Difference between revisions of "Angiokeratoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = Angiokeratoma_- | | Image = Angiokeratoma_-_low_mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
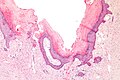
| Caption = Angiokeratoma. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Angiokeratoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:24, 28 October 2014
| Angiokeratoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
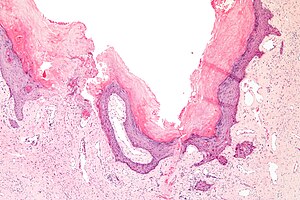 Angiokeratoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | ectatic superficial dermal vessels with overlying hyperkeratosis (thick stratum corneum); should have "epidermal collarette" (vascular space is surrounded by epidermis on three sides) |
| LM DDx | venous lake |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Fabry disease |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | melanocytic lesions, other vascular lesions |
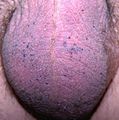
Angiokeratoma is a benign skin lesion.
General
- Rare.
- May be seen in the context of Fabry disease.[1]
Notes:
- Shouldn't be confused with angiofibroma which is associated tuberous sclerosis.
Gross
- Dark lesions.
Clinical DDx:
Images
Microscopic
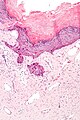
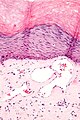
Features:[1]
- Ectatic superficial dermal vessels.
- Overlying hyperkeratosis (thick stratum corneum).
- Should have "epidermal collarette".[2]
- Vascular space surrounded by epidermis on three sides.
Others features:[citation needed]
- Irregular acanthosis.
- Longer rete ridges.
DDx:
- Venous lake.
- Angiokeratoma-like changes in lichen sclerosus.[3]
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, LEFT POPITEAL FOSSA, PUNCH BIOPSY: - ANGIOKERATOMA.
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Karen, JK.; Hale, EK.; Ma, L. (2005). "Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease).". Dermatol Online J 11 (4): 8. PMID 16403380.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 548. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Luzar, B.; Neil, SM.; Calonje, E. (May 2009). "Angiokeratoma-like changes in extragenital and genital lichen sclerosus.". J Cutan Pathol 36 (5): 540-2. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2008.01091.x. PMID 19187108.