelial carcinoma]] | ||
| LMDDx = [[low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]], [[urothelial carcinoma in situ]], [[squamous cell carcinoma]] | | LMDDx = [[low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]], [[urothelial carcinoma in situ]], [[squamous cell carcinoma]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = Ki-67 high (>35% of cells) | | IHC = Ki-67 high (>35% of cells), PAX8 -ve | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Aggressive. | *Aggressive. | ||
*May be associated with [[Lynch syndrome]].<ref name=pmid12673555>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hartmann | first1 = A. | last2 = Dietmaier | first2 = W. | last3 = Hofstädter | first3 = F. | last4 = Burgart | first4 = LJ. | last5 = Cheville | first5 = JC. | last6 = Blaszyk | first6 = H. | title = Urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: inverted growth pattern is predictive of microsatellite instability. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 34 | issue = 3 | pages = 222-7 | month = Mar | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1053/hupa.2003.22 | PMID = 12673555 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 57: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]]. | *[[Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma]]. | ||
**Stanford criteria has a 5% rule -- if the high-grade component is <5% it is low-grade.<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/bladder/tcc-papillary-transitional-urothelial-carcinoma/ http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/bladder/tcc-papillary-transitional-urothelial-carcinoma/]. Accessed on: 27 January 2014.</ref> | |||
***There is some evidence to suggest low-grade with <5% high-grade behaves similar to low-grade.<ref name=pmid26520419>{{Cite journal | last1 = Reis | first1 = LO. | last2 = Taheri | first2 = D. | last3 = Chaux | first3 = A. | last4 = Guner | first4 = G. | last5 = Mendoza Rodriguez | first5 = MA. | last6 = Bivalacqua | first6 = TJ. | last7 = Schoenberg | first7 = MP. | last8 = Epstein | first8 = JI. | last9 = Netto | first9 = GJ. | title = Significance of a minor high-grade component in a low-grade noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of bladder. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 47 | issue = 1 | pages = 20-5 | month = Jan | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.09.007 | PMID = 26520419 }}></ref> | |||
*[[Prostate carcinoma]] with pseudopapillae<ref name=pmid24503758>{{cite journal |author=Gordetsky J, Epstein JI |title=Pseudopapillary features in prostatic adenocarcinoma mimicking urothelial carcinoma: a diagnostic pitfall |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=38 |issue=7 |pages=941–5 |year=2014 |month=July |pmid=24503758 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000000178 |url=}}</ref> - see ''[[urothelial carcinoma-like prostatic carcinoma]]''. | |||
**Should be considered if a [[urethra]]l tumour. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
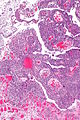
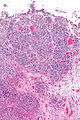
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma -- low mag.jpg | HGPUC - low mag. | |||
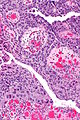
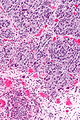
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma -- intermed mag.jpg | HGPUC - intermed. mag. | |||
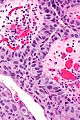
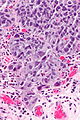
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma -- high mag.jpg | HGPUC - high mag. | |||
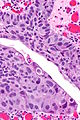
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma - alt -- high mag.jpg | HGPUC - high mag. | |||
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma - inv -- low mag.jpg | HGPUC - low mag. | |||
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma - inv -- intermed mag.jpg | HGPUC - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma - inv -- high mag.jpg | HGPUC - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 78: | ||
**Rajcani ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid23944616>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rajcani | first1 = J. | last2 = Kajo | first2 = K. | last3 = Adamkov | first3 = M. | last4 = Moravekova | first4 = E. | last5 = Lauko | first5 = L. | last6 = Felcanova | first6 = D. | last7 = Bencat | first7 = M. | title = Immunohistochemical characterization of urothelial carcinoma. | journal = Bratisl Lek Listy | volume = 114 | issue = 8 | pages = 431-8 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 23944616 }}</ref> <25% of tumour cells for low-grade versus >50% tumour cell for high-grade. | **Rajcani ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid23944616>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rajcani | first1 = J. | last2 = Kajo | first2 = K. | last3 = Adamkov | first3 = M. | last4 = Moravekova | first4 = E. | last5 = Lauko | first5 = L. | last6 = Felcanova | first6 = D. | last7 = Bencat | first7 = M. | title = Immunohistochemical characterization of urothelial carcinoma. | journal = Bratisl Lek Listy | volume = 114 | issue = 8 | pages = 431-8 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 23944616 }}</ref> <25% of tumour cells for low-grade versus >50% tumour cell for high-grade. | ||
**Pich ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid7910097>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pich | first1 = A. | last2 = Chiusa | first2 = L. | last3 = Comino | first3 = A. | last4 = Navone | first4 = R. | title = Cell proliferation indices, morphometry and DNA flow cytometry provide objective criteria for distinguishing low and high grade bladder carcinomas. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 424 | issue = 2 | pages = 143-8 | month = | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 7910097 }}</ref> 11%/17% for G1/G2 versus 34% for G3. | **Pich ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid7910097>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pich | first1 = A. | last2 = Chiusa | first2 = L. | last3 = Comino | first3 = A. | last4 = Navone | first4 = R. | title = Cell proliferation indices, morphometry and DNA flow cytometry provide objective criteria for distinguishing low and high grade bladder carcinomas. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 424 | issue = 2 | pages = 143-8 | month = | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 7910097 }}</ref> 11%/17% for G1/G2 versus 34% for G3. | ||
**Mai ''et al.'' suggest there is overlap:<ref name=pmid23913166>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mai | first1 = KT. | last2 = Flood | first2 = TA. | last3 = Williams | first3 = P. | last4 = Kos | first4 = Z. | last5 = Belanger | first5 = EC. | title = Mixed low- and high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma: histopathogenetic and clinical significance. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 463 | issue = 4 | pages = 575-81 | month = Oct | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-013-1456-7 | PMID = 23913166 }}</ref> 10-30% for low-grade versus 20-50% for high-grade. | |||
*p53 +ve - more common in pT2 than pT1 and HGPUC than LGPUC... but not useful to definitively separate.<ref name=pmid23924551>{{Cite journal | last1 = Koyuncuer | first1 = A. | title = Immunohistochemical expression of p63, p53 in urinary bladder carcinoma. | journal = Indian J Pathol Microbiol | volume = 56 | issue = 1 | pages = 10-5 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0377-4929.116141 | PMID = 23924551 }}</ref> | *p53 +ve - more common in pT2 than pT1 and HGPUC than LGPUC... but not useful to definitively separate.<ref name=pmid23924551>{{Cite journal | last1 = Koyuncuer | first1 = A. | title = Immunohistochemical expression of p63, p53 in urinary bladder carcinoma. | journal = Indian J Pathol Microbiol | volume = 56 | issue = 1 | pages = 10-5 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0377-4929.116141 | PMID = 23924551 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 91: | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
<pre> | |||
Urinary Bladder Tumour, Transurethral Resection: | |||
- HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA. | |||
-- NEGATIVE for lamina propria invasion. | |||
-- NEGATIVE for lymphovascular invasion. | |||
-- Please see synoptic report. | |||
- Muscularis propria present and NEGATIVE for invasion. | |||
- NEGATIVE for (flat) urothelial carcinoma in situ. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Block letters==== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION: | URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION: | ||
| Line 82: | Line 111: | ||
===Invasion into the lamina propria=== | ===Invasion into the lamina propria=== | ||
<pre> | |||
Urinary Bladder Tumour, Transurethral Resection: | |||
- INVASIVE HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA with lamina propria invasion. | |||
-- Muscularis propria present, NEGATIVE for muscularis propria invasion. | |||
-- NEGATIVE for lymphovascular invasion. | |||
-- Please see synoptic report. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Block letters==== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION URINARY BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT): | URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION URINARY BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT): | ||
| Line 110: | Line 148: | ||
====Micro==== | ====Micro==== | ||
The sections show urothelial mucosa with thick papillary structures. Focally, nuclei are large (~3-4x resting lymphocyte), hyperchromatic and have nucleoli. Mitotic activity is present and focally brisk (4 mitoses in 1 HPF, 1 HPF~0.2376 mm*mm). Umbrella cells are seen only focally. | |||
=====Alternate===== | |||
The sections show a small fragment of urothelial mucosa with two papillary structures, | The sections show a small fragment of urothelial mucosa with two papillary structures, | ||
enlarged nuclei (~3-4x resting lymphocyte) and moderate nuclear size variation. Mitotic activity is seen focally. Umbrella | enlarged nuclei (~3-4x resting lymphocyte) and moderate nuclear size variation. Mitotic activity is seen focally. Umbrella | ||
| Line 117: | Line 158: | ||
contains a nest with smaller cells, cystic spaces and no appreciable mitoses | contains a nest with smaller cells, cystic spaces and no appreciable mitoses | ||
(cystitis cystica). | (cystitis cystica). | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Urothelium]]. | *[[Urothelium]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:43, 22 February 2017
| High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
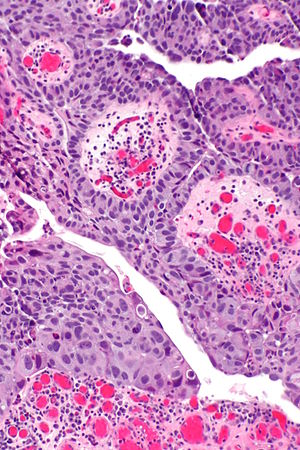 High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | papillae with "architectural complexity" (fused papillae, branching of papillae), +/-nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear enlargement - often 4-5x the size of stromal lymphocytes, mitoses (common), +/-invasion into the lamina propria (common) |
| Subtypes | subtype of urothelial carcinoma |
| LM DDx | low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma in situ, squamous cell carcinoma |
| IHC | Ki-67 high (>35% of cells), PAX8 -ve |
| Gross | exophytic mass, frond-like appearance, friable |
| Site | urothelium - usu. urinary bladder |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Lynch syndrome |
|
| |
| Signs | hematuria |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | dependent on stage, usu. moderate |
| Clin. DDx | low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma |
High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma, abbreviated HGPUC, is a common form of cancer that arises from the urothelium.
It is also known as high-grade papillary urothelial cell carcinoma, abbreviated HGPUCC.
General
- Aggressive.
- May be associated with Lynch syndrome.[1]
Gross
- Exophytic mass.
- Frond-like appearance.
- Friable.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- "High grade nuclear features":
- Nuclear pleomorphism - often 4-5x the size of stromal lymphocytes.[3]
- Papillae with "architectural complexity":
- Fused papillae - common.
- Branching of papillae common.
- Mitoses - common.
- +/-Invasion into the lamina propria - relatively common.
Note:
- The presence/absence of muscle should be commented on in biopsy specimens.
- Adipose tissue may be seen in the lamina propria; tumour adjacent to adipose tissue on a biopsy does not imply invasion deep to the muscularis propria.[4]
DDx:
- Low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma.
- Prostate carcinoma with pseudopapillae[7] - see urothelial carcinoma-like prostatic carcinoma.
- Should be considered if a urethral tumour.
Images
IHC
- Ki-67:
- p53 +ve - more common in pT2 than pT1 and HGPUC than LGPUC... but not useful to definitively separate.[11]
Molecular
Molecular changes:[12]
- p53.
- p21.
- RB.
- E-cadherin - decreased bad.
- RhoGD12 - increased bad.
- VEGF - increased bad.
Sign out
Urinary Bladder Tumour, Transurethral Resection: - HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA. -- NEGATIVE for lamina propria invasion. -- NEGATIVE for lymphovascular invasion. -- Please see synoptic report. - Muscularis propria present and NEGATIVE for invasion. - NEGATIVE for (flat) urothelial carcinoma in situ.
Block letters
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION:
- HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA.
- NO LAMINA PROPRIA INVASION APPARENT.
- NEGATIVE FOR LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION.
- NO MUSCULARIS PROPRIA IDENTIFIED.
Invasion into the lamina propria
Urinary Bladder Tumour, Transurethral Resection: - INVASIVE HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA with lamina propria invasion. -- Muscularis propria present, NEGATIVE for muscularis propria invasion. -- NEGATIVE for lymphovascular invasion. -- Please see synoptic report.
Block letters
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION URINARY BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT):
- INVASIVE HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA WITH LAMINA PROPRIA INVASION.
- MUSCULARIS PROPRIA NEGATIVE FOR INVASIVE MALIGNANCY.
- NEGATIVE FOR LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION.
Invasion into the muscularis propria
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION URINARY BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT):
- INVASIVE HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA AT LEAST INTO MUSCULARIS PROPRIA.
- LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION PRESENT.
Low-grade versus high-grade
URINARY BLADDER LESION ("TUMOUR"), TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION URINARY BLADDER TUMOUR (TURBT):
- HIGH-GRADE PAPILLARY UROTHELIAL CARCINOMA, SEE COMMENT.
- NEGATIVE FOR LAMINA PROPRIA INVASION.
- NO MUSCULARIS PROPRIA PRESENT.
COMMENT:
The sections show papillary branching, papillary fusion and scattered large cells (~4-5 a
resting lymphocyte). Atypical for a high-grade lesion is that mitotic activity is scarce
and prominent nucleoli are not present.
Micro
The sections show urothelial mucosa with thick papillary structures. Focally, nuclei are large (~3-4x resting lymphocyte), hyperchromatic and have nucleoli. Mitotic activity is present and focally brisk (4 mitoses in 1 HPF, 1 HPF~0.2376 mm*mm). Umbrella cells are seen only focally.
Alternate
The sections show a small fragment of urothelial mucosa with two papillary structures, enlarged nuclei (~3-4x resting lymphocyte) and moderate nuclear size variation. Mitotic activity is seen focally. Umbrella cells are seen only focally.
A mild lymphocyte-predominant inflammatory infiltrate is present. The lamina propria contains a nest with smaller cells, cystic spaces and no appreciable mitoses (cystitis cystica).
See also
References
- ↑ Hartmann, A.; Dietmaier, W.; Hofstädter, F.; Burgart, LJ.; Cheville, JC.; Blaszyk, H. (Mar 2003). "Urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: inverted growth pattern is predictive of microsatellite instability.". Hum Pathol 34 (3): 222-7. doi:10.1053/hupa.2003.22. PMID 12673555.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 310. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 161. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Bochner, BH.; Nichols, PW.; Skinner, DG. (Mar 1995). "Overstaging of transitional cell carcinoma: clinical significance of lamina propria fat within the urinary bladder.". Urology 45 (3): 528-31. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(99)80030-2. PMID 7879346.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/bladder/tcc-papillary-transitional-urothelial-carcinoma/. Accessed on: 27 January 2014.
- ↑ Reis, LO.; Taheri, D.; Chaux, A.; Guner, G.; Mendoza Rodriguez, MA.; Bivalacqua, TJ.; Schoenberg, MP.; Epstein, JI. et al. (Jan 2016). "Significance of a minor high-grade component in a low-grade noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of bladder.". Hum Pathol 47 (1): 20-5. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2015.09.007. PMID 26520419.>
- ↑ Gordetsky J, Epstein JI (July 2014). "Pseudopapillary features in prostatic adenocarcinoma mimicking urothelial carcinoma: a diagnostic pitfall". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 38 (7): 941–5. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000178. PMID 24503758.
- ↑ Rajcani, J.; Kajo, K.; Adamkov, M.; Moravekova, E.; Lauko, L.; Felcanova, D.; Bencat, M. (2013). "Immunohistochemical characterization of urothelial carcinoma.". Bratisl Lek Listy 114 (8): 431-8. PMID 23944616.
- ↑ Pich, A.; Chiusa, L.; Comino, A.; Navone, R. (1994). "Cell proliferation indices, morphometry and DNA flow cytometry provide objective criteria for distinguishing low and high grade bladder carcinomas.". Virchows Arch 424 (2): 143-8. PMID 7910097.
- ↑ Mai, KT.; Flood, TA.; Williams, P.; Kos, Z.; Belanger, EC. (Oct 2013). "Mixed low- and high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma: histopathogenetic and clinical significance.". Virchows Arch 463 (4): 575-81. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1456-7. PMID 23913166.
- ↑ Koyuncuer, A.. "Immunohistochemical expression of p63, p53 in urinary bladder carcinoma.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 56 (1): 10-5. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.116141. PMID 23924551.
- ↑ Ehdaie, B.; Theodorescu, D. (Jan 2008). "Molecular markers in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: New insights into mechanisms and prognosis.". Indian J Urol 24 (1): 61-7. doi:10.4103/0970-1591.38606. PMC 2684226. PMID 19468362. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2684226/.