Difference between revisions of "Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(split + image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
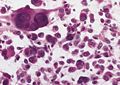
| Image = Pleo xantho.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma''', abbreviated '''PXA''', is [[neuropathology tumour]] classically associated with seizures. | '''Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma''', abbreviated '''PXA''', is [[neuropathology tumour]] classically associated with seizures. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 54: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pleo xantho.jpg | PXA. (WC/AFIP) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case499.html Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case499.html Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case511.html Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - another case - several images (upmc.edu)]. | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case511.html Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - another case - several images (upmc.edu)]. | ||
Revision as of 06:43, 10 December 2014
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
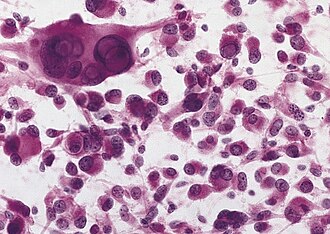 Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. |
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, abbreviated PXA, is neuropathology tumour classically associated with seizures.
General
Features:
- Classically in the temporal lobe in children and young adults.
- Associated with seizures.
- Moderately aggressive (WHO Grade II).[1]
Gross
- Temporal lobe - classic.
- Usually assoc. with the leptomeninges,[1] i.e. superficial.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Marked nuclear atypia.
- Eosinophilic granular bodies - very common.[1]
- Inflammation (chronic).
Notes:
- No mitoses.
- No necrosis.
Images
www:
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - another case - several images (upmc.edu).
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplasia - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Cerebellar pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma - case 4 - several image (upmc.edu).
Stains
- Reticulin stain - intercellular, prominent.[3]
Image:
IHC
- GFAP +ve.
- CD68 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Fouladi, M.; Jenkins, J.; Burger, P.; Langston, J.; Merchant, T.; Heideman, R.; Thompson, S.; Sanford, A. et al. (Jul 2001). "Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: favorable outcome after complete surgical resection.". Neuro Oncol 3 (3): 184-92. PMID 11465399.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1333. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dias-Santagata, D.; Lam, Q.; Vernovsky, K.; Vena, N.; Lennerz, JK.; Borger, DR.; Batchelor, TT.; Ligon, KL. et al. (2011). "BRAF V600E mutations are common in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: diagnostic and therapeutic implications.". PLoS One 6 (3): e17948. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017948. PMID 21479234.