Difference between revisions of "Cytogenetics"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=General= | =General= | ||
*Detects "large" changes (in chromosomes). | *Detects "large" changes (in chromosomes). | ||
**Conventional karyotyping has a maximum resolution 3-4 megabase pairs (3-4 million base pairs); may be less - dependent on band density.<ref>{{Ref WMSP|695}}</ref> | **Conventional karyotyping has a maximum resolution 3-4 megabase pairs (3-4 million base pairs); may be less - dependent on band density.<ref name=Ref_WMSP695>{{Ref WMSP|695}}</ref> | ||
*Cytogenetics is morphologic data | *Cytogenetics is morphologic (data); thus, the interpretation has a greater degree of subjectivity vis-à-vis genetic sequencing. | ||
=Techniques (overview)= | =Techniques (overview)= | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
***Several different techniques (stains) are used:<ref>URL: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC355922/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC355922/]. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.</ref> | ***Several different techniques (stains) are used:<ref>URL: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC355922/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC355922/]. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.</ref> | ||
****Examples: Q-banding (Q=Quinacrine), C-banding (C=constitutive heterchromatin), G-banding (G=Giemsa), R-banding (R=reverse). | ****Examples: Q-banding (Q=Quinacrine), C-banding (C=constitutive heterchromatin), G-banding (G=Giemsa), R-banding (R=reverse). | ||
Analysis: | Analysis: | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*Typically done with karyotyping software (e.g. ''Ikaros'' from ''MetaSystems''<ref>URL: [http://www.metasystems-international.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=46:ikaros-general&catid=34:ikarosisis&Itemid=119 http://www.metasystems-international.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=46:ikaros-general&catid=34:ikarosisis&Itemid=119]. Accessed on: 12 May 2011.</ref>). | *Typically done with karyotyping software (e.g. ''Ikaros'' from ''MetaSystems''<ref>URL: [http://www.metasystems-international.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=46:ikaros-general&catid=34:ikarosisis&Itemid=119 http://www.metasystems-international.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=46:ikaros-general&catid=34:ikarosisis&Itemid=119]. Accessed on: 12 May 2011.</ref>). | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Quinacrine dye - AT-rich regions brighter than GC-rich regions. | *Quinacrine dye - AT-rich regions brighter than GC-rich regions. | ||
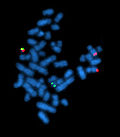
====Image==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:NHGRI_human_male_karyotype.png | Karyotype (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Virtual karyotyping=== | ===Virtual karyotyping=== | ||
*An evolving technique based on SNP microarrays<ref name=pmid20736741>{{Cite journal | last1 = Alvarez | first1 = K. | last2 = Kash | first2 = SF. | last3 = Lyons-Weiler | first3 = MA. | last4 = Kim | first4 = HJ. | last5 = Peterson | first5 = LE. | last6 = Mathai | first6 = B. | last7 = Hagenkord | first7 = JM. | last8 = Monzon | first8 = FA. | title = Reproducibility and performance of virtual karyotyping with SNP microarrays for the detection of chromosomal imbalances in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. | journal = Diagn Mol Pathol | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 127-34 | month = Sep | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1097/PDM.0b013e3181d527c5 | PMID = 20736741 }} | *An evolving technique based on SNP microarrays<ref name=pmid20736741>{{Cite journal | last1 = Alvarez | first1 = K. | last2 = Kash | first2 = SF. | last3 = Lyons-Weiler | first3 = MA. | last4 = Kim | first4 = HJ. | last5 = Peterson | first5 = LE. | last6 = Mathai | first6 = B. | last7 = Hagenkord | first7 = JM. | last8 = Monzon | first8 = FA. | title = Reproducibility and performance of virtual karyotyping with SNP microarrays for the detection of chromosomal imbalances in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. | journal = Diagn Mol Pathol | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 127-34 | month = Sep | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1097/PDM.0b013e3181d527c5 | PMID = 20736741 }} | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
* † This could be considered a break apart ''and'' fusion probe; it has both elements. | * † This could be considered a break apart ''and'' fusion probe; it has both elements. | ||
Image | ====Image==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Bcrablmet.jpg| Fusion signal suggesting a BCR-ABL translocation. (WC/Pmx) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Tests=== | ===Tests=== | ||
| Line 106: | Line 108: | ||
*[http://homepage.mac.com/wildlifeweb/cyto/human/ Cytogenetics (homepage.mac.com)] - has ideograms (banding maps) of the human chromosomes. | *[http://homepage.mac.com/wildlifeweb/cyto/human/ Cytogenetics (homepage.mac.com)] - has ideograms (banding maps) of the human chromosomes. | ||
*[http://ccr.coriell.org/sections/support/global/iscn_help.aspx?PgId=263 ISCN symbols and abbreviated terms (coriell.org)] - cytogenetics nomenclature. | *[http://ccr.coriell.org/sections/support/global/iscn_help.aspx?PgId=263 ISCN symbols and abbreviated terms (coriell.org)] - cytogenetics nomenclature. | ||
*[http://www.sickkids.ca/paediatriclabmedicinems/test-catalogue/cytogenetics-listing.html Cytogenetics catalogue (sickkids.ca)]. | |||
[[Category:Molecular pathology]] | [[Category:Molecular pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 11 May 2016
This article deals with cytogenetics. An introduction to molecular pathology is found in the molecular pathology article.
General
- Detects "large" changes (in chromosomes).
- Conventional karyotyping has a maximum resolution 3-4 megabase pairs (3-4 million base pairs); may be less - dependent on band density.[1]
- Cytogenetics is morphologic (data); thus, the interpretation has a greater degree of subjectivity vis-à-vis genetic sequencing.
Techniques (overview)
- ISH = in situ hybridization.
- FISH = fluorescent in situ hybridization.
- SISH = silver in situ hybridization.[2]
- Karyotyping.
Karyotyping
What?
- Metaphase nuclei.
- The number of metapase nuclei (in samples) is enhanced by added a microtubule inhibitor (colcemid), that prevents progression to anaphase.
- Cells are bathed in a hypotonic solution to make 'em larger and spread out the nuclear material.
How?
- Chromosomes are identified by:
- Size (chromosome 1 = largest, chromosome 22 = smallest).
- Position of centromere.
- Banding pattern - using (special) stains:
- Several different techniques (stains) are used:[3]
- Examples: Q-banding (Q=Quinacrine), C-banding (C=constitutive heterchromatin), G-banding (G=Giemsa), R-banding (R=reverse).
- Several different techniques (stains) are used:[3]
Analysis:
- Based on comparison to maps of the chromosomes (ideograms).
- Detailed ideograms are in ISCN 2009.[4]
- The detail of an ideogram is given in "band levels"; a 850 band ideogram has a higher resolution than a 400 band ideogram. The typical range for band level is 300-850. The band level, for a given specimen, is determined by an empirical standard and based on the number of bands an observer sees in a subset of the chromosomes.[5]
- Detailed ideograms are in ISCN 2009.[4]
- Typically done with karyotyping software (e.g. Ikaros from MetaSystems[6]).
Notes:
- Quinacrine dye - AT-rich regions brighter than GC-rich regions.
Image
Virtual karyotyping
- An evolving technique based on SNP microarrays[7] or comparative genomic hybridization (CGH).
In situ hybridization
- Typically abbreviated ISH.
Overview
- ISH is a relatively high resolution cytogenetic technique (vis-à-vis karyotyping) used to identify specific DNA sequences and, with multiple probes, determine their relative location.
- Usually done on interphase nuclei.
- DNA probe size ~20-1000 base pairs.
Comes in different flavours:
- FISH = fluorescent in situ hybridization.
- SISH = silver in situ hybridization.[8]
May be prepared from:
- In situ paraffin sections (section 4 micrometers thick).
- Isolated nuclei (section 10 micrometers thick).
- Cytospin.
- Cultured cells.
Probe types
Types:
- Fusion - usually two colours , e.g. IGH/BCL2 translocation, BCR/ABL translocation.
- Two colour - two different probes with different colours.
- Two colour fusion with extra signal - similar two colour fusion.[9]
- Three-colour † - two probes (e.g. red and blue) straddle the break point.[10]
- One of the (true) translocations (e.g. presence of a Philadelphia chromosome) will have only two colours (red and green or yellow).
- The derivative chromosome (e.g. derivative 9 chromosome in Philadelphia chromosome cells), which may be lost, will have all three colours.
- A (non-pathologic) coincidental colocalization (or overlap) of probes will consist of all three colours.
- Break apart - two colour, e.g. c-MYC rearrangement.
- Deletion/duplication (e.g. trisomy) - one colour.
Notes:
- † This could be considered a break apart and fusion probe; it has both elements.
Image
Tests
ERBB2
- AKA HER2,[11] AKA HER2/neu.
- Important in invasive breast cancer.
Protocol:
- ISH label for HER2.
- ISH label for CEP17 (D17Z1 -- labels centromere of chromosome 17).[12]
- In 60 nuclei:
- Count number of HER2 signals.
- Count number of CEP17 signals.
- Calculate ratio HER2/D17Z1 signals:[13]
- >2.2 --> HER2 amplification.
- 1.8-2.2 --> equivocal.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 695. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.immunoportal.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=186. Accessed on: 2 May 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC355922/. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.
- ↑ Shaffer, Lisa G.; Slovak, Marilyn L.; Campbell, Lynda J. (2009). ISCN 2009: an international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature (2009 ed.). S. Karger AG. ISBN 978-3805589857.
- ↑ Welborn, JL.; Welborn, R. (Dec 1993). "Banding resolution of human chromosomes: a method of accuracy and simplicity.". Am J Med Genet 47 (8): 1180-3. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320470810. PMID 8291552.
- ↑ URL: http://www.metasystems-international.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=46:ikaros-general&catid=34:ikarosisis&Itemid=119. Accessed on: 12 May 2011.
- ↑ Alvarez, K.; Kash, SF.; Lyons-Weiler, MA.; Kim, HJ.; Peterson, LE.; Mathai, B.; Hagenkord, JM.; Monzon, FA. (Sep 2010). "Reproducibility and performance of virtual karyotyping with SNP microarrays for the detection of chromosomal imbalances in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues.". Diagn Mol Pathol 19 (3): 127-34. doi:10.1097/PDM.0b013e3181d527c5. PMID 20736741.
- ↑ URL: http://www.immunoportal.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=186. Accessed on: 2 May 2011.
- ↑ Primo, D.; Tabernero, MD.; Rasillo, A.; Sayagués, JM.; Espinosa, AB.; Chillón, MC.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Gutierrez, N. et al. (Jun 2003). "Patterns of BCR/ABL gene rearrangements by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in BCR/ABL+ leukemias: incidence and underlying genetic abnormalities.". Leukemia 17 (6): 1124-9. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402963. PMID 12764379. http://www.nature.com/leu/journal/v17/n6/full/2402963a.html.
- ↑ Sinclair, PB.; Green, AR.; Grace, C.; Nacheva, EP. (Aug 1997). "Improved sensitivity of BCR-ABL detection: a triple-probe three-color fluorescence in situ hybridization system.". Blood 90 (4): 1395-402. PMID 9269756. http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/90/4/1395.full.html.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 164870
- ↑ URL: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/546925_3. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.
- ↑ ASCO/CAP 2007 guidelines. URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/cap.portal?_nfpb=true&cntvwrPtlt_actionOverride=%2Fportlets%2FcontentViewer%2Fshow&_windowLabel=cntvwrPtlt&cntvwrPtlt%7BactionForm.contentReference%7D=committees%2Fimmunohistochemistry%2Fher2_index.html. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.
External links
- Cytogenetics (homepage.mac.com) - has ideograms (banding maps) of the human chromosomes.
- ISCN symbols and abbreviated terms (coriell.org) - cytogenetics nomenclature.
- Cytogenetics catalogue (sickkids.ca).