Difference between revisions of "Papanicolaou stain"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Image:Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.jpg|Cervix - LSIL - Pap stain. (WC) | Image:Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.jpg|Cervix - LSIL - Pap stain. (WC) | ||
Image:High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.jpg|Cervix - HSIL - Pap stain. (WC) | Image:High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.jpg|Cervix - HSIL - Pap stain. (WC) | ||
Image:Lung small cell carcinoma -- extremely high mag.jpg|Lung - SmCC - Pap stain. (WC) | |||
Image:Urine_citology_urothelial_carcinoma_2.jpg | [[Urine cytology]] - UCC - Pap stain. (WC) | Image:Urine_citology_urothelial_carcinoma_2.jpg | [[Urine cytology]] - UCC - Pap stain. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:17, 24 April 2016
| Papanicolaou stain | |
|---|---|
| Stain in short | |
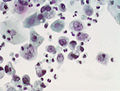
 Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion. | |
| Abbreviation | Pap stain |
| Similar stains | Romanowsky stains |
| Use | the standard stain in cytopathology |
| Interpretation | blue/purple = nucleus, pink/green = cytoplasm, orange = keratin |
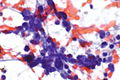
Papanicolaou stain, abbreviated Pap stain, is a standard stain used in cytopathology.[1] It is a modified H&E stain.
General
- Can be thought of as the H&E of cytopathology.
- It is a modified H&E stain.
- Specimens are fixed in ethanol.
- Good for seeing nuclear detail.[1]
- Out-of-focus cytoplasm is translucent; allows one to focus overlapped cells in different planes.
Use
Interpretation
- Blue/purple = nucleus.
- Green/pink = cytoplasm.
- Orange = keratin.
Images
Urine cytology - UCC - Pap stain. (WC)