Difference between revisions of "Desquamative interstitial pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
**Usually peripheral predominant (~60% of cases) and lower lobe predominant (~70-75% of cases). | **Usually peripheral predominant (~60% of cases) and lower lobe predominant (~70-75% of cases). | ||
**Typically all lobes are involved - though upper lobe spared in ~20% of cases. | **Typically all lobes are involved - though upper lobe spared in ~20% of cases. | ||
*Fibrotic (radiologic) changes ~50% of cases. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 02:17, 4 April 2016
| Desquamative interstitial pneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
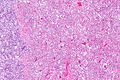
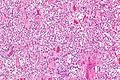
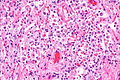
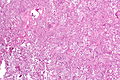
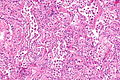
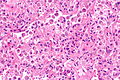
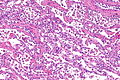
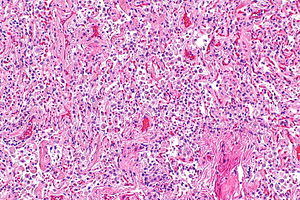 Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron) | |
|
| |
| LM | abundant brown pigmented airspace macrophages (smoker's macrophages), architecture preserved ("linear fibrosis") |
| LM DDx | amiodarone toxicity, fibrotic NSIP, RBILD |
| Site | lung - see diffuse lung diseases |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | +/-smoking |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Radiology | ground glass airspaces changes - usu. all lobes but peripheral predominant and in lower lobe predominant |
| Treatment | stop smoking/remove insult |
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia, abbreviated DIP, is a diffuse lung disease that is strongly associated with smoking.
The term desquamative interstitial pneumonia is a misnomer. The airspace cells that characterize the condition were once thought to represent desquamated epithelial cells, but they are now know to represent macrophages.[1]
General
- Rare.[2]
- Strong association with smoking.[3][4]
- Thought to be advanced RBILD.
- May be seen in non-smokers (up to ~40% of cases) due to occupational exposures, drugs, viral illnesses and autoimmune diseases.[5]
Diagnosis:
- Requires - surgical biopsy.[5]
Treatment:
- Stop smoking/remove or manage underlying cause.
Gross/Radiology
Features:[6]
- Ground glass (airspace changes).
- Usually peripheral predominant (~60% of cases) and lower lobe predominant (~70-75% of cases).
- Typically all lobes are involved - though upper lobe spared in ~20% of cases.
- Fibrotic (radiologic) changes ~50% of cases.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Abundant airspace macrophages - usually with brown pigment (so called smoker's macrophages) - key feature.
- Interstitial inflammation or interstitial fibrosis with a preserved architecture - so called "linear fibrosis".
Notes:
- Some fields of view may be indistinguishable from RBILD.
DDx:
Images
www
Stains
- Macrophages PAS +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Attili, AK.; Kazerooni, EA.; Gross, BH.; Flaherty, KR.; Myers, JL.; Martinez, FJ.. "Smoking-related interstitial lung disease: radiologic-clinical-pathologic correlation.". Radiographics 28 (5): 1383-96; discussion 1396-8. doi:10.1148/rg.285075223. PMID 18794314. http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.285075223.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tazelaar, HD.; Wright, JL.; Churg, A. (Mar 2011). "Desquamative interstitial pneumonia.". Histopathology 58 (4): 509-16. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03649.x. PMID 20854463.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 93. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Margaritopoulos, GA.; Vasarmidi, E.; Jacob, J.; Wells, AU.; Antoniou, KM. (Sep 2015). "Smoking and interstitial lung diseases.". Eur Respir Rev 24 (137): 428-35. doi:10.1183/16000617.0050-2015. PMID 26324804.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Godbert, B.; Wissler, MP.; Vignaud, JM. (Jun 2013). "Desquamative interstitial pneumonia: an analytic review with an emphasis on aetiology.". Eur Respir Rev 22 (128): 117-23. doi:10.1183/09059180.00005812. PMID 23728865.
- ↑ Hartman, TE.; Primack, SL.; Swensen, SJ.; Hansell, D.; McGuinness, G.; Müller, NL. (Jun 1993). "Desquamative interstitial pneumonia: thin-section CT findings in 22 patients.". Radiology 187 (3): 787-90. doi:10.1148/radiology.187.3.8497631. PMID 8497631.