Difference between revisions of "Mucinous breast carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
*Malignant mucin producing glands. | *Malignant mucin producing glands. | ||
**Mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour - '''required for diagnosis'''.<ref name=pmid22006768>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dogan | first1 = E. | last2 = Aksoy | first2 = S. | last3 = Dizdar | first3 = O. | last4 = Arslan | first4 = C. | last5 = Dede | first5 = DS. | last6 = Ozisik | first6 = Y. | last7 = Altundag | first7 = K. | title = Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a single center experience. | journal = J BUON | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | pages = 565-7 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 22006768 }}</ref> | **Mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour - '''required for diagnosis'''.<ref name=pmid22006768>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dogan | first1 = E. | last2 = Aksoy | first2 = S. | last3 = Dizdar | first3 = O. | last4 = Arslan | first4 = C. | last5 = Dede | first5 = DS. | last6 = Ozisik | first6 = Y. | last7 = Altundag | first7 = K. | title = Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a single center experience. | journal = J BUON | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | pages = 565-7 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 22006768 }}</ref> | ||
** | **Small clusters of cells should float in the mucin - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Glands typically have irregular edges. | **Glands typically have irregular edges. | ||
**+/-Vessels within the mucin pools. | **+/-Vessels within the mucin pools. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
*[[DCIS]] with a mucinous component. | *[[DCIS]] with a mucinous component. | ||
**Mucin has a homogenous appearance, mucin lacks vascularization, mucin pools have a regular border. | **Mucin has a homogenous appearance, mucin lacks vascularization, mucin pools have a regular border. | ||
*[[Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast]] with a mucinous component - more common than ''mucinous breast carcinoma''. | *[[Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast]] with a mucinous component - more common than ''mucinous breast carcinoma''. Any 'no special type' component imparts a worse prognosis so the diagnosis 'mucinous carcinoma' is reserved for tumours with pure mucinous features. | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*The amount of mucinous component to call ''[[mucinous carcinoma]]'' varies by anatomical site. | *The amount of mucinous component to call ''[[mucinous carcinoma]]'' varies by anatomical site. | ||
* | *A breast core biopsy that show any degree of mucinous change is an indication for excision to exclude mucinous carcinoma.<ref name=pmid12218567>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jacobs | first1 = TW. | last2 = Connolly | first2 = JL. | last3 = Schnitt | first3 = SJ. | title = Nonmalignant lesions in breast core needle biopsies: to excise or not to excise? | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 26 | issue = 9 | pages = 1095-110 | month = Sep | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12218567 }}</ref> | ||
*Size and margins are assessed from edge of mucin, even if it does not contain epithelial cells | |||
*These tumors can be very difficult to assess lymphovascular invasion. Look for tumour cells in areas where lymphatics are expected ie. tumour in arc-shape around vascular bundle | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Revision as of 09:47, 27 March 2015
| Mucinous breast carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
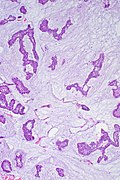
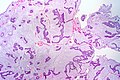
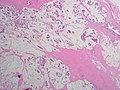
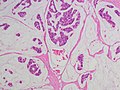
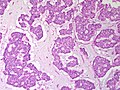
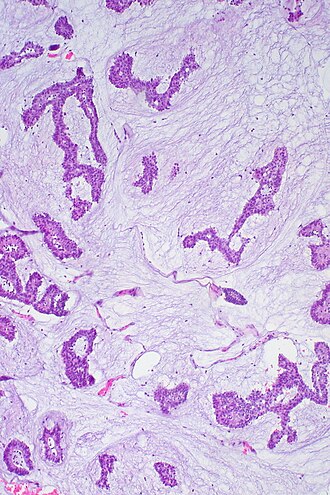 Mucinous breast carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
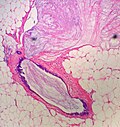
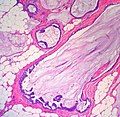
| LM | malignant mucin producing glands - where mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour, tumour cells should float in the mucin, glands typically have irregular edges, +/-vessels within the mucin pools |
| LM DDx | other type of breast cancer with a mucinous component (very common), other mucinous tumours |
| IHC | ER +ve, PR +ve, HER2 -ve |
| Gross | pale, glistening, jelly-like appearance |
| Site | breast - see invasive breast cancer |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good compared to the usual ductal carcinoma |
| Clin. DDx | other breast tumours |
Mucinous breast carcinoma is an uncommon form of breast cancer that has a good prognosis compared to the common invasive ductal carcinoma.
It is also known as mucinous carcinoma of the breast, and colloid carcinoma of the breast.
General
- Rare.
- Good prognosis.[1]
- Usually older women.
Gross
- Pale, glistening, jelly-like appearance.
- Well-circumscribed.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Malignant mucin producing glands.
- Mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour - required for diagnosis.[2]
- Small clusters of cells should float in the mucin - key feature.
- Glands typically have irregular edges.
- +/-Vessels within the mucin pools.
DDx:
- DCIS with a mucinous component.
- Mucin has a homogenous appearance, mucin lacks vascularization, mucin pools have a regular border.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with a mucinous component - more common than mucinous breast carcinoma. Any 'no special type' component imparts a worse prognosis so the diagnosis 'mucinous carcinoma' is reserved for tumours with pure mucinous features.
Note:
- The amount of mucinous component to call mucinous carcinoma varies by anatomical site.
- A breast core biopsy that show any degree of mucinous change is an indication for excision to exclude mucinous carcinoma.[3]
- Size and margins are assessed from edge of mucin, even if it does not contain epithelial cells
- These tumors can be very difficult to assess lymphovascular invasion. Look for tumour cells in areas where lymphatics are expected ie. tumour in arc-shape around vascular bundle
Images
IHC
- ER +ve.
- PR +ve.
- HER2 -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Barkley, CR.; Ligibel, JA.; Wong, JS.; Lipsitz, S.; Smith, BL.; Golshan, M. (Oct 2008). "Mucinous breast carcinoma: a large contemporary series.". Am J Surg 196 (4): 549-51. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.06.013. PMID 18809061.
- ↑ Dogan, E.; Aksoy, S.; Dizdar, O.; Arslan, C.; Dede, DS.; Ozisik, Y.; Altundag, K.. "Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a single center experience.". J BUON 16 (3): 565-7. PMID 22006768.
- ↑ Jacobs, TW.; Connolly, JL.; Schnitt, SJ. (Sep 2002). "Nonmalignant lesions in breast core needle biopsies: to excise or not to excise?". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (9): 1095-110. PMID 12218567.